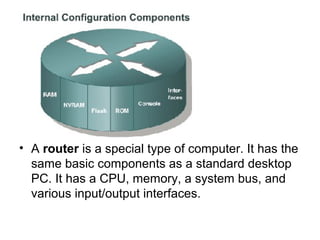
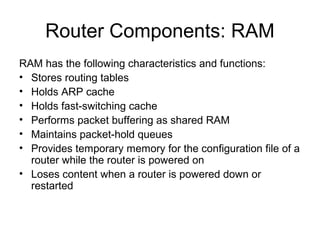
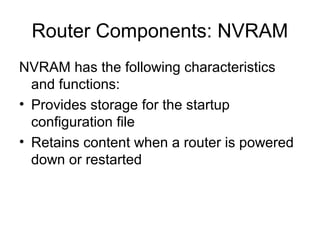
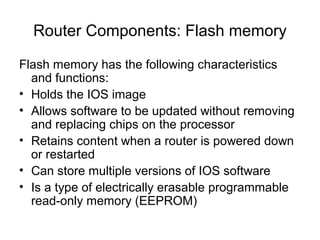
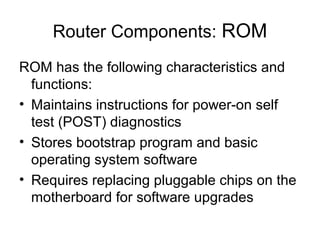
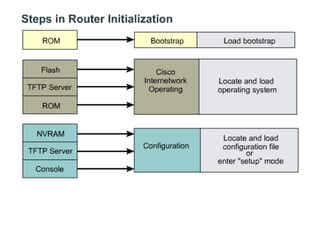
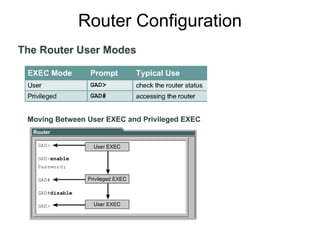
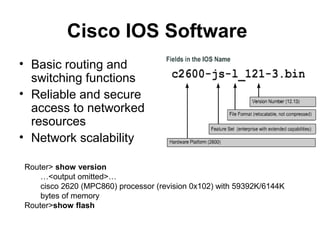
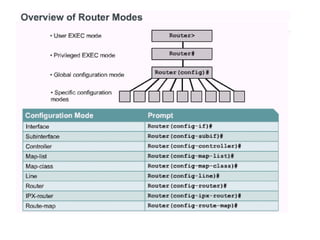
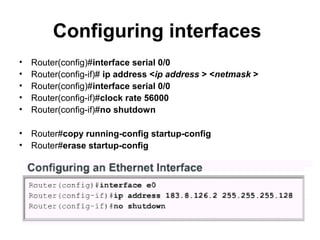
Router configuration involves configuring the components of a router like RAM, NVRAM, flash memory, interfaces, and ROM. RAM stores routing tables and caches. NVRAM stores the startup configuration. Flash memory stores the IOS image. Interfaces connect routers to networks. Dynamic routing protocols like RIP, IGRP, OSPF, and EIGRP can be configured to exchange routing information. Static routes can also be configured using the ip route command. Troubleshooting commands help monitor router operation and troubleshoot issues.




![Routing and Routing Protocols
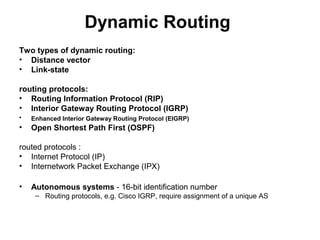
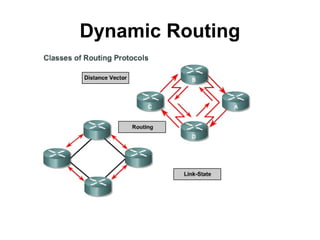
• dynamic routing,
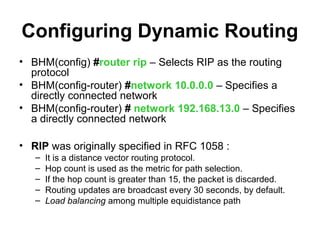
• static routing
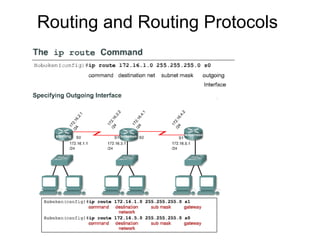
– ip route command to manually configure a static
route.
– administrative distance is an optional parameter that
indicates the reliability of a route.
– waycross(config)# ip route 172.16.3.0 255.255.255.0
172.16.4.1 130
– Route can be configure by outgoing interface or next
hop ip address.
– default route is given by ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
[next-hop-address | outgoing interface ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routerconfiguration-130310055828-phpapp02/85/Router-configuration-22-320.jpg)