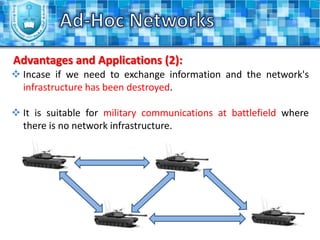
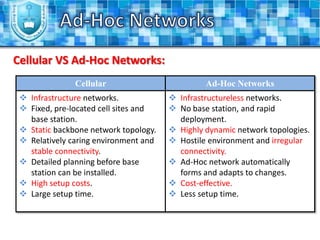
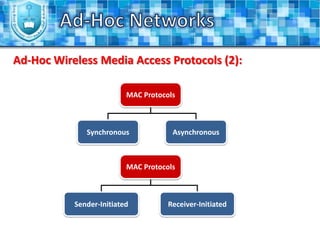
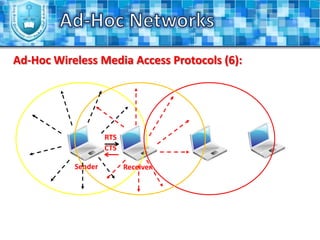
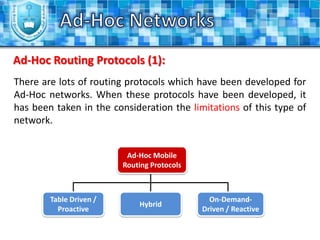
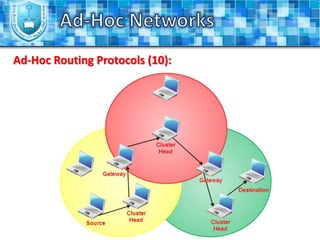
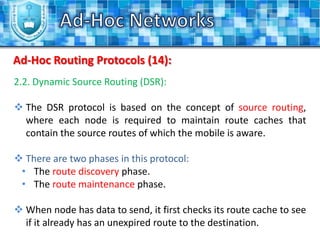
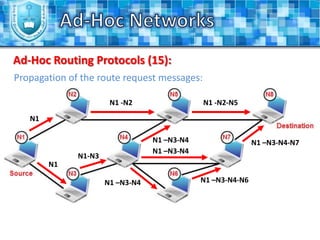
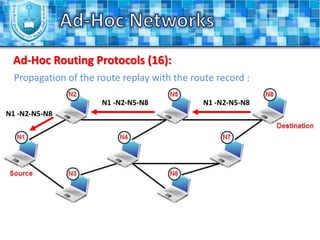
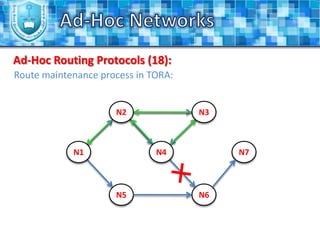
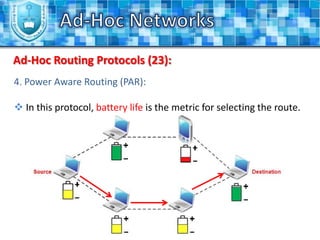
The document discusses ad-hoc networks and their key characteristics. It describes several challenges in ad-hoc networks including limited battery power, dynamic network topology, and scalability issues. It also summarizes several ad-hoc network routing protocols (e.g. DSDV, AODV, DSR), addressing both table-driven and on-demand approaches. Additionally, it outlines some ad-hoc MAC protocols like MACA and PAMAS that aim to manage shared wireless medium access.