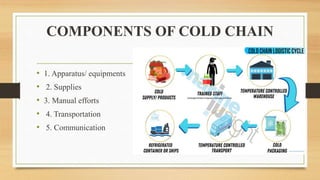
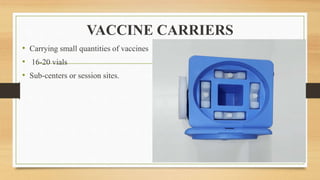
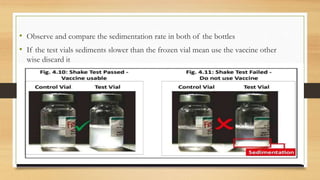
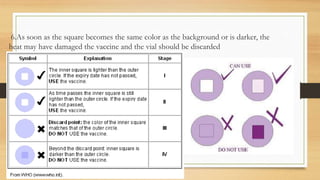
The cold chain is a system for storing and transporting vaccines at the proper temperature from manufacture to point of use. It involves transporting, storing, and maintaining vaccines within a specific temperature range to keep them potent. Breaks in the cold chain can compromise vaccine effectiveness and must be avoided by properly using equipment like refrigerators, freezers, and vaccine carriers with ice packs. The cold chain is crucial for ensuring vaccines retain their ability to prevent disease.