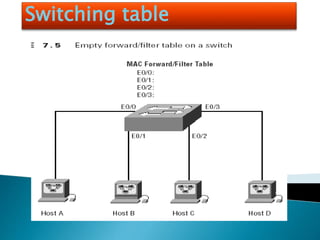
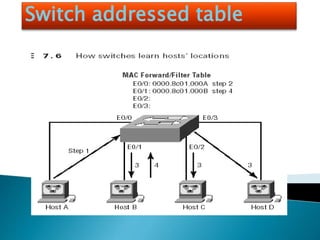
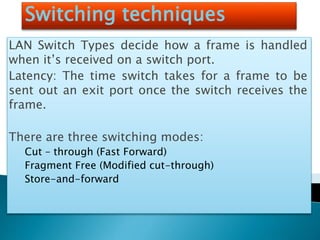
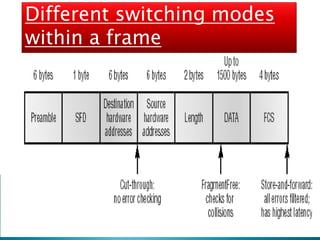
The document explains the fundamentals of switching in networking, highlighting the roles of switches, VLANs, and the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). It details how layer 2 switches operate by using MAC address learning and forwarding frames efficiently while avoiding network loops. Additionally, it covers VLANs' benefits in enhancing network security, scalability, and managing broadcast domains.