The document provides information about India's Universal Immunization Programme (UIP), including:
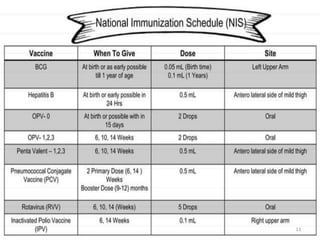
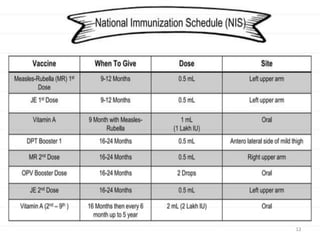
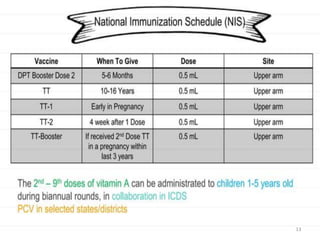
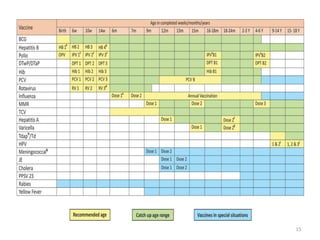
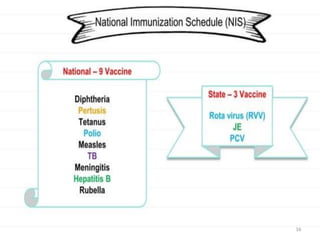
- UIP was started in 1985 and aims to provide several vaccines to infants, children, and pregnant women to protect against six vaccine-preventable diseases.
- It is the largest immunization program in the world, targeting over 56 million people annually.
- The program provides vaccines for diseases like tuberculosis, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, and measles. It also includes two new vaccines for JE and hepatitis B in select areas.
- Implementation of the program relies on components like maintaining a strong cold chain for vaccine storage, injection safety, adverse event monitoring, communication,