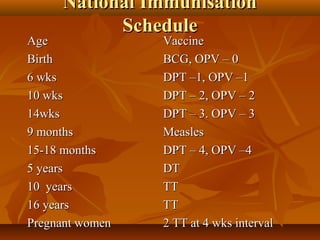
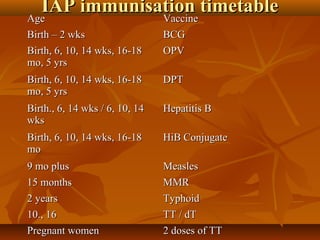
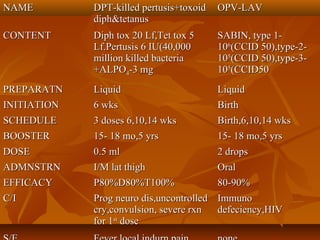
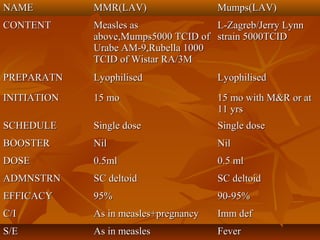
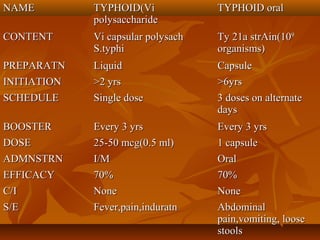
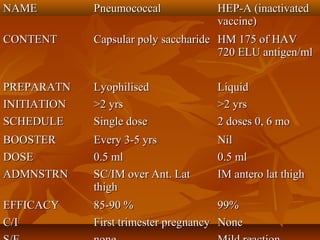
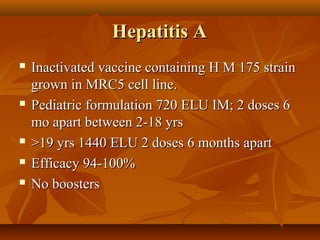
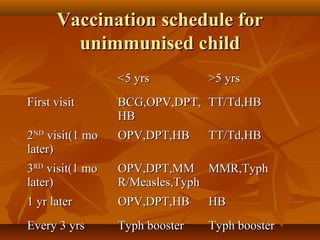
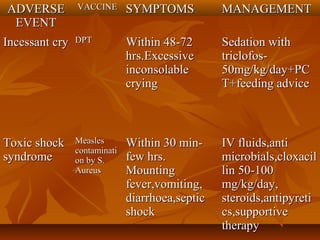
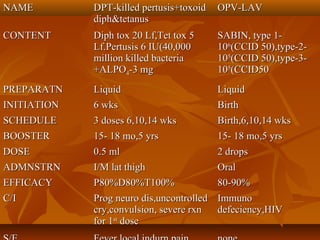
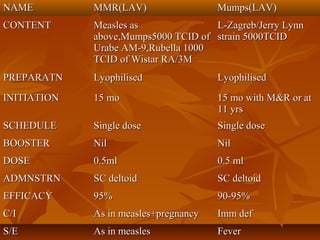
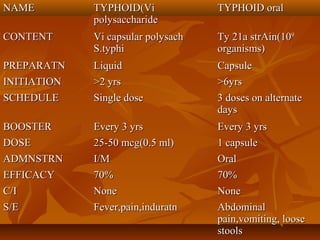
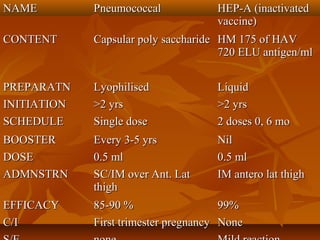
This document provides information on various vaccines used in India's national immunization schedule. It defines key terms related to immunization and vaccination. The national schedule recommends vaccines for diseases like tuberculosis, polio, diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, hepatitis B, Hib, measles, and others to be administered to infants and children at specific ages. Details are provided on vaccine names, ingredients, dosage, administration route and effectiveness. The history and achievements of immunization programs in India and globally are also summarized.