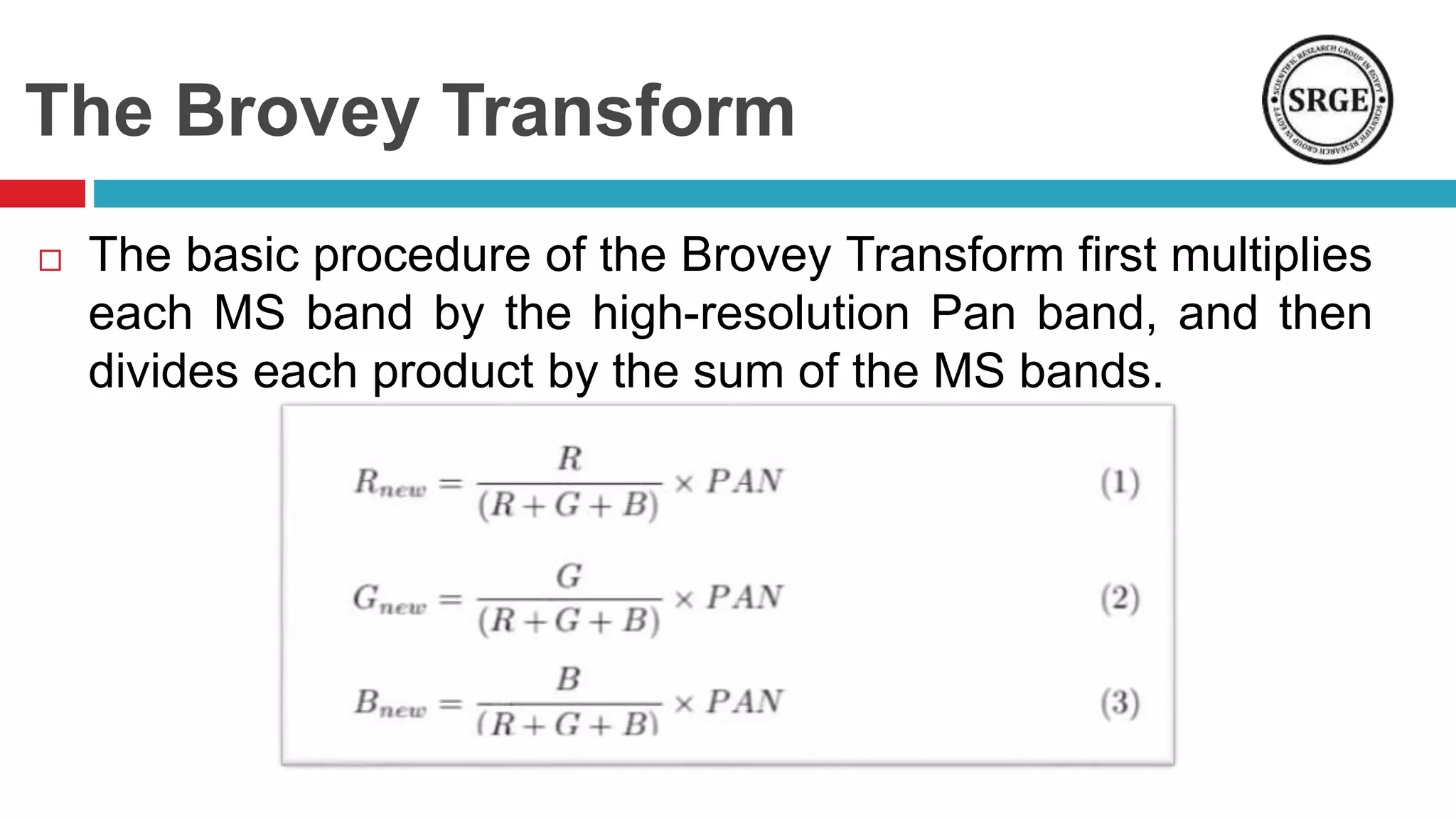
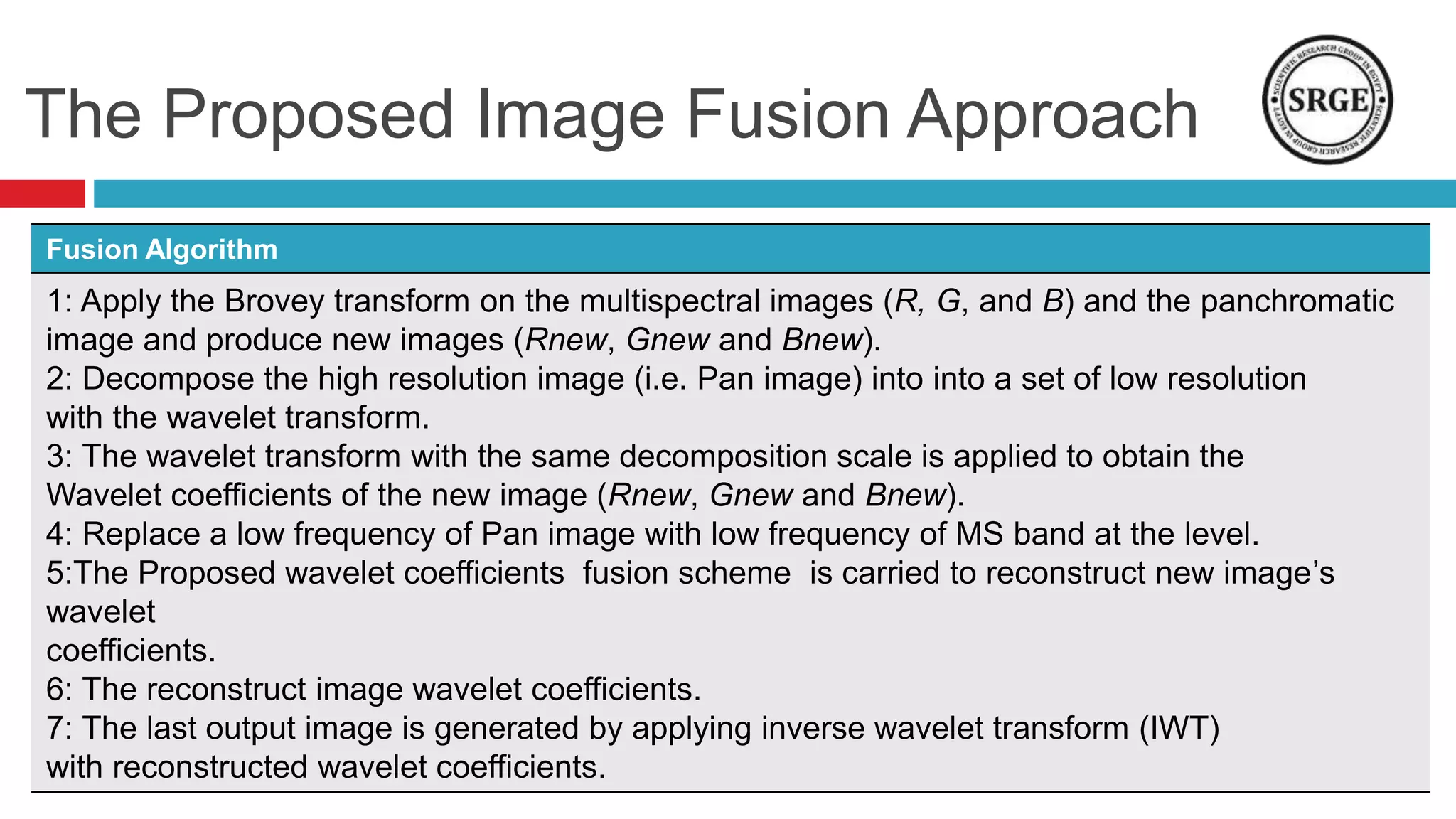
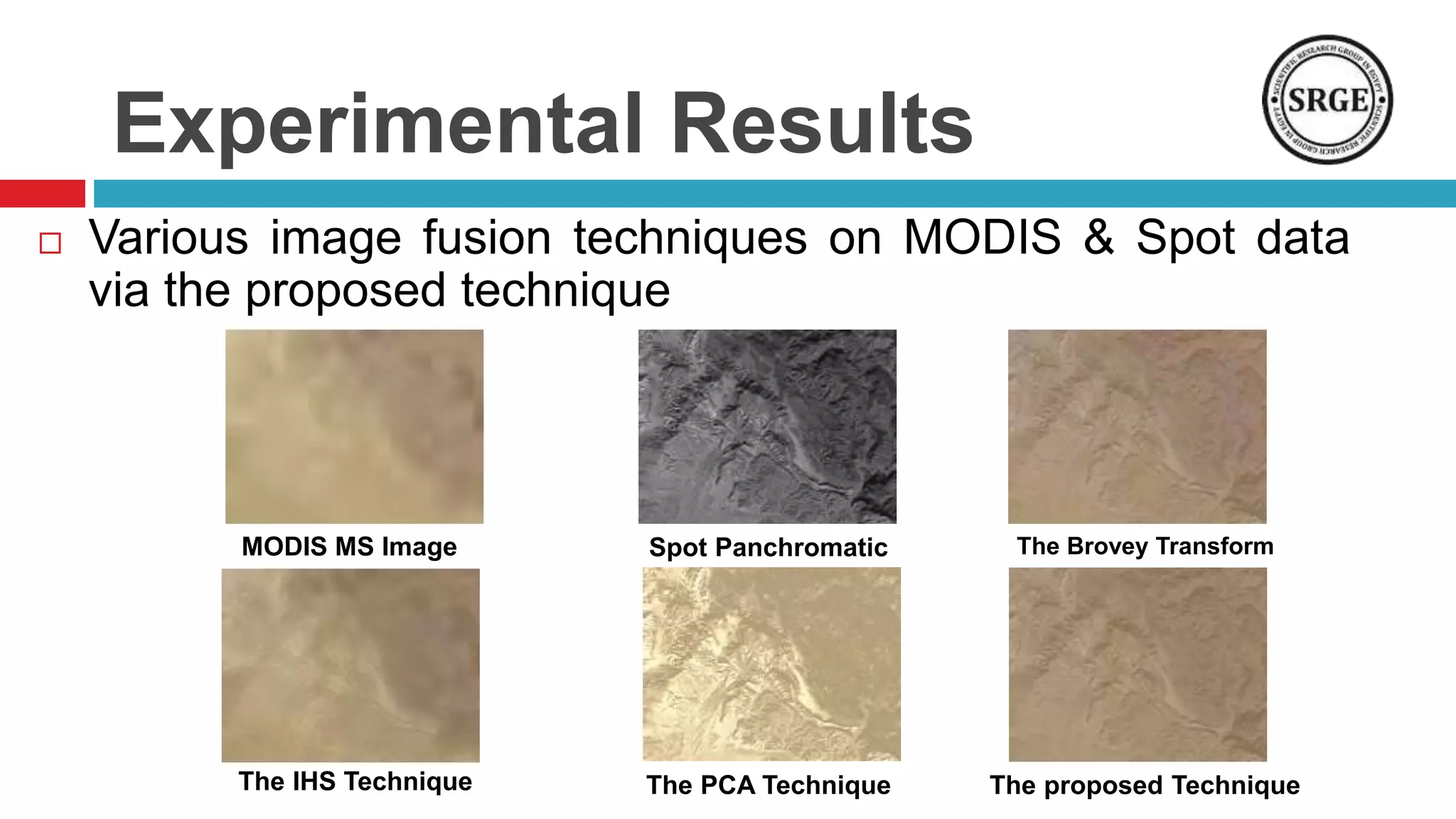
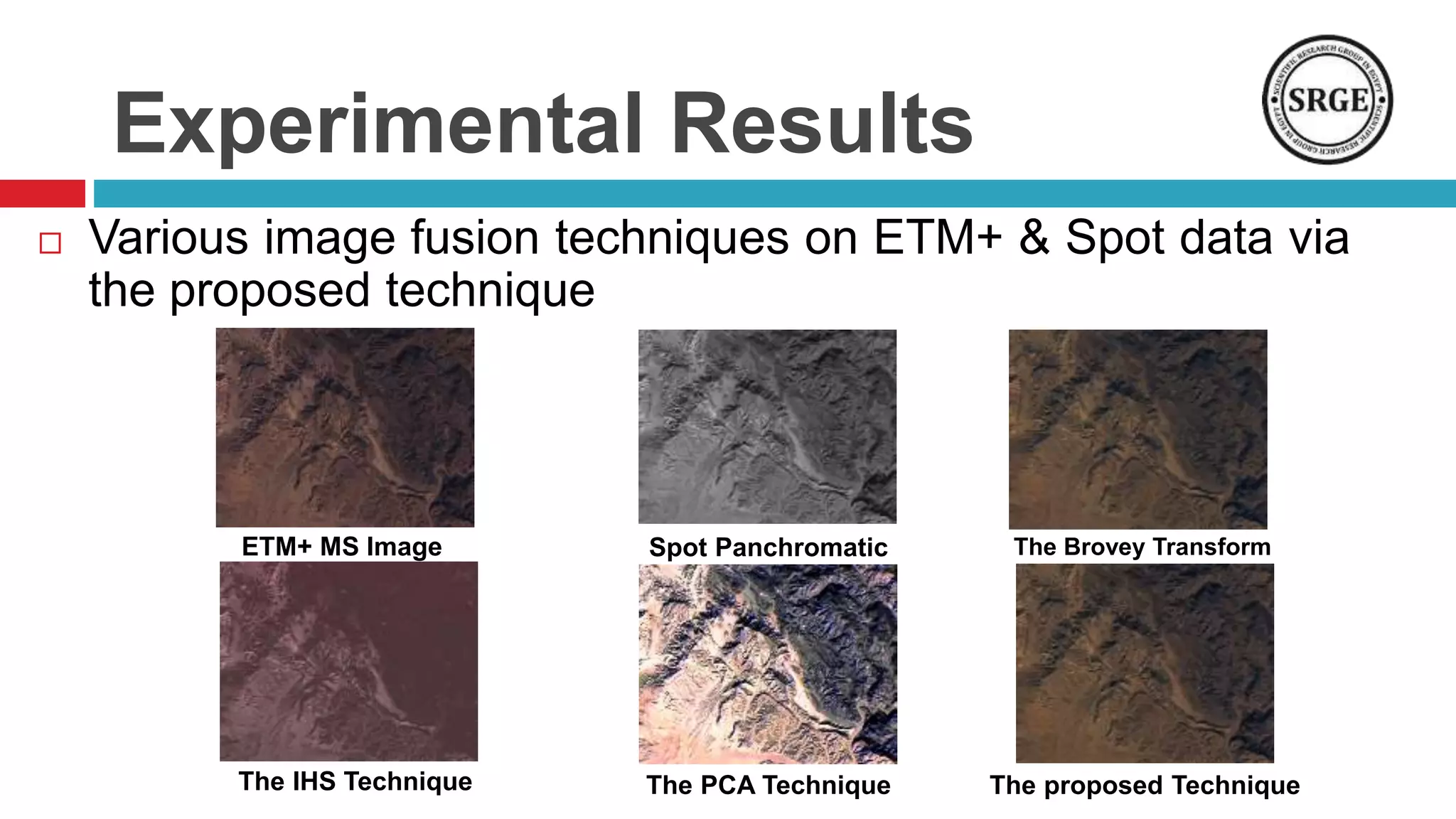
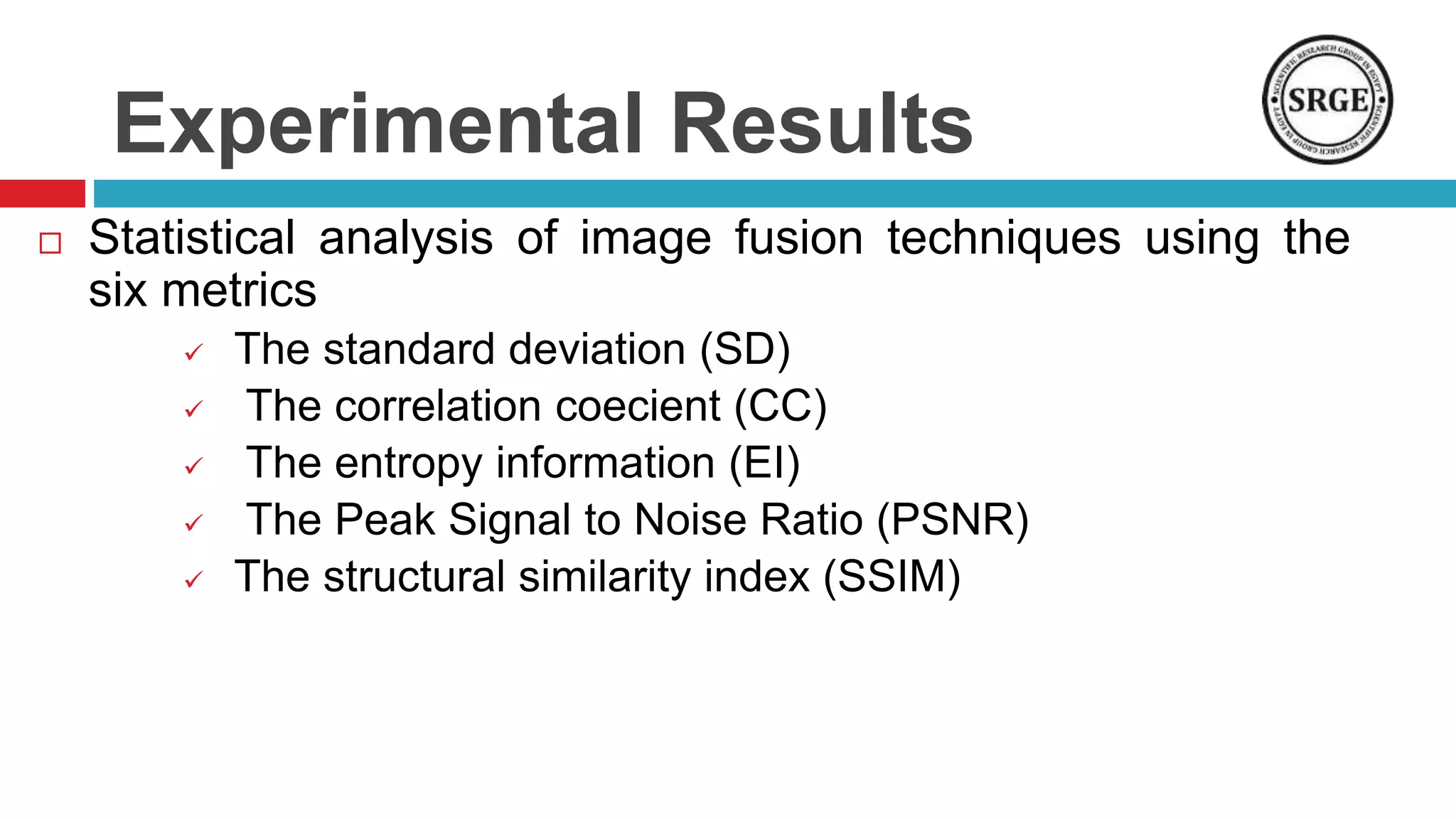
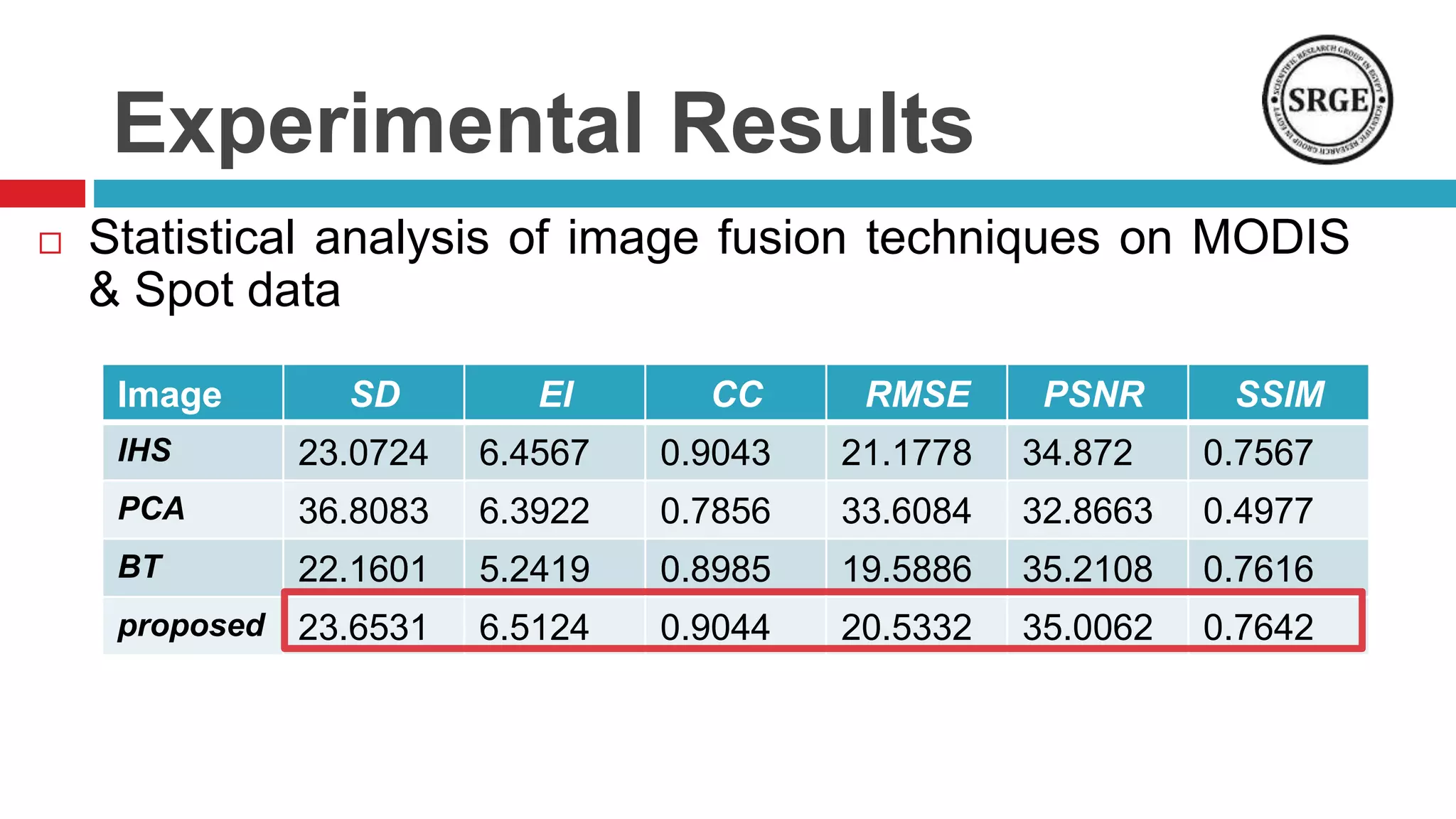
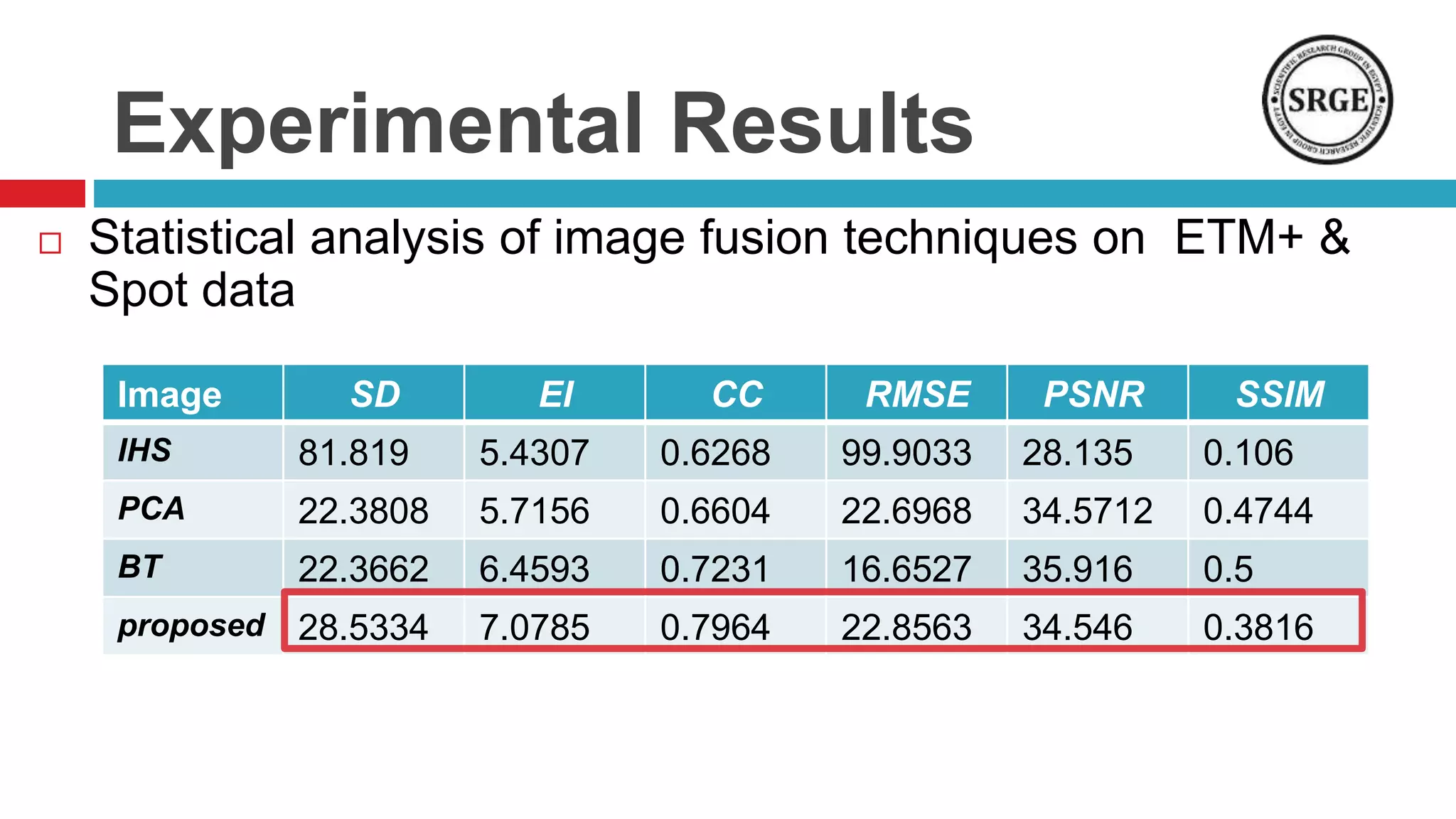
This document proposes a remote sensing image fusion approach that combines the Brovey transform and wavelet transforms. The Brovey transform is used first to reduce spectral distortion, followed by a wavelet transform to reduce spatial distortion. The approach was tested on MODIS and SPOT data as well as ETM+ and SPOT data. Statistical analysis showed the proposed technique performed better than traditional fusion techniques like IHS, PCA, and the Brovey transform alone in terms of metrics like correlation coefficient, entropy, and structural similarity. Future work will focus on improving the technique and applying fused images to classification tasks.