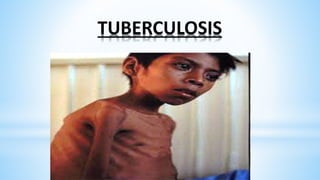
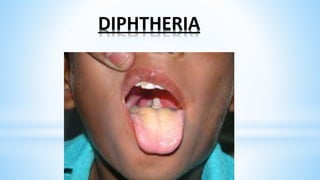
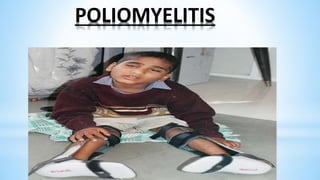
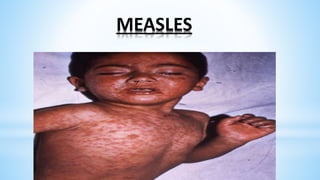
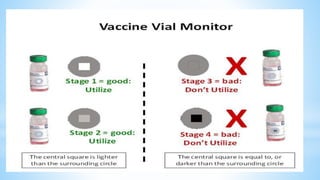
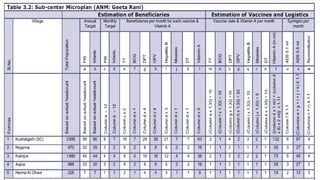
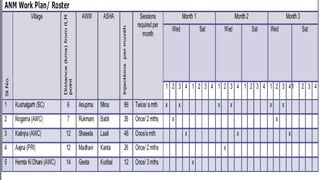
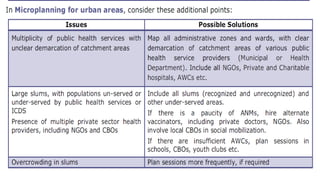
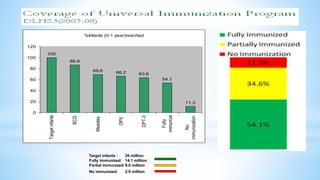
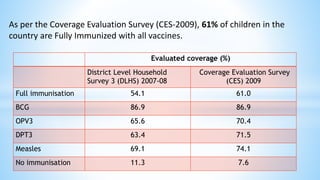
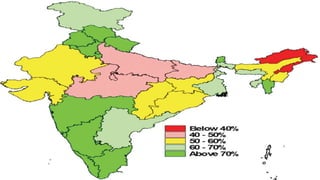
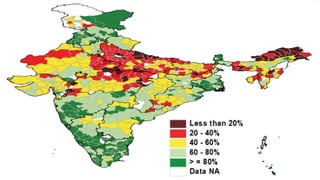
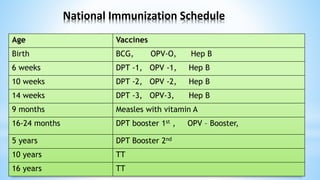
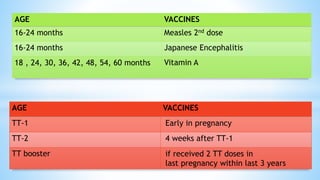
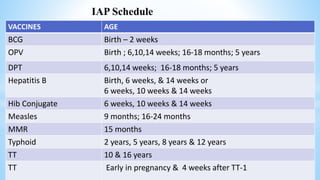
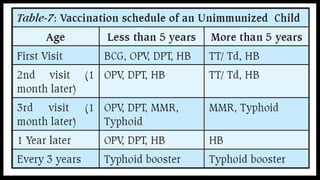
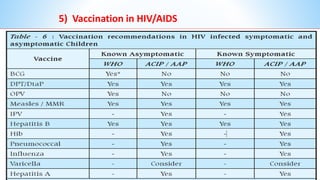
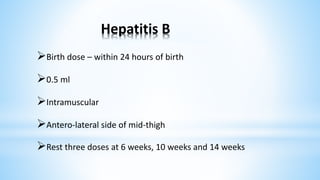
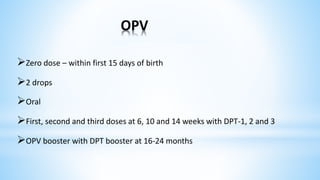
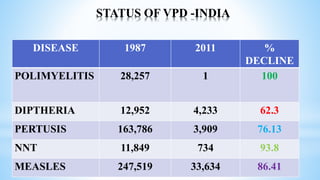
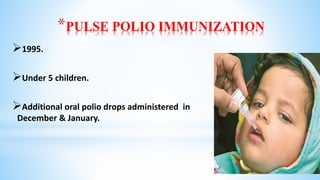
This document provides information about India's National Immunization Programme (UIP). It discusses the targeted vaccine preventable diseases (VPDs), the history and objectives of the Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI) and Universal Immunization Programme (UIP). It outlines the national immunization schedule, components of UIP including vaccination of pregnant women and children, and strategies to achieve coverage goals. Coverage levels from surveys are presented. The document also discusses vaccine administration techniques for different vaccines.