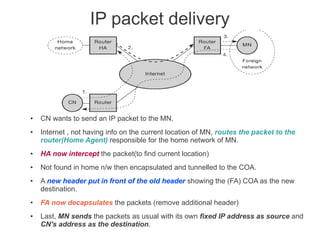
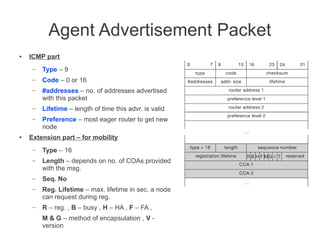
Mobile Network Layer protocols and mechanisms allow nodes to change their point of attachment to different networks while maintaining ongoing communication. Key concepts include:
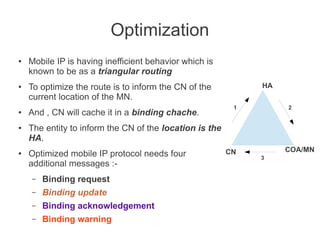
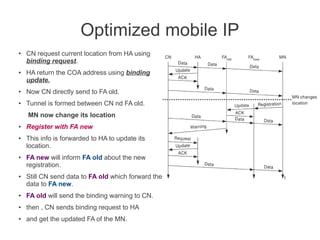
- Mobile IP adds mobility support to IP, allowing nodes to use the same IP address even when changing networks. It relies on home agents and care-of addresses.
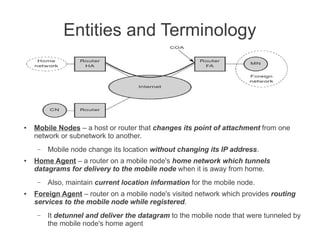
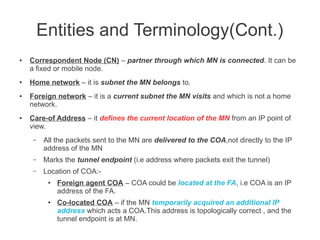
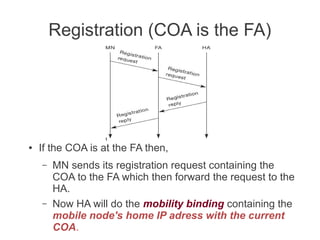
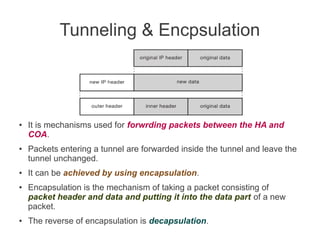
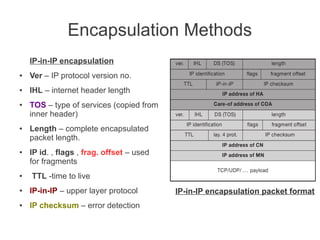
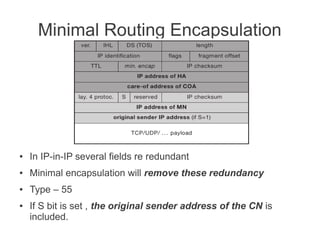
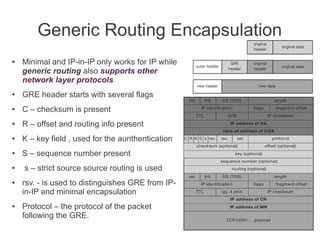
- Registration allows mobile nodes to inform their home agent of their current location when visiting foreign networks. Tunneling and encapsulation techniques are used to forward packets to mobile nodes' current locations.
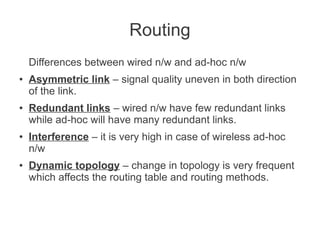
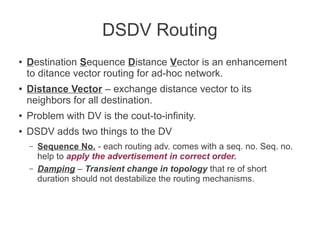
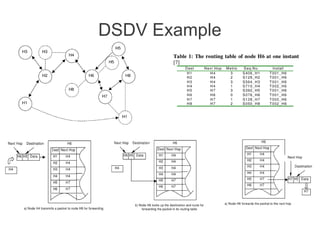
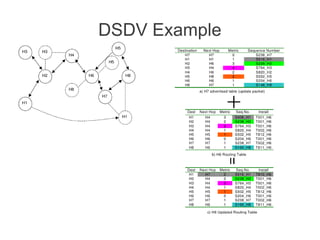
- Various routing protocols like DSDV have been developed for mobile ad hoc networks which have no fixed infrastructure and dynamic topologies.