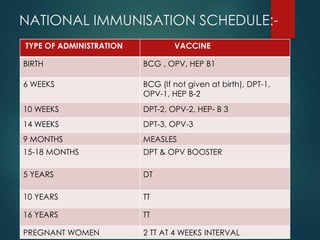
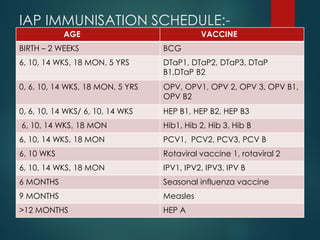
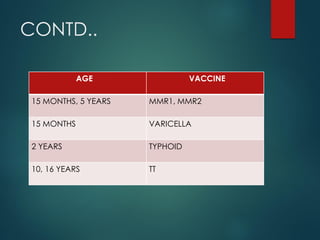
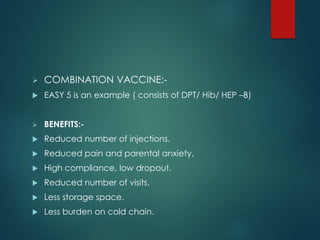
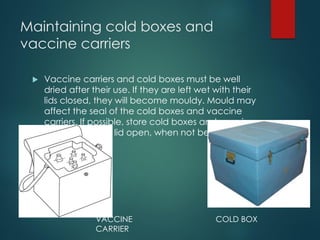
The document provides a comprehensive overview of immunization, detailing the definitions, types (active and passive), historical developments, and achievements in vaccination efforts. It outlines the national immunization schedule, types of vaccines administered at specific ages, and their contraindications and side effects. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of maintaining a cold chain for vaccine storage and administration, along with guidelines for future immunization practices.