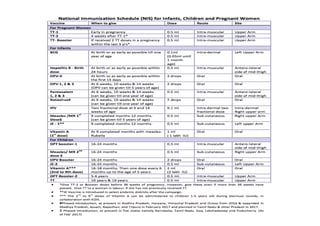
The document summarizes India's Universal Immunization Programme (UIP). It discusses how the program was launched in 1978 to reduce mortality from vaccine-preventable diseases. Over time, it expanded its vaccine coverage and introduced new vaccines. Coverage rates increased significantly from 29-41% in 1985-86 to over 70% for most vaccines by 2014. The program continues to introduce new vaccines and aims to vaccinate all children through intensified drives like Mission Indradhanush. India has achieved the major successes of eliminating smallpox and becoming polio-free. The UIP demonstrates how immunization can significantly reduce deaths from vaccine-preventable diseases.