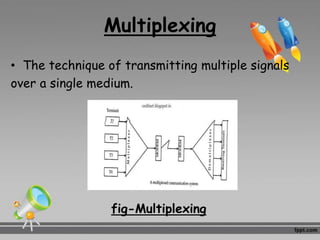
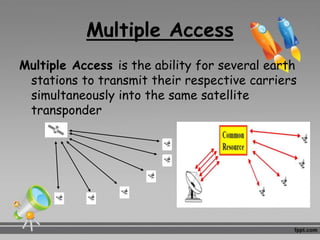
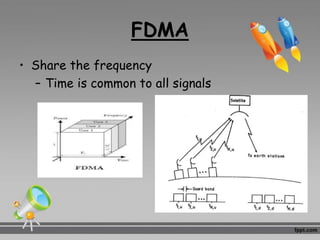
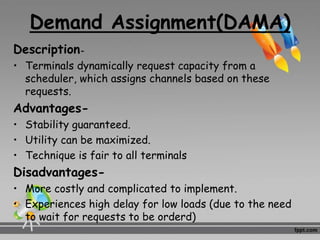
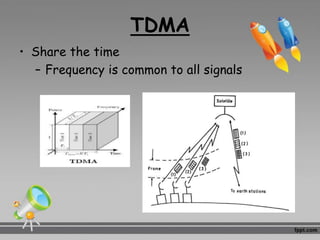
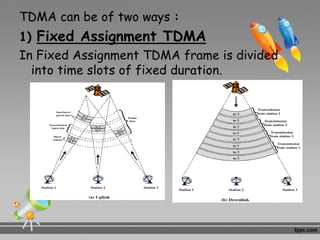
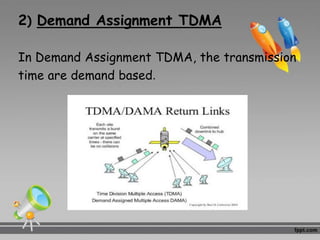
This document discusses multiplexing and multiple access techniques used in communication networks. It describes multiplexing as transmitting multiple signals over a single medium, such as frequency division multiplexing (FDM) and time division multiplexing (TDM). Multiple access allows several stations to transmit simultaneously into the same network using techniques like frequency division multiple access (FDMA), time division multiple access (TDMA), and code division multiple access (CDMA). FDMA divides the available bandwidth into frequency slots, TDMA divides transmission time into time slots, and CDMA assigns unique codes to signals.