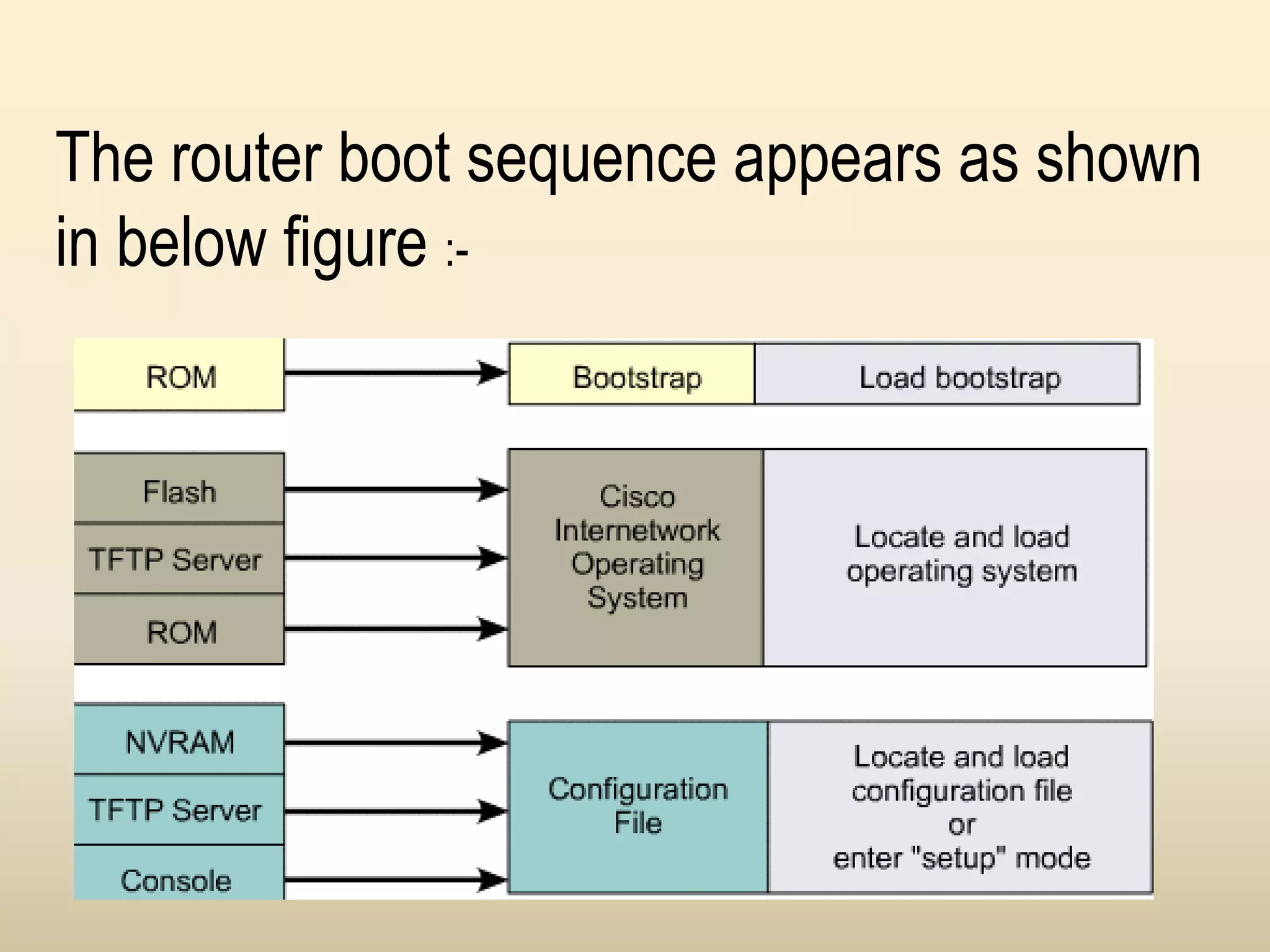
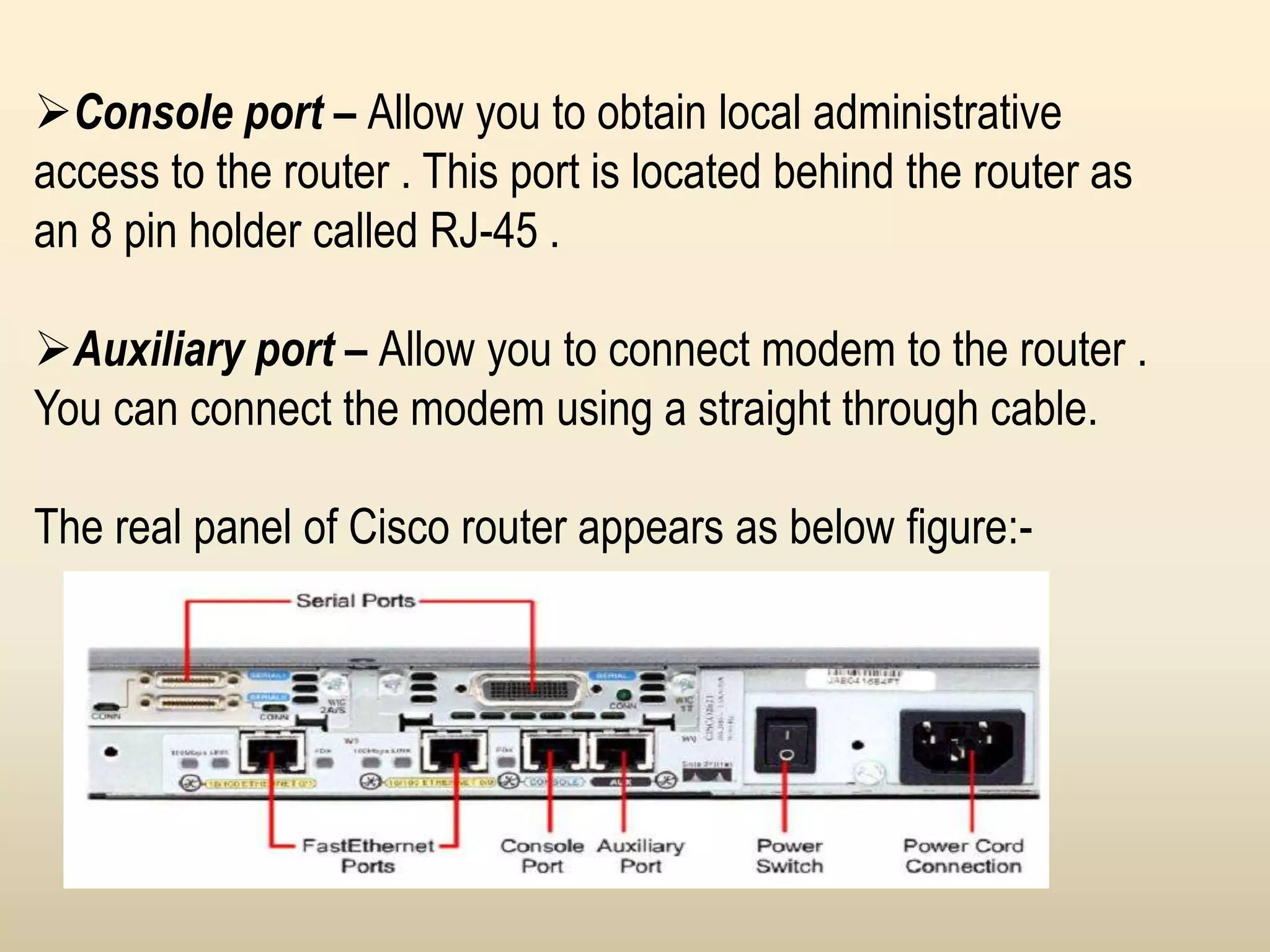
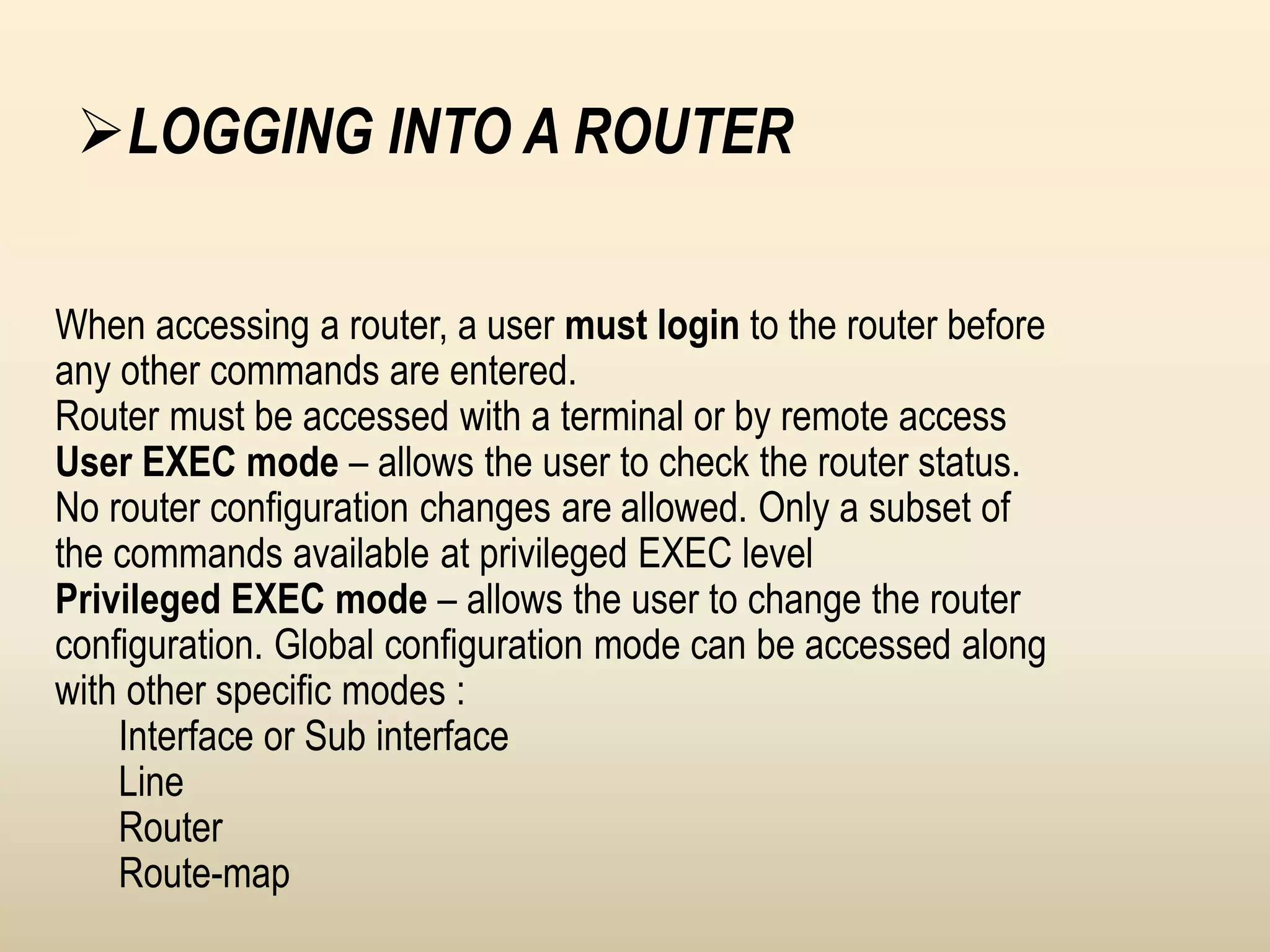
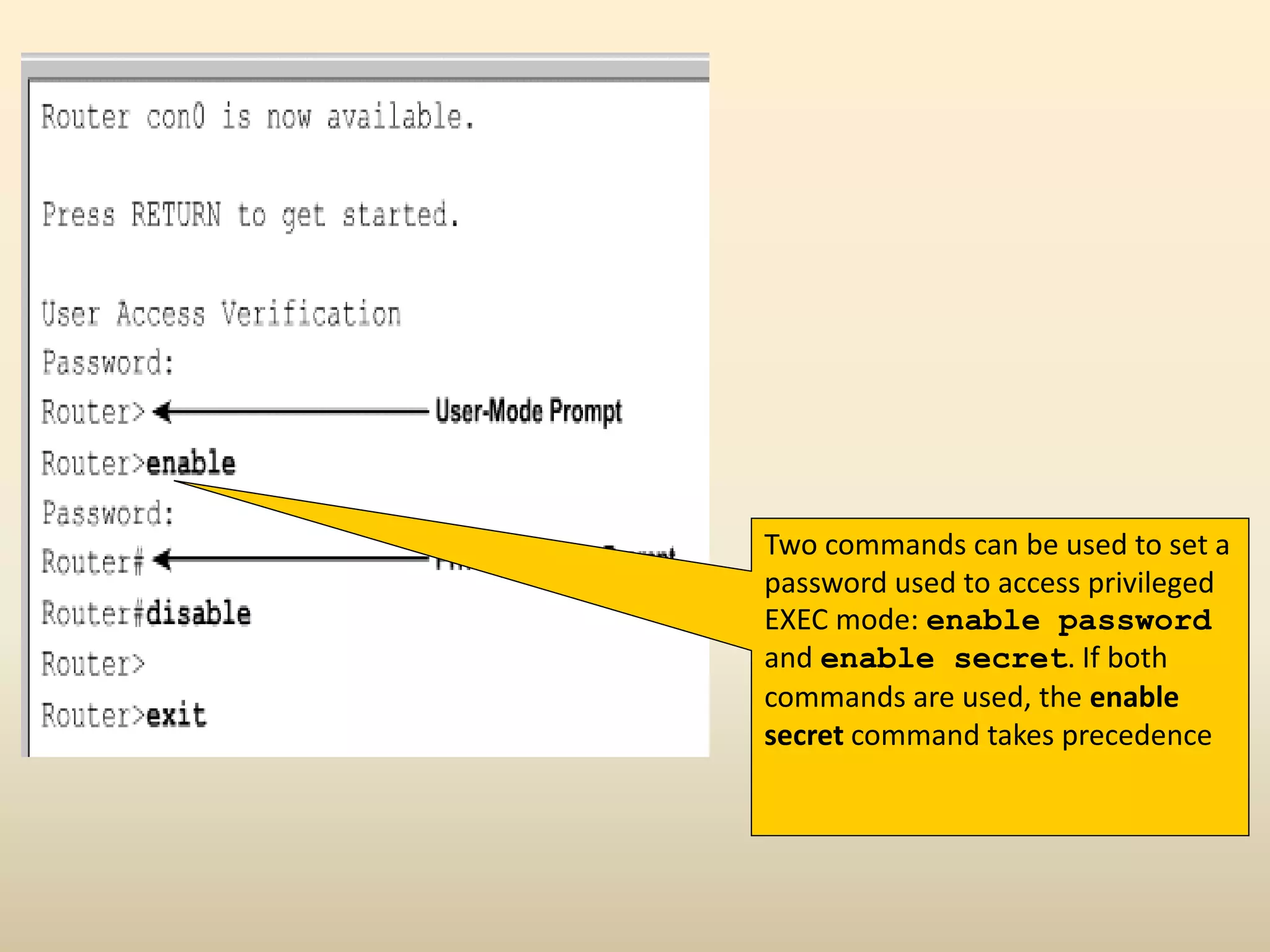
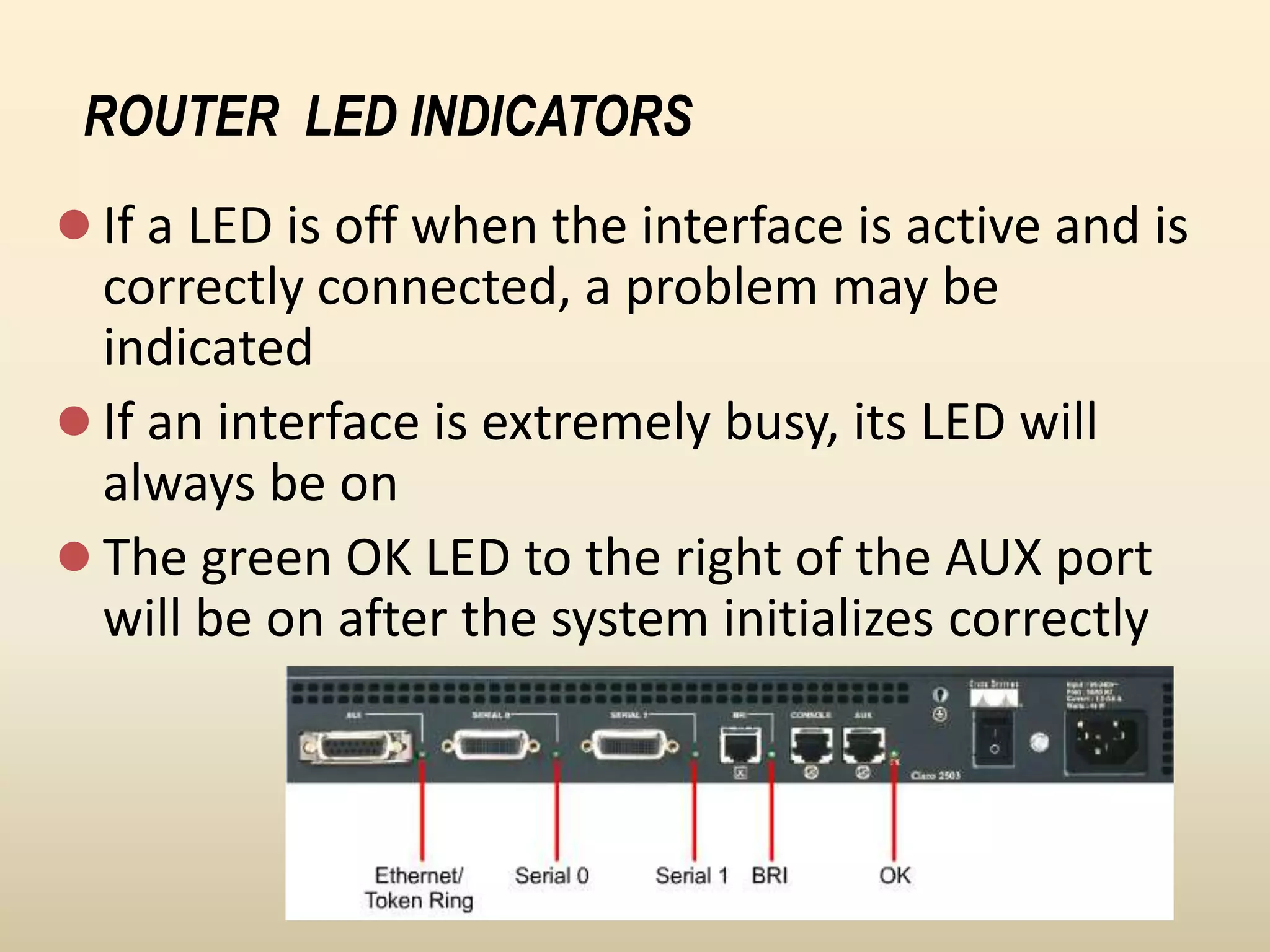
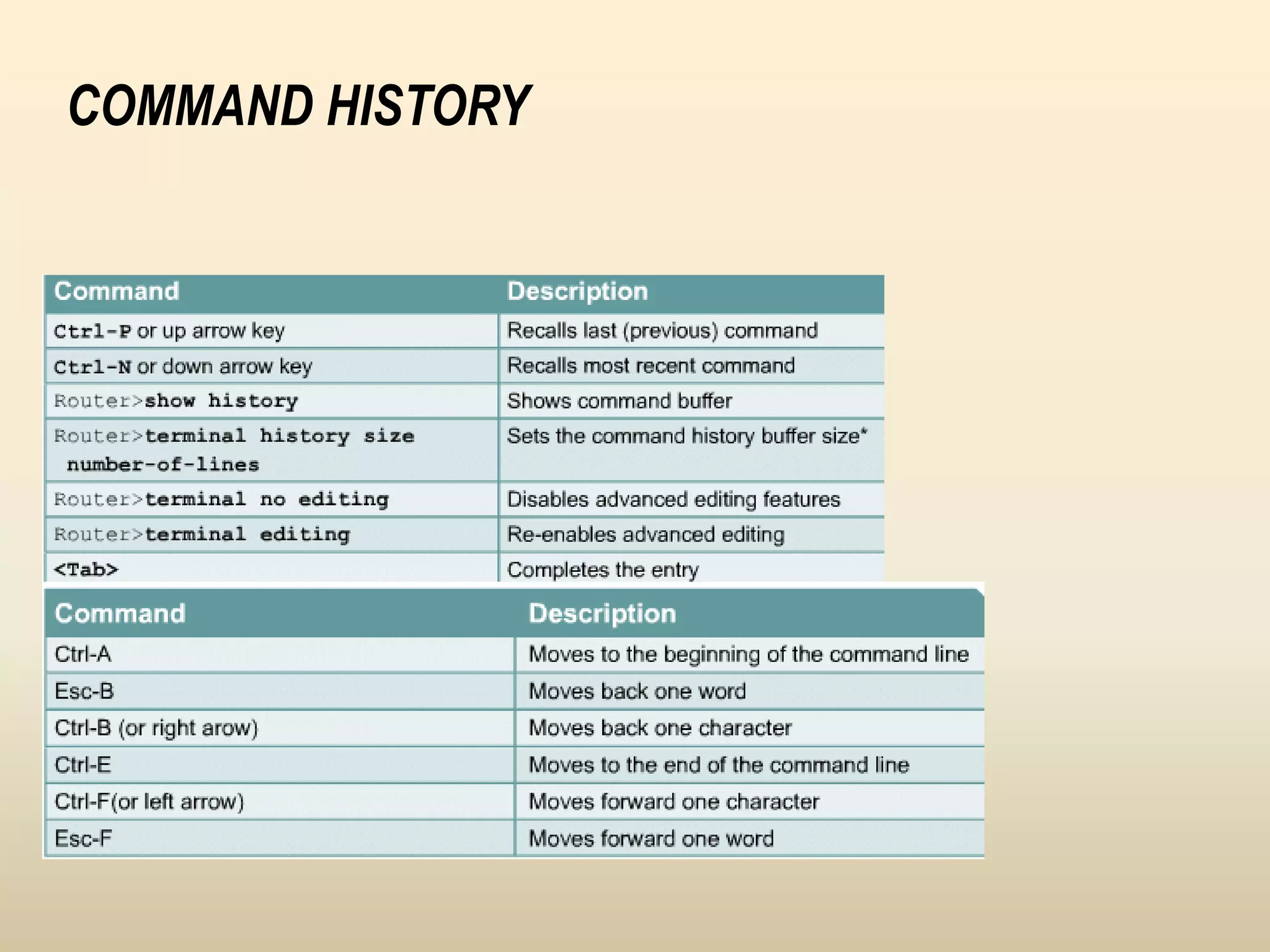
Chapter 4 discusses the fundamentals of routers, detailing their components including processors, memory types, and the boot sequence. It explains the role of the Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) which facilitates interaction between the user and the hardware. Additionally, it covers how to connect to a Cisco router and the command line interface (CLI) used for configuration and management.