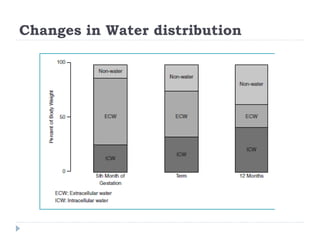
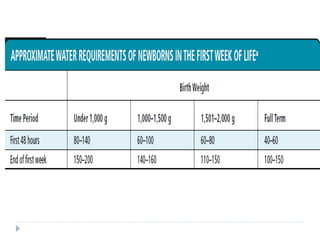
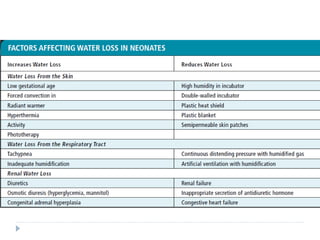
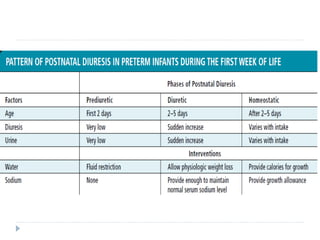
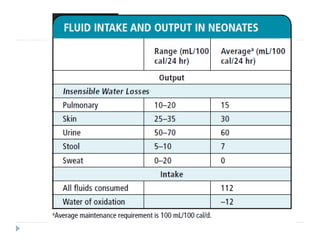
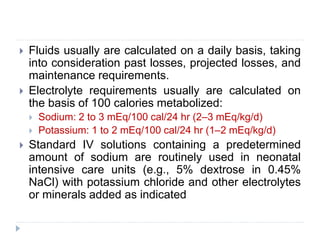
This document discusses fluid calculation and homeostasis in neonates. It notes that water and electrolyte balance is vital but different in neonates compared to older children and adults due to rapid developmental changes. It outlines the physiology of total body water, intracellular water, and extracellular water. It also discusses changes that occur at birth and how to assess hydration status in neonates through monitoring things like urine output, weight, physical exam findings and lab tests. Maintaining appropriate fluid and electrolyte balance is important for health in preterm infants.