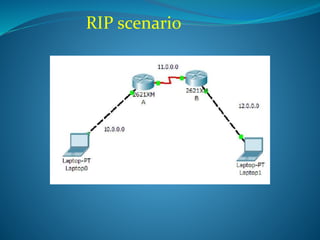
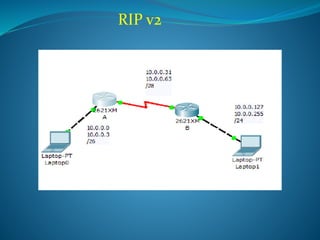
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) version 1 is a distance vector routing protocol that updates every 30 seconds and uses hop count for routing decisions, with a maximum of 15 hops. It is classful and only supports subnetting with the same subnet mask for all networks, while version 2 supports classless routing and variable length subnet masking (VLSM). RIP utilizes various timers to manage route updates and invalidation, and specific commands are provided for configuring both RIP v1 and v2 on routers.






![RIP version 1 RIP version2
1.Distance vector 1.Distance vector
2.Max hop count=15 2.Max hop count=15
3.Classful [subnet 3. classless[subnet infor-
information is not sent mation is sent with
With route updates] the route updates]
4.broadcast based 4. multicast based[use
224.0.0.9 broadcast
address]
5.FLSM 5.VLSM
6. NO authentication 6. MD5 authentication](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rip-1rip2-150514064837-lva1-app6891/85/Rip-1-rip-2-7-320.jpg)