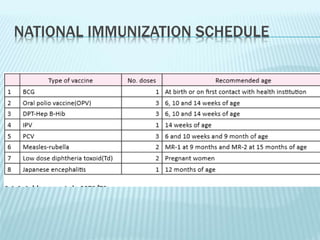
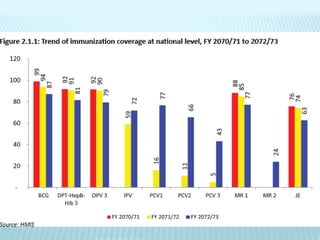
The National Immunization Programme (NIP) in Nepal aims to reduce child mortality from vaccine-preventable diseases. Launched in 1977, it has met goals like MDG 4 on child mortality reduction. The NIP delivers vaccines through health clinics and outreach sessions nationwide. Its goals are to achieve and maintain at least 90% vaccination coverage nationally and end diseases like polio, which Nepal was declared free of in 2010. The NIP targets children under 1 for vaccines like BCG, DPT and measles, and also provides tetanus vaccines for pregnant women. It conducts over 16,000 immunization sessions monthly across the country.