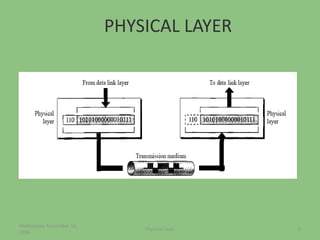
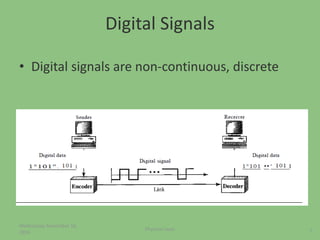
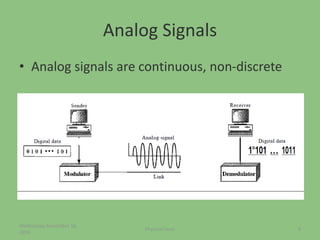
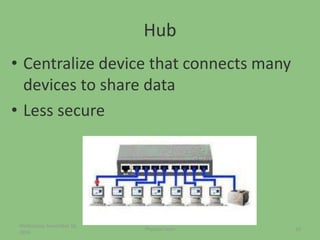
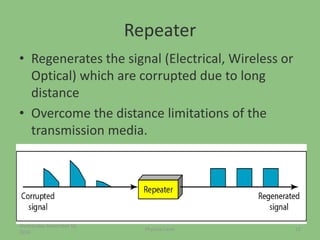
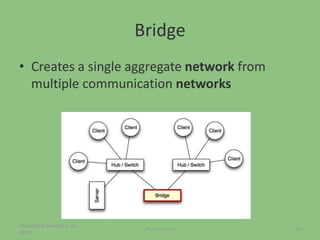
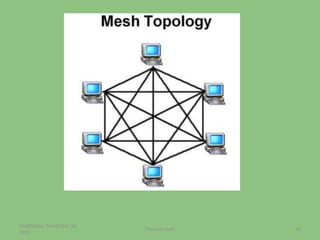
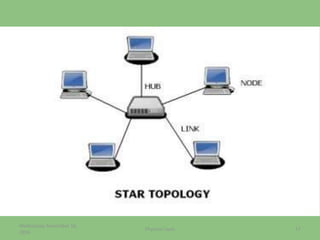
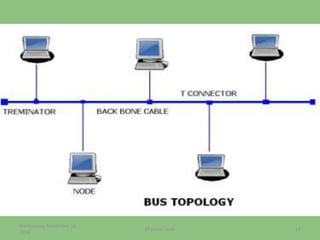
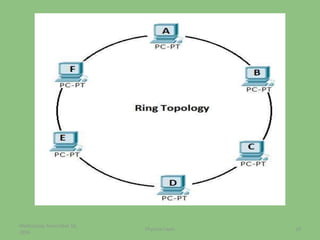
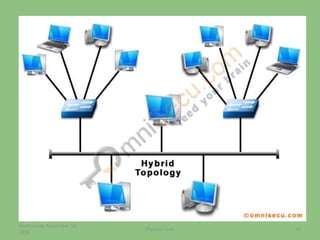
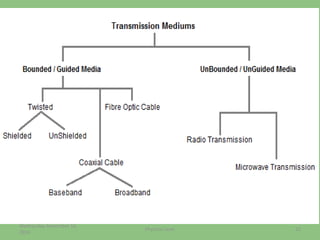
This document provides an overview of the physical layer of the OSI model, detailing its role in data transmission and the types of signals (analog and digital) used. It describes common devices such as hubs, switches, repeaters, bridges, and modems that facilitate network connectivity, as well as different physical topologies and transmission media. The physical layer is crucial for defining the mechanical and electrical specifications of interfaces and the medium used for communication.