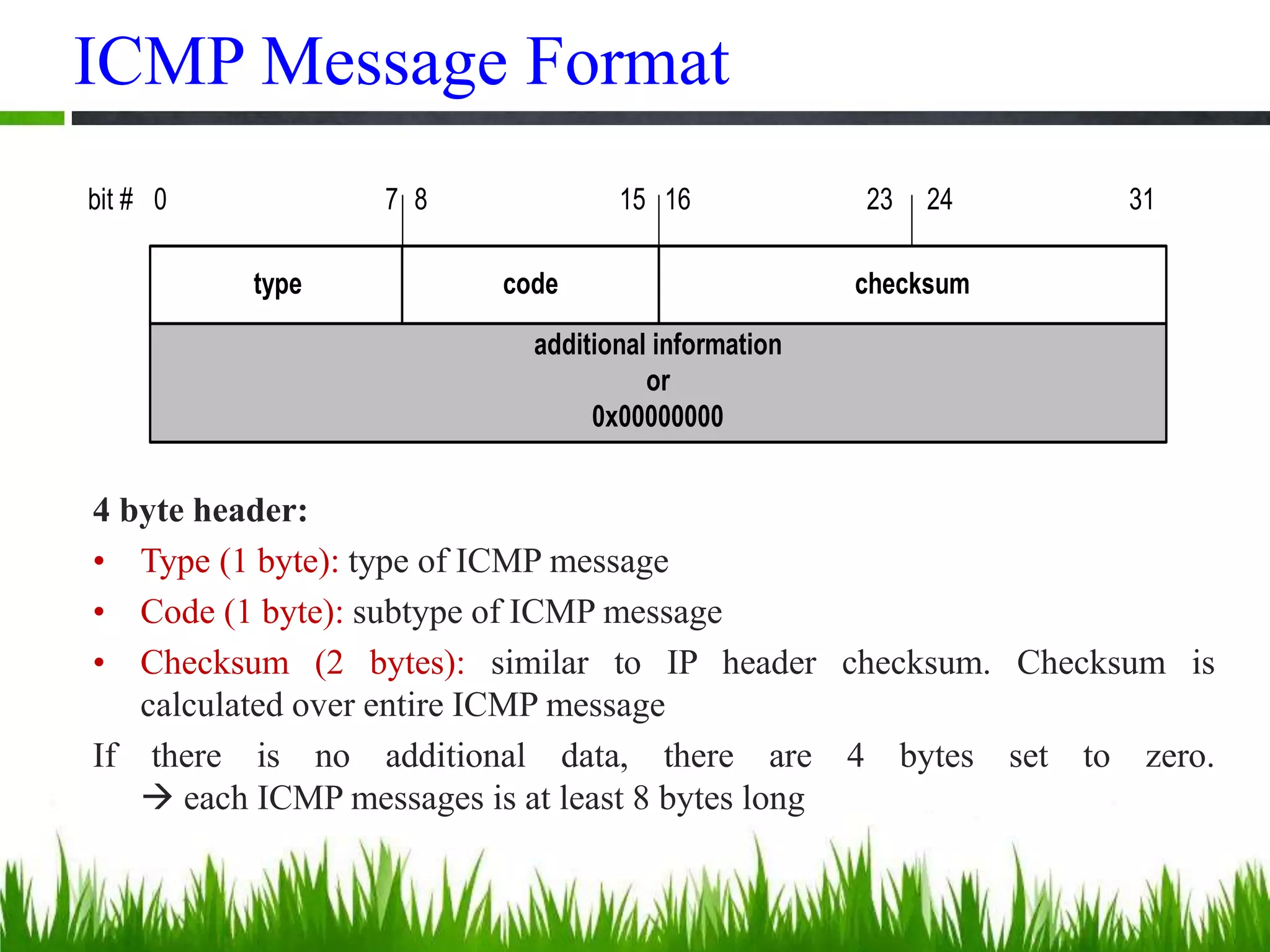
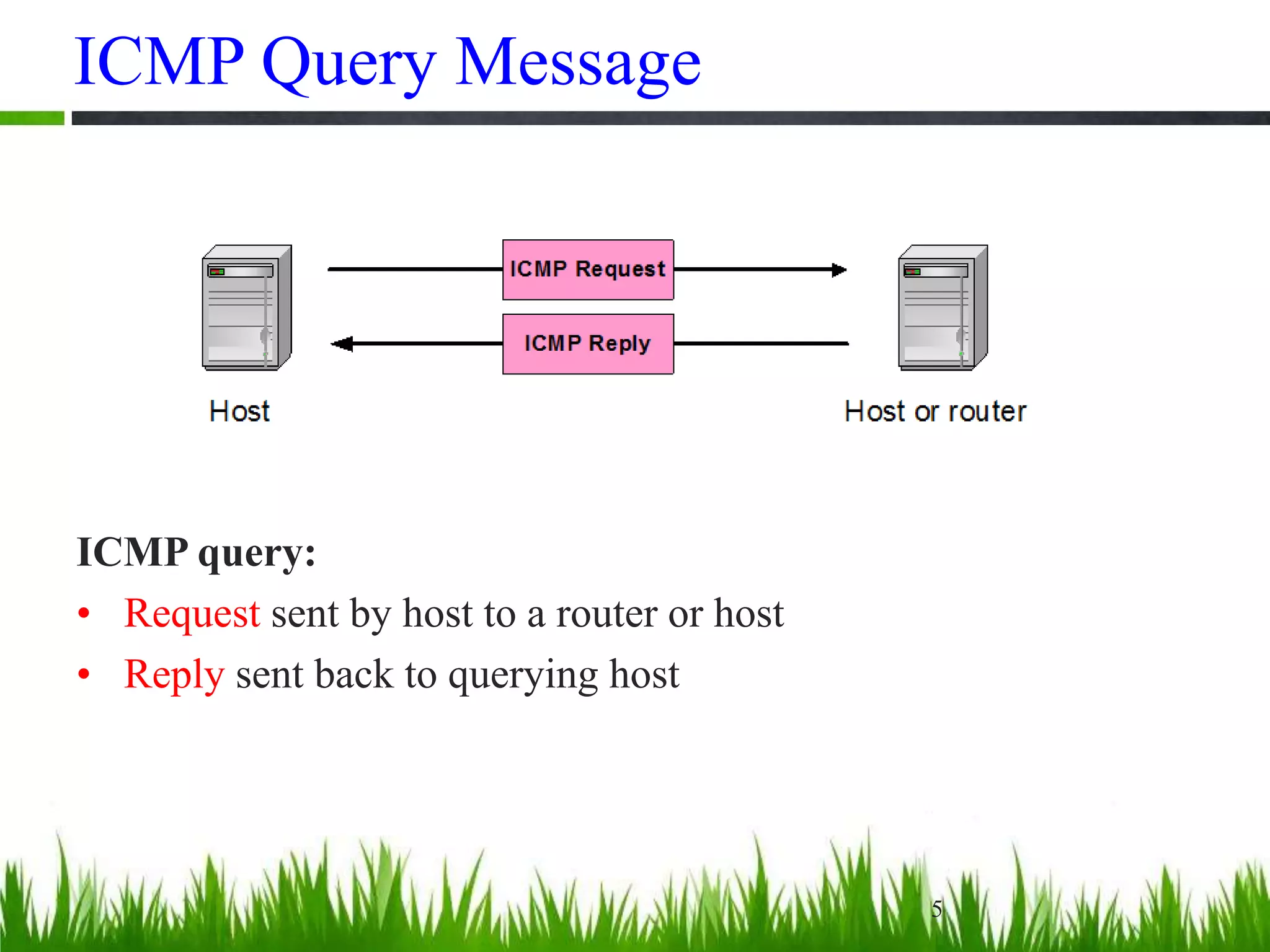
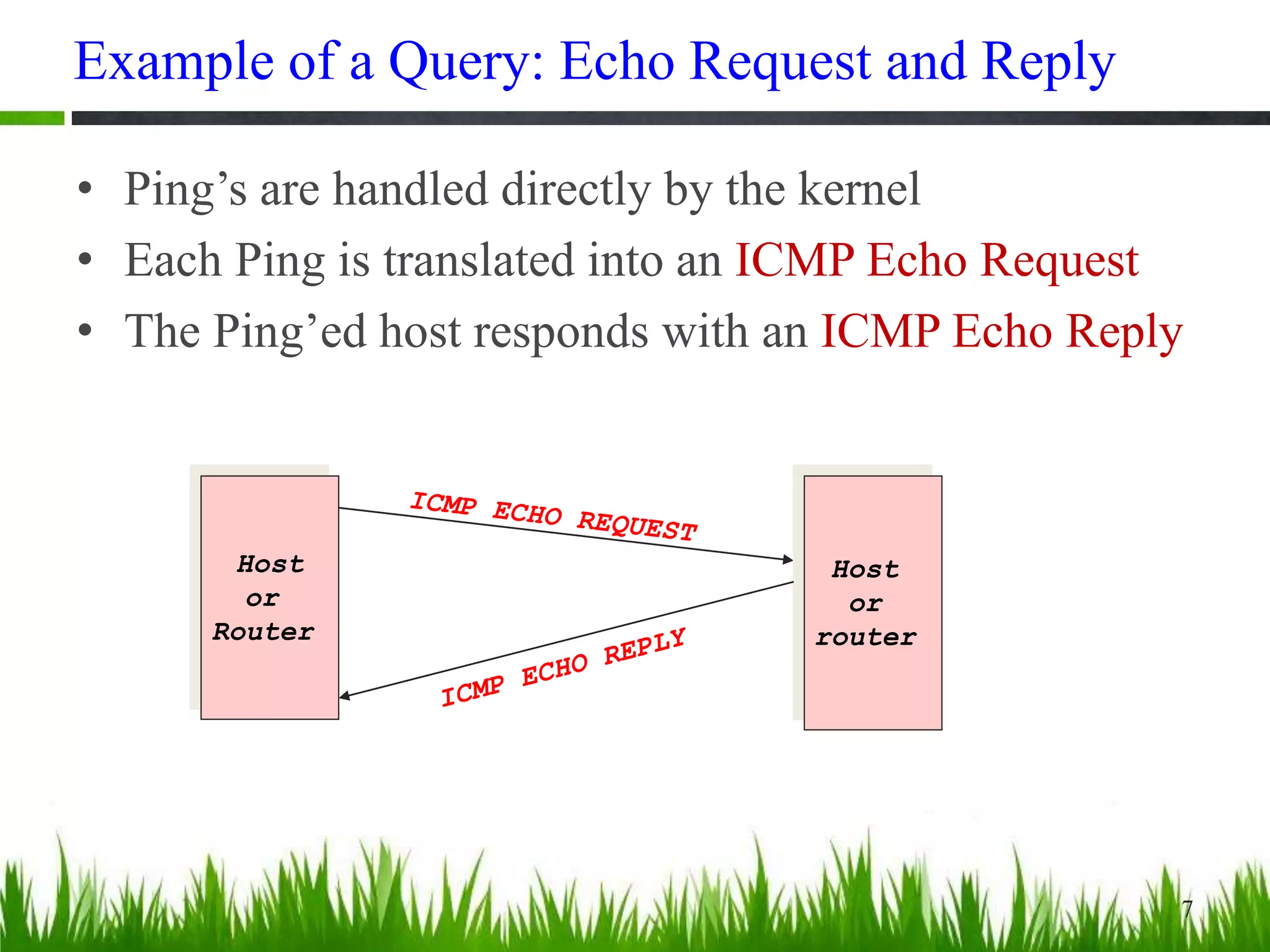
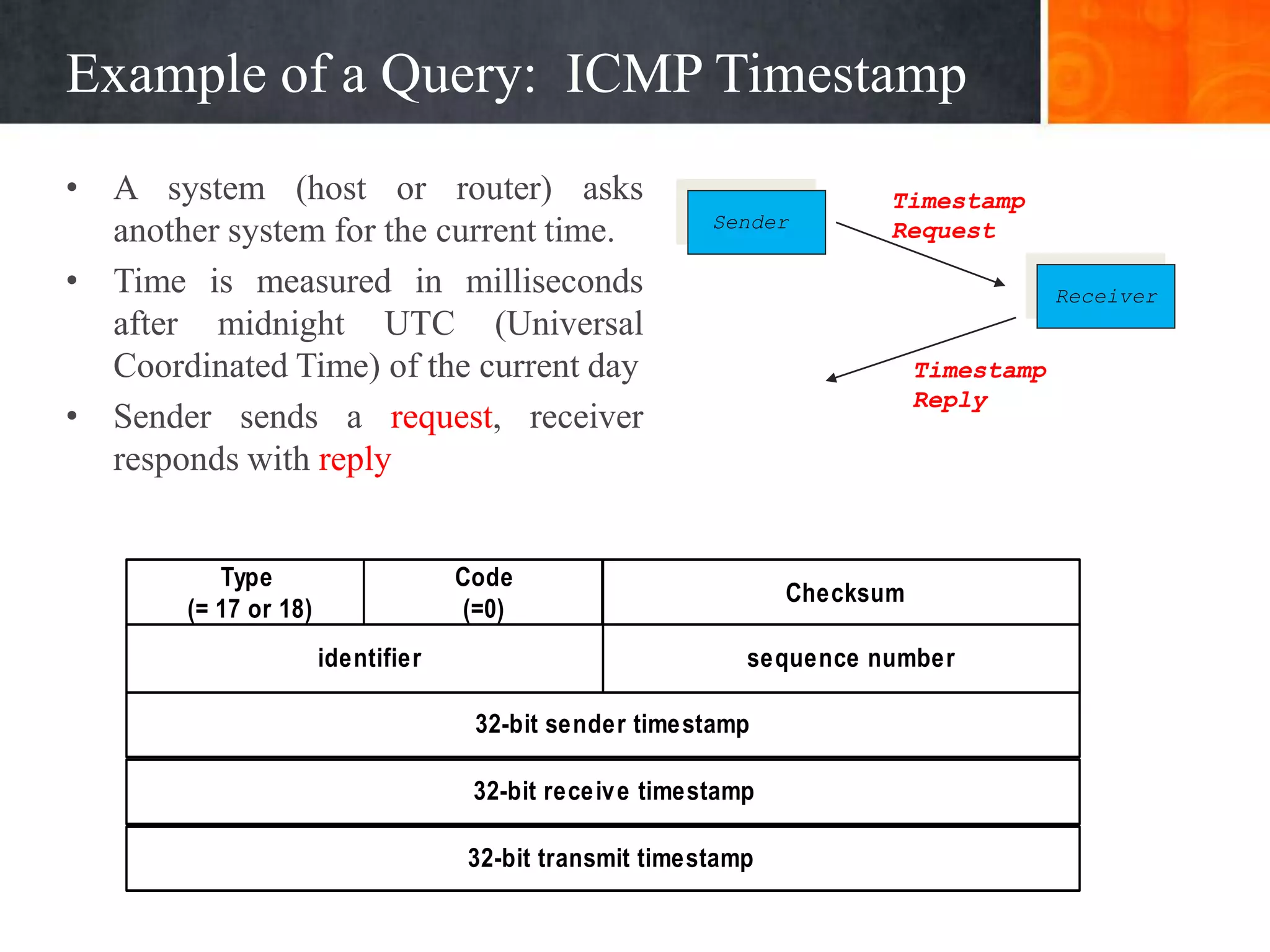
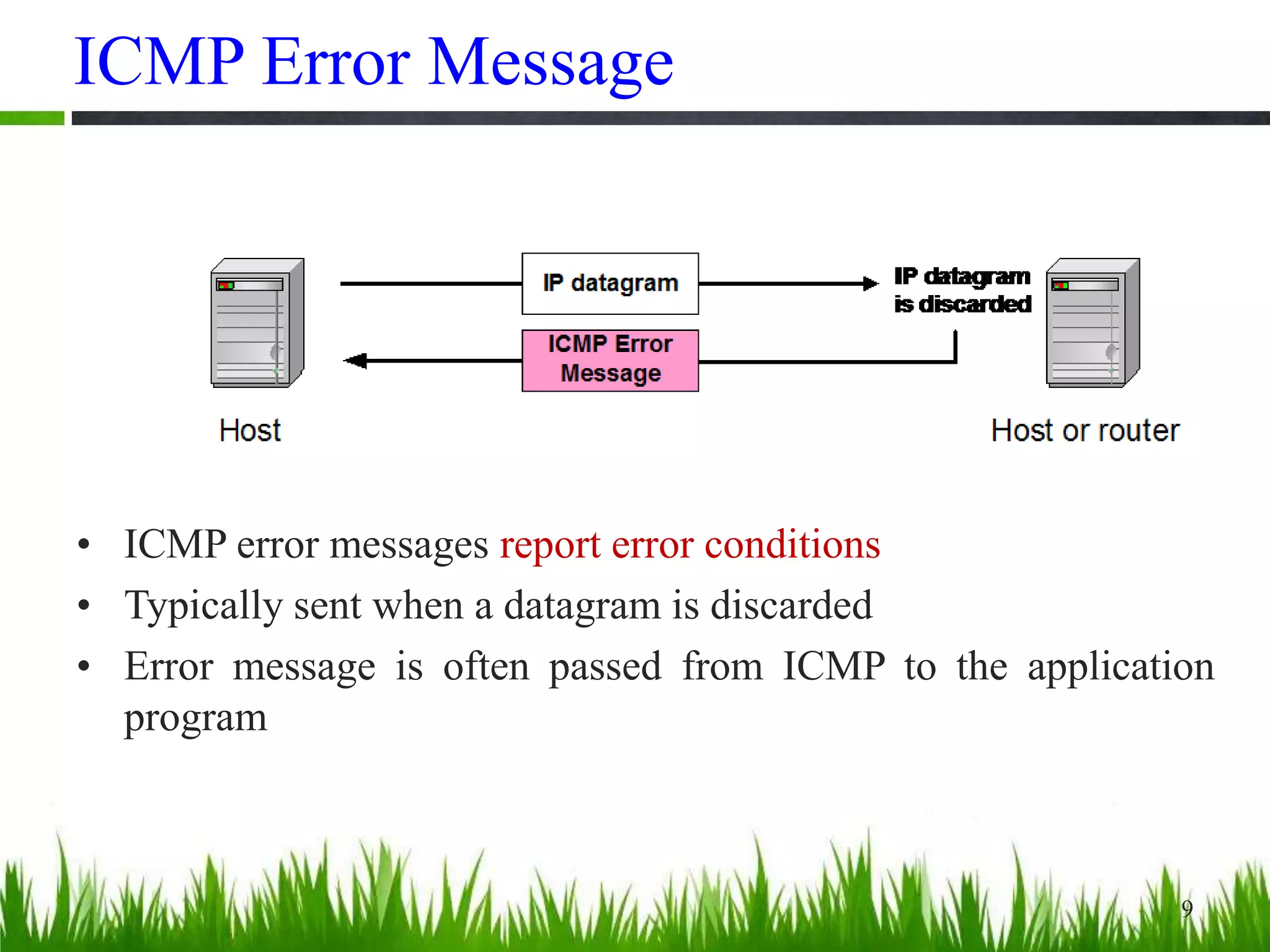
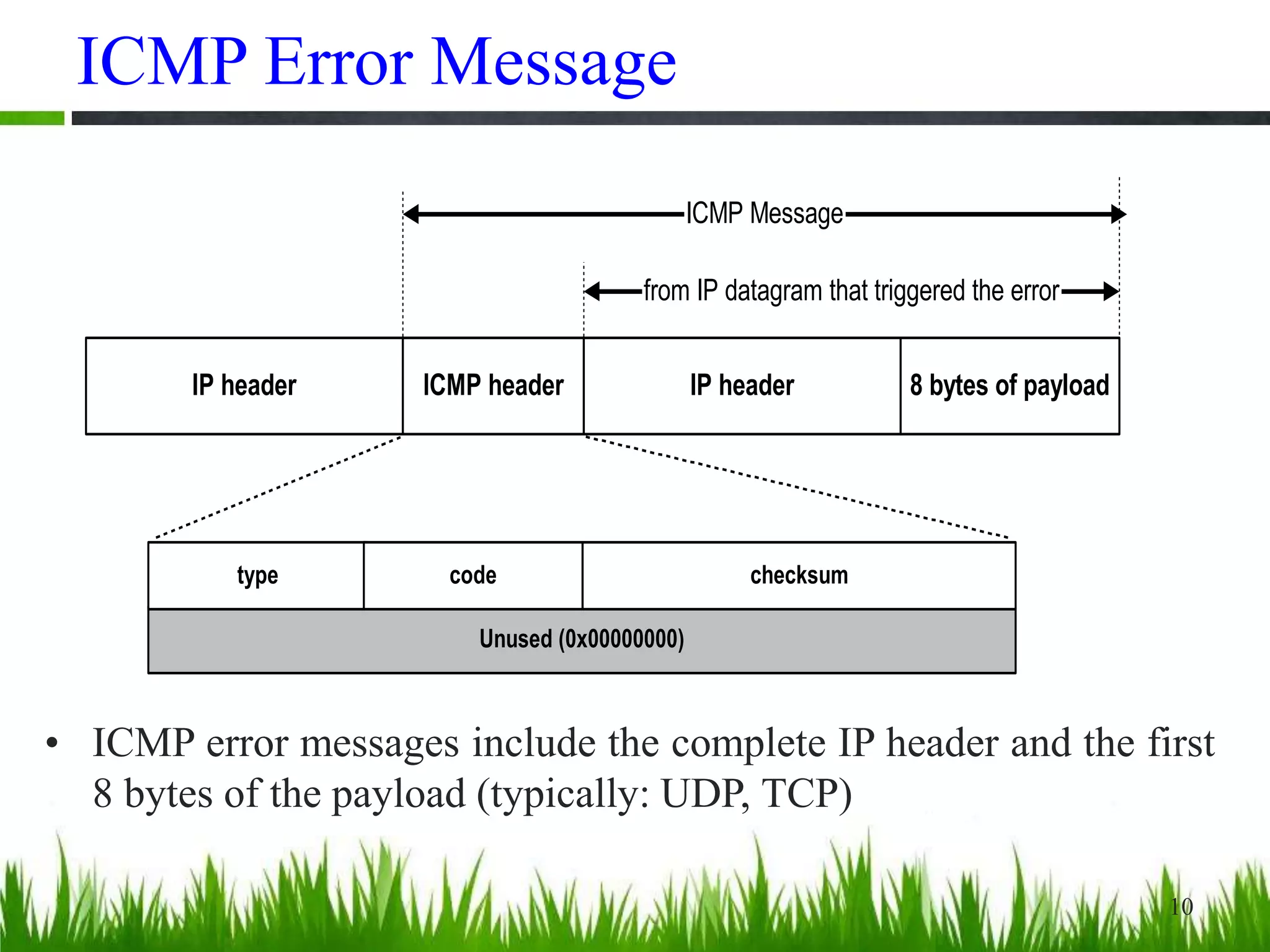
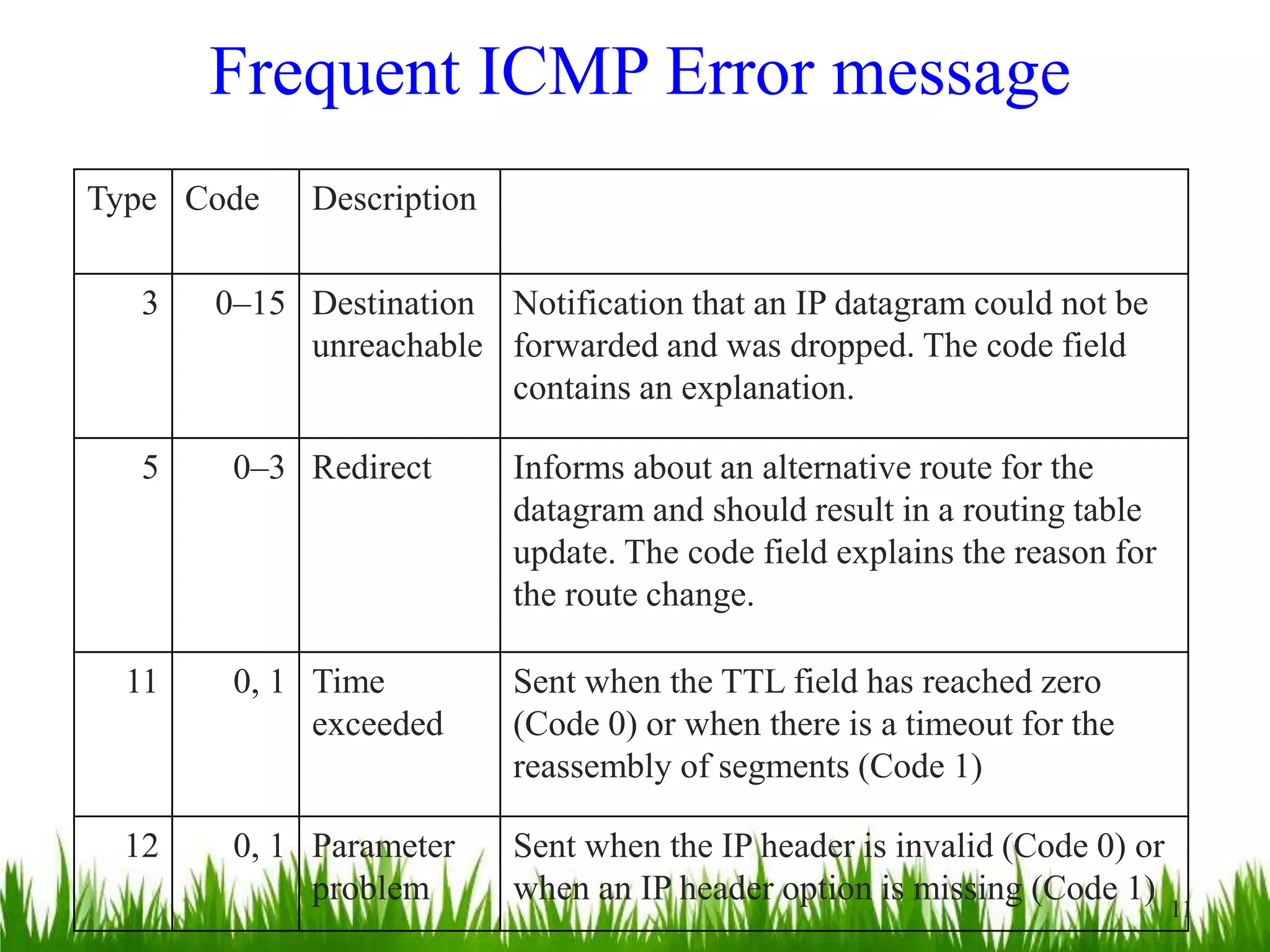
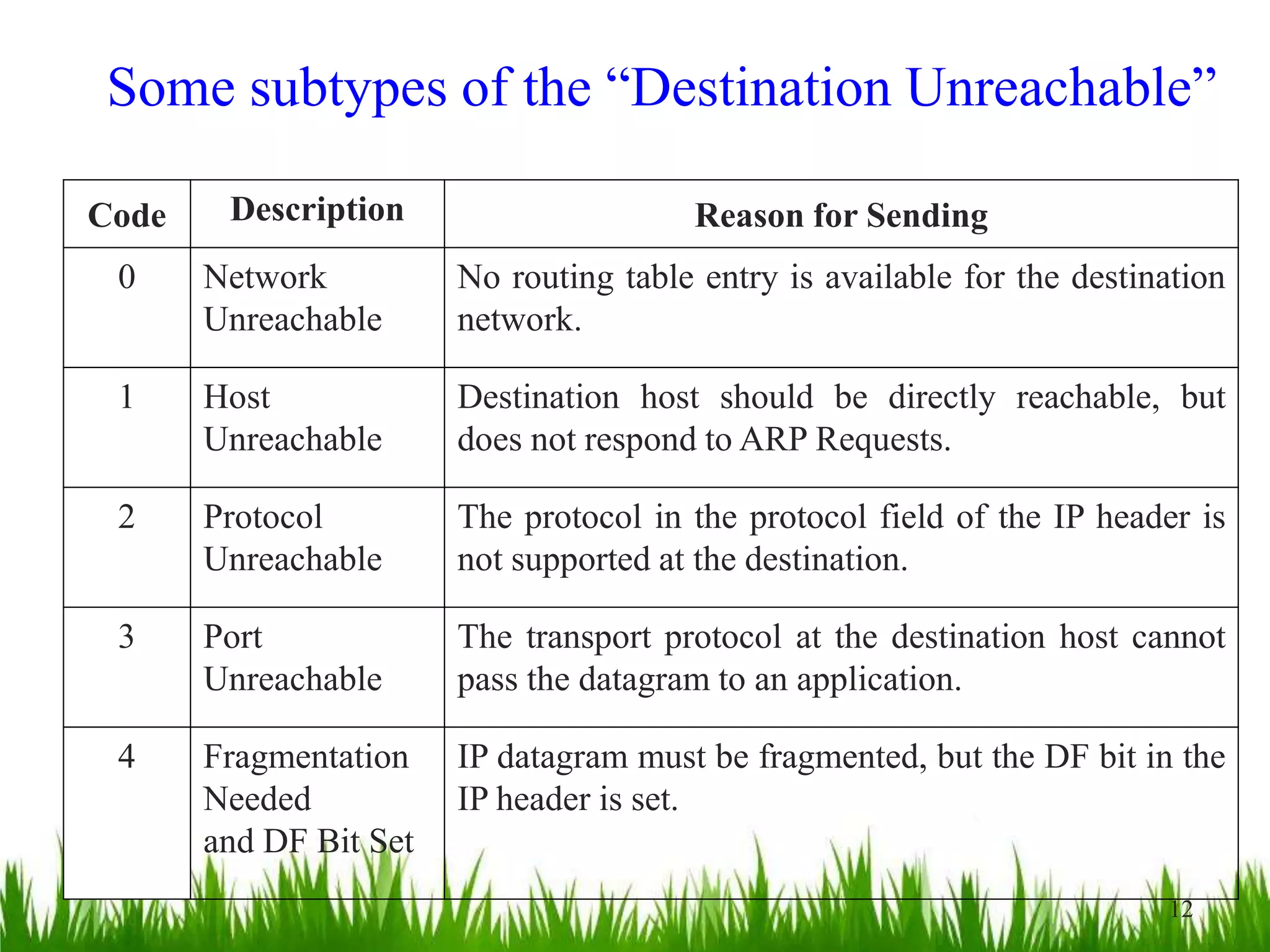
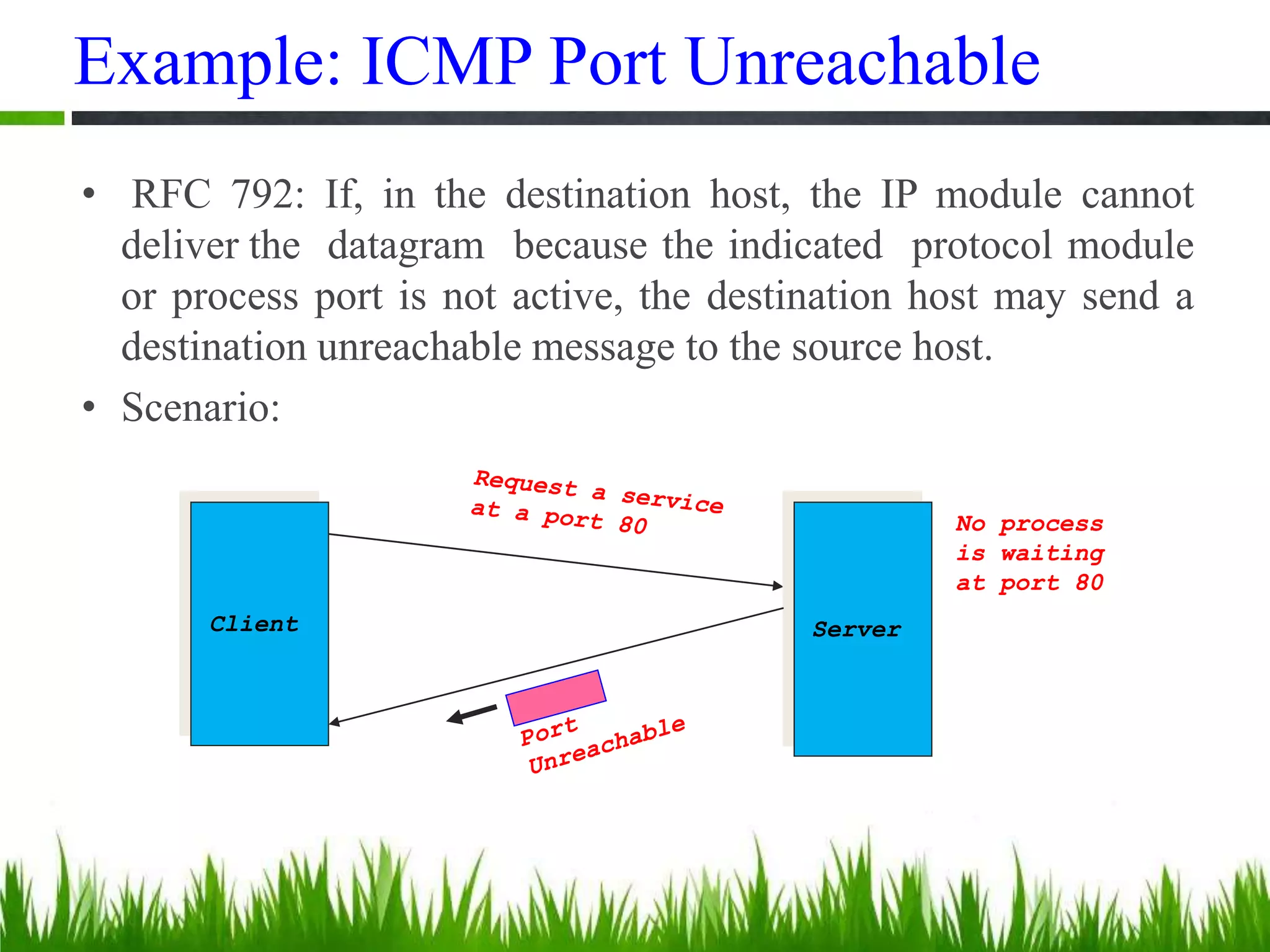
This document provides an overview of the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). It discusses how ICMP supports IP by providing error reporting and simple queries. It describes the ICMP message format including type, code, and checksum fields. It gives examples of common ICMP query messages like echo request/reply and timestamp request/reply. It also discusses ICMP error messages, including how they are formatted and common error types like destination unreachable, redirect, time exceeded, and parameter problem. It provides details on some destination unreachable error subtypes and gives an example of an ICMP port unreachable message.