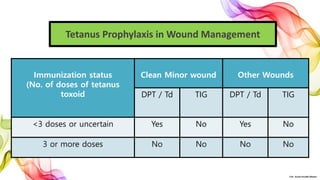
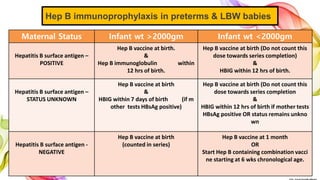
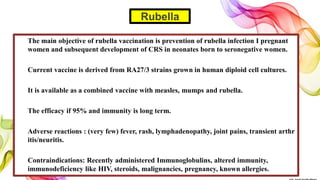
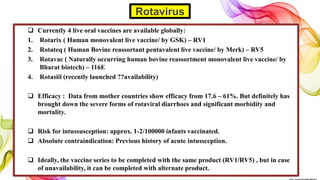
The document discusses the fundamentals of immunization in pediatrics, focusing on the types of immunity, vaccine classifications, and schedules for vaccine administration. It outlines the processes involved in the body's immune response, including the role of antigens and antibodies, as well as detailing specific vaccines for diseases such as tuberculosis, diphtheria, and hepatitis B. Additionally, it provides guidance on age-specific vaccination schedules and special cases for immunization in various populations.