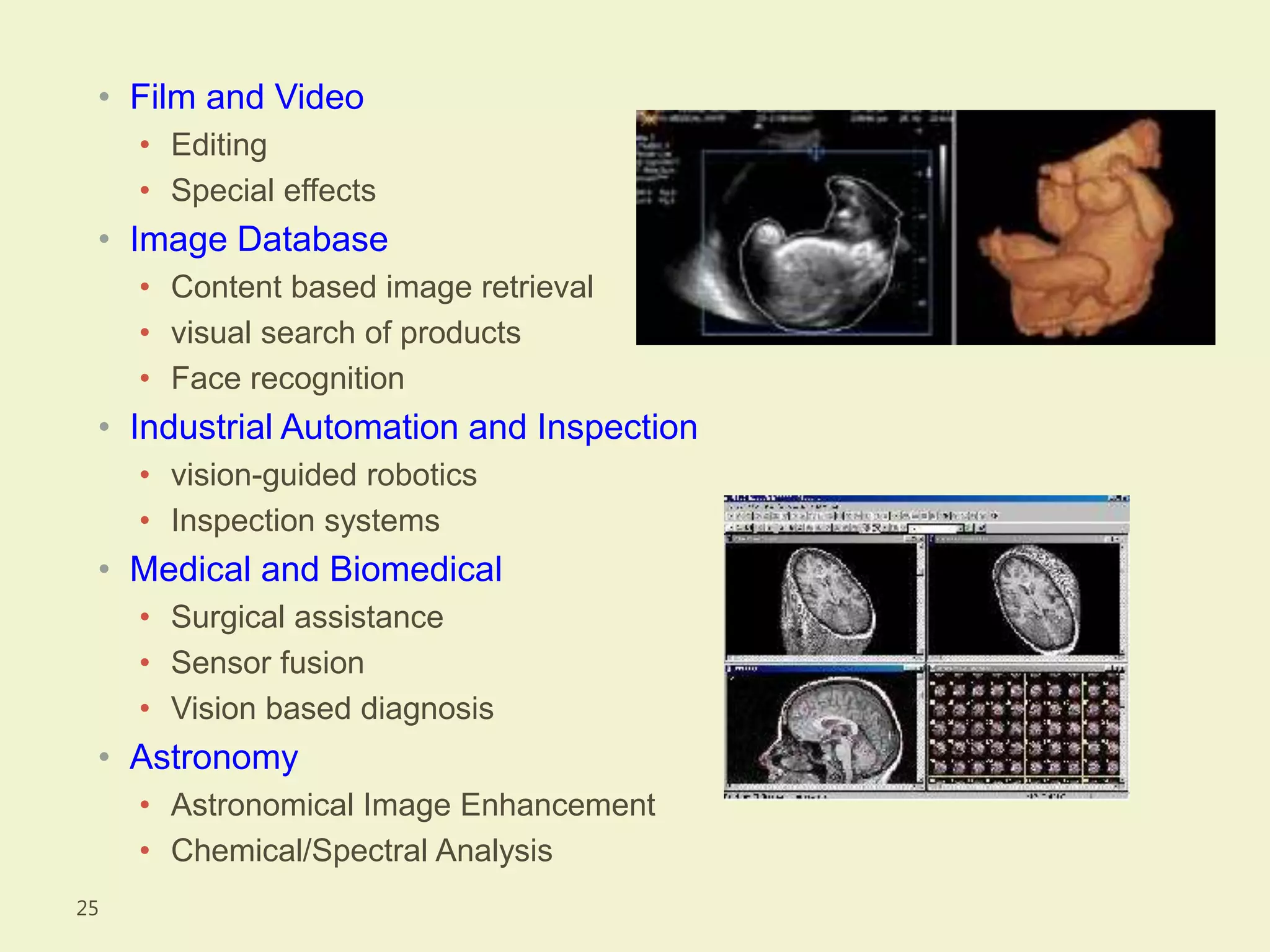
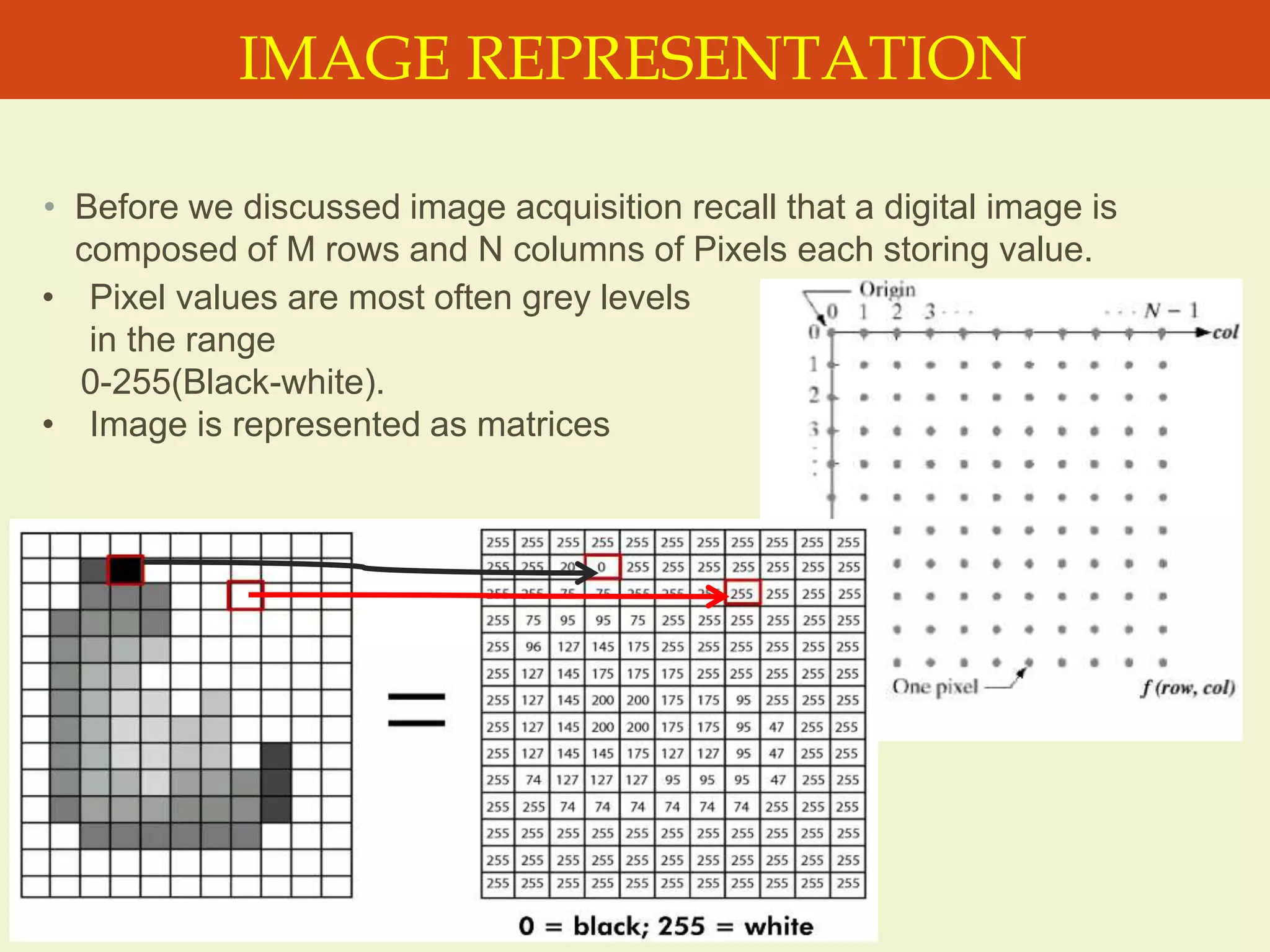
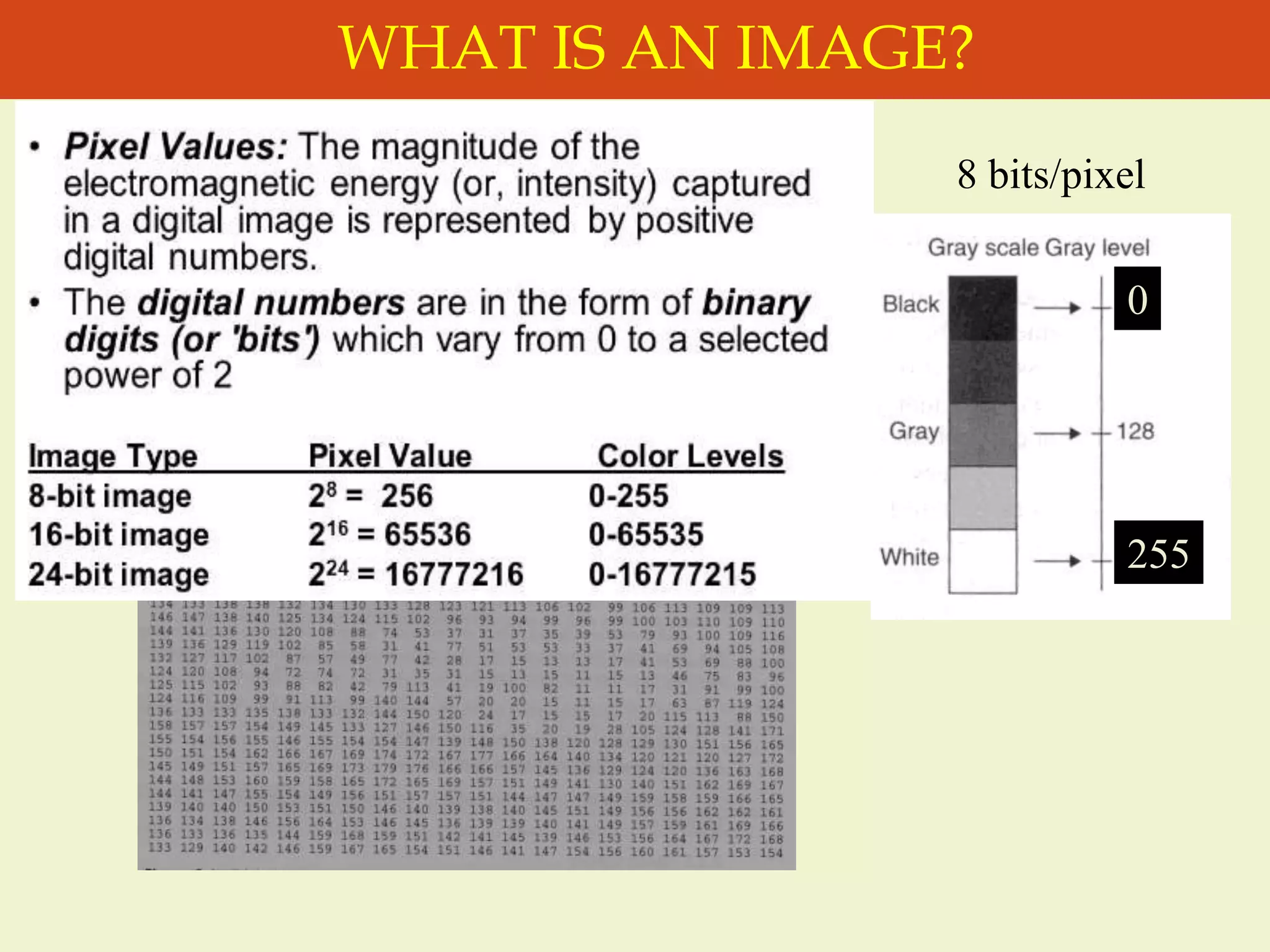
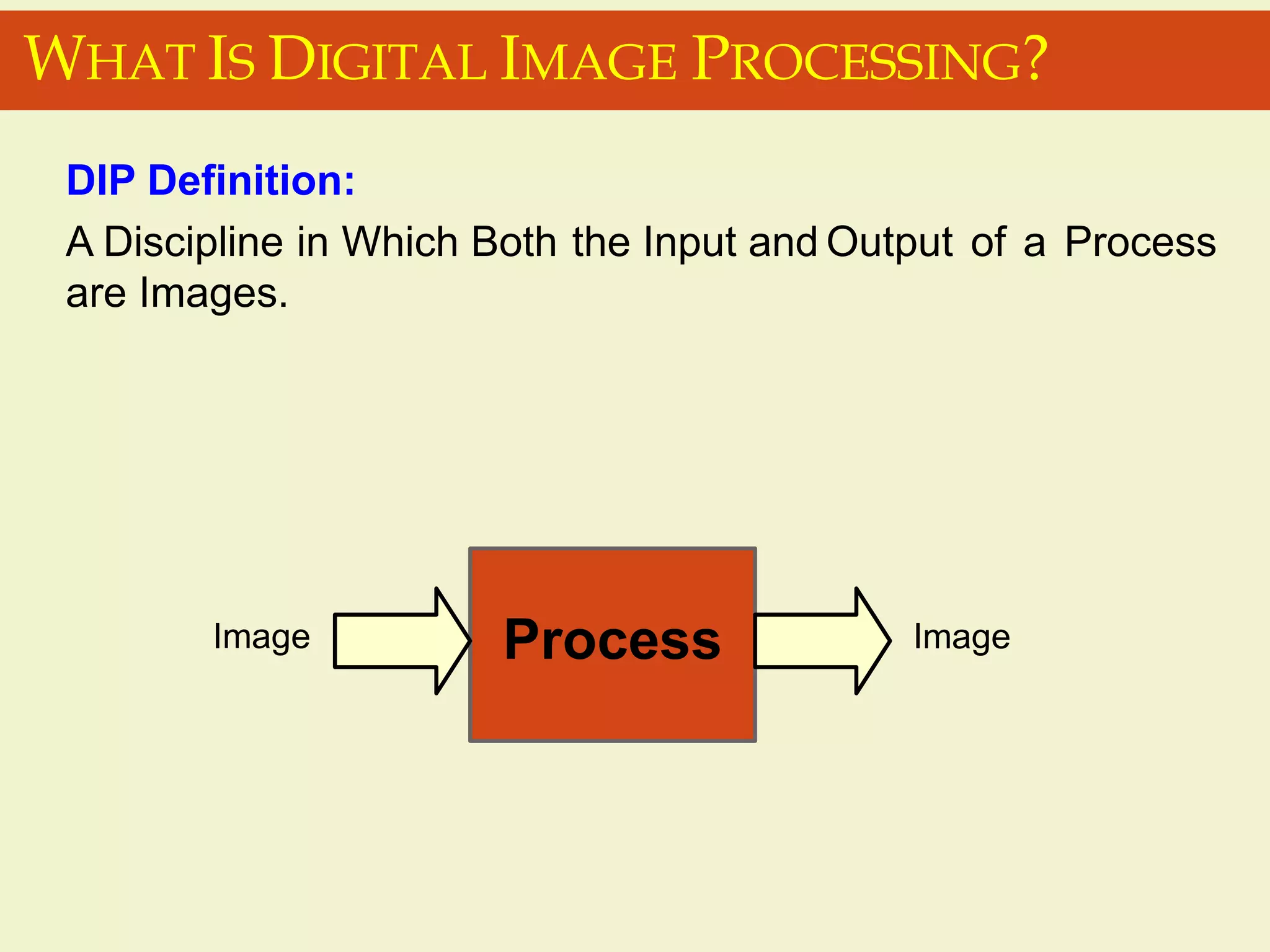
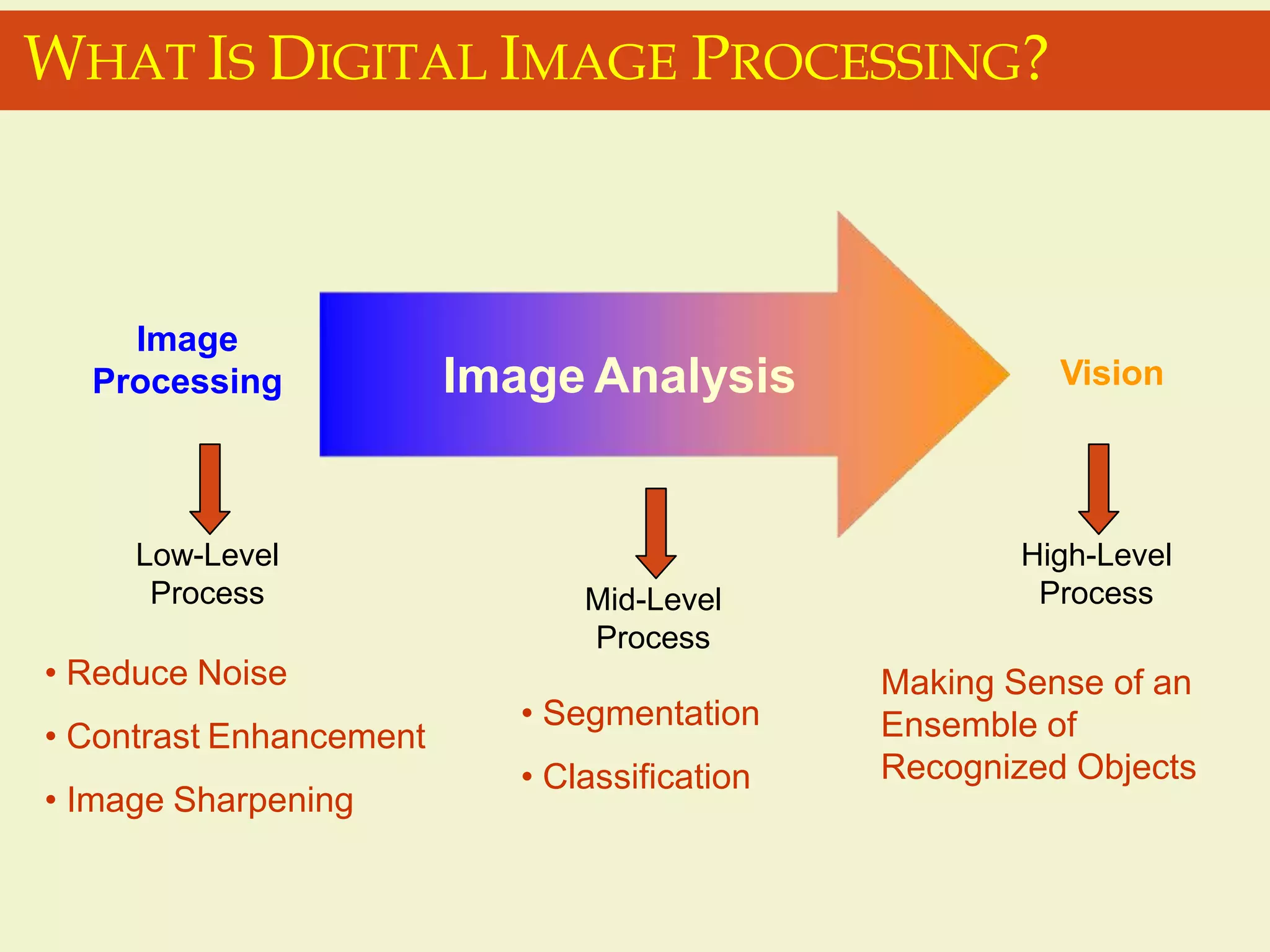
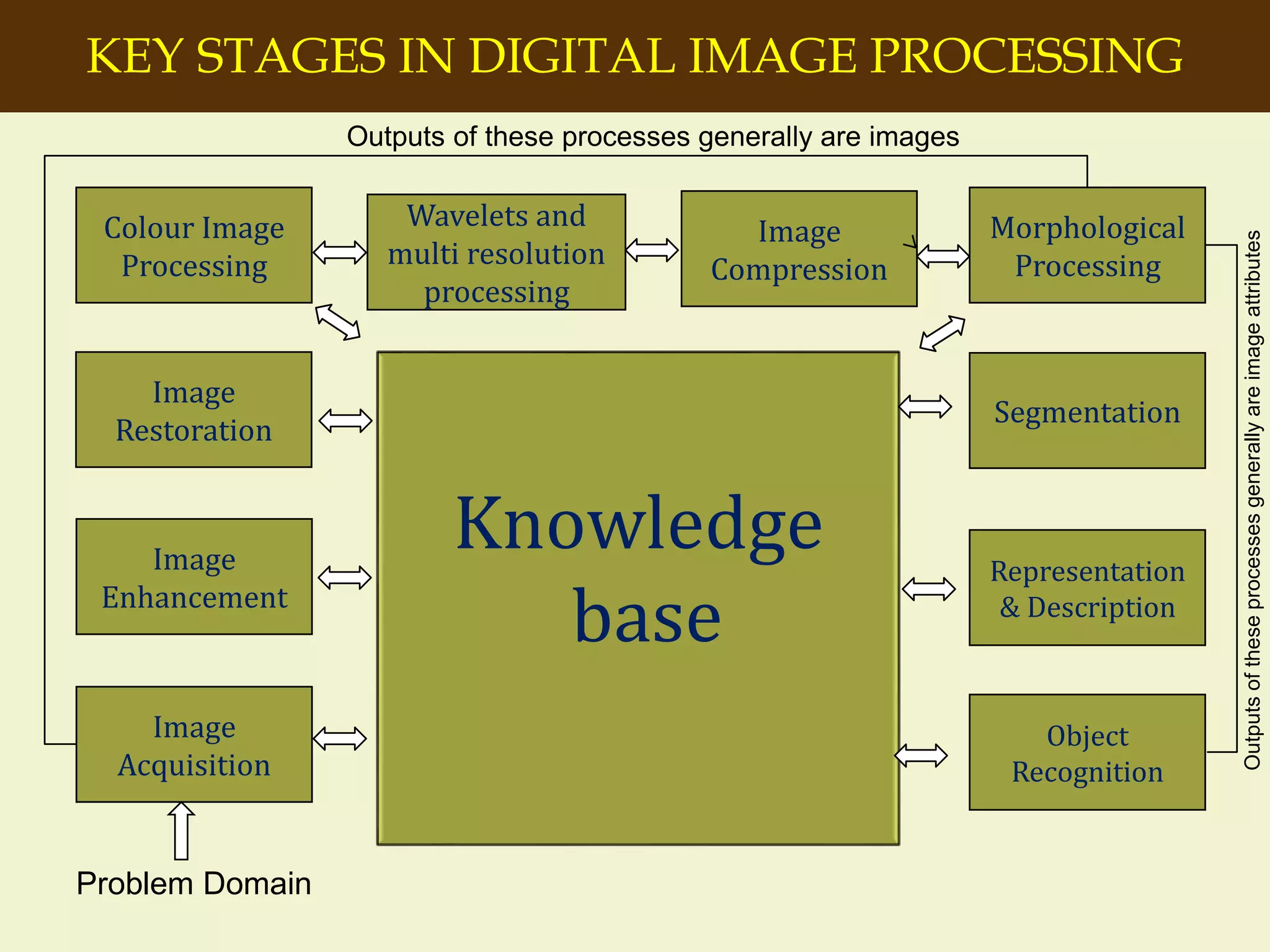
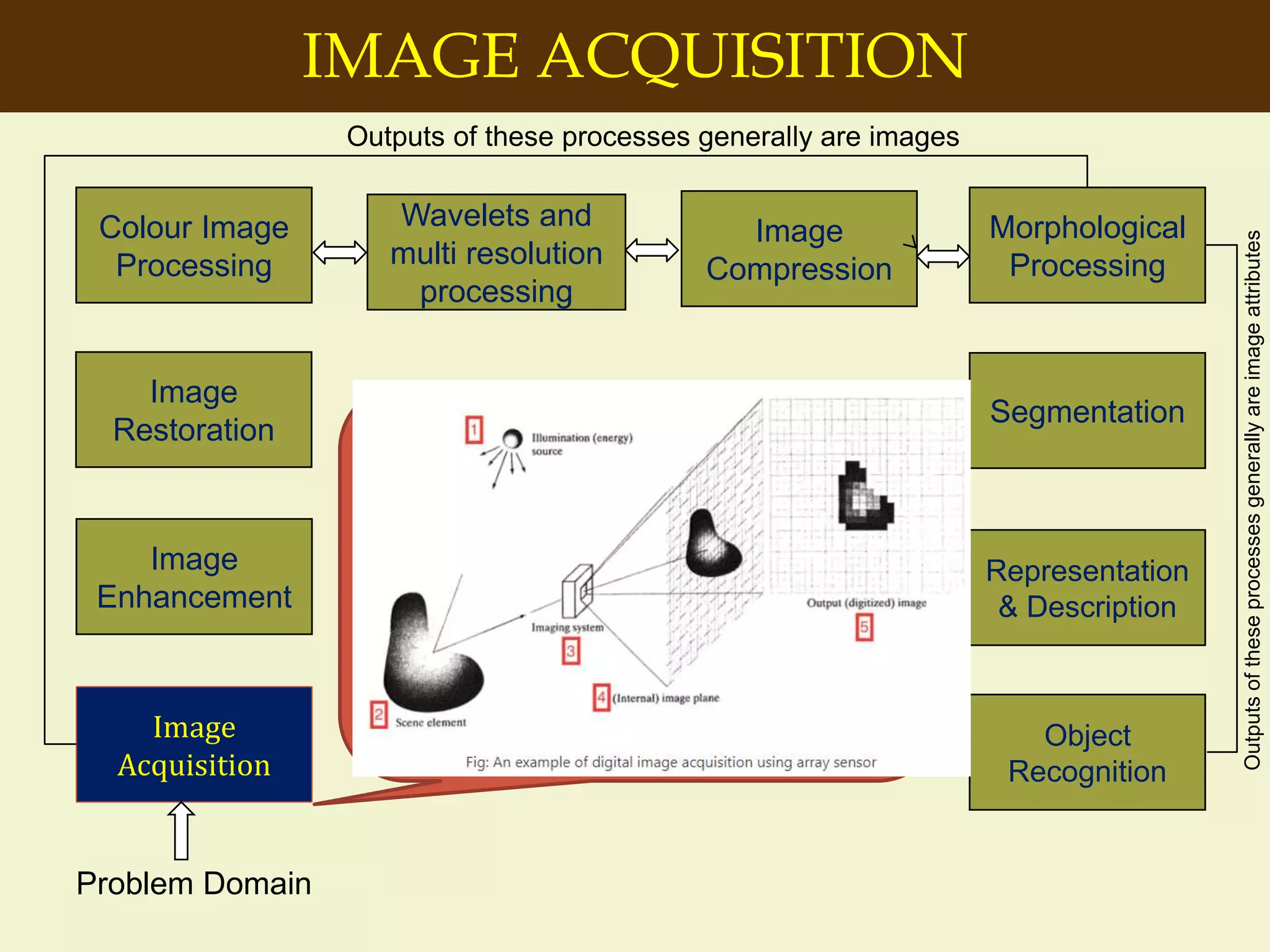
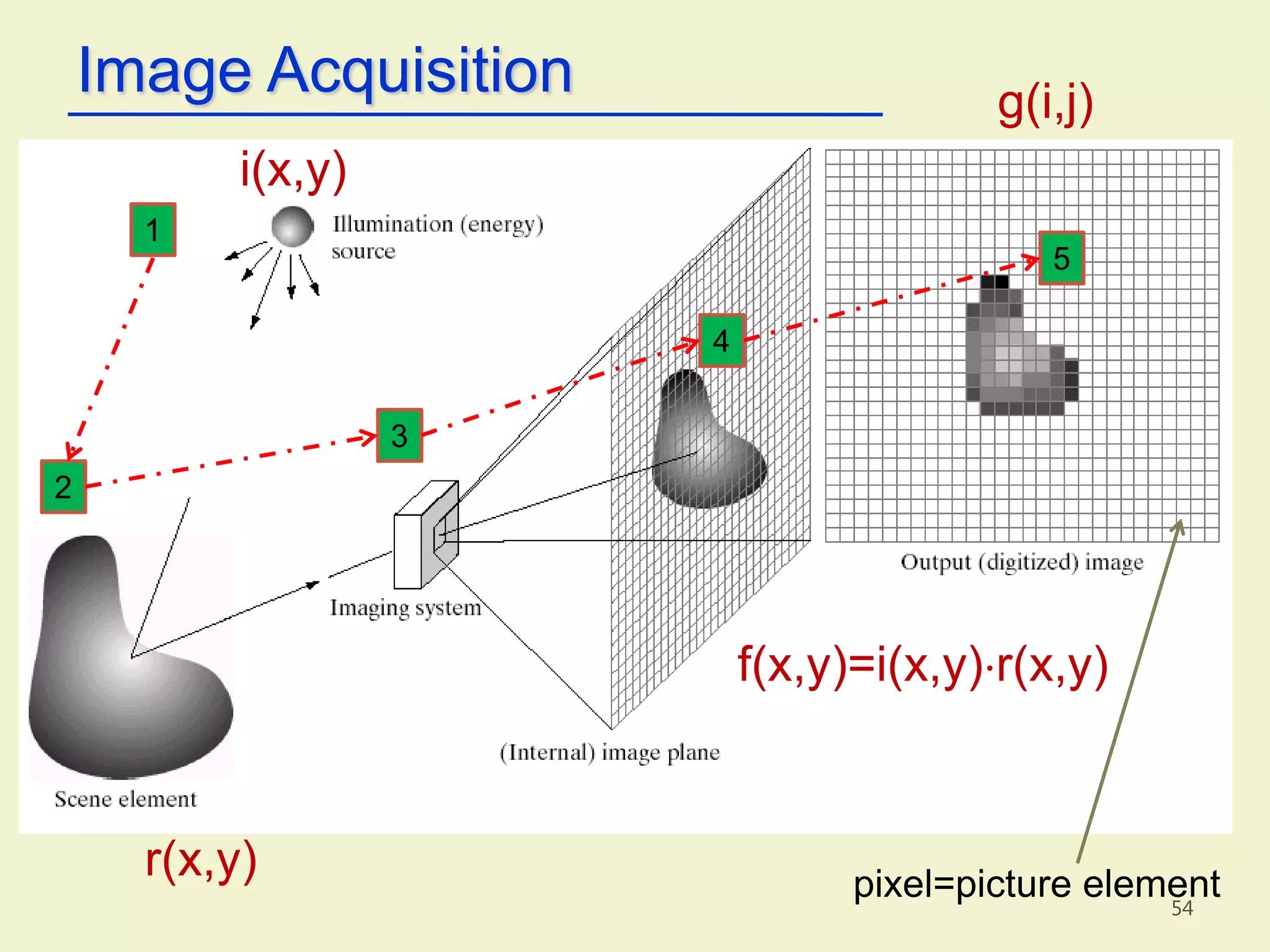
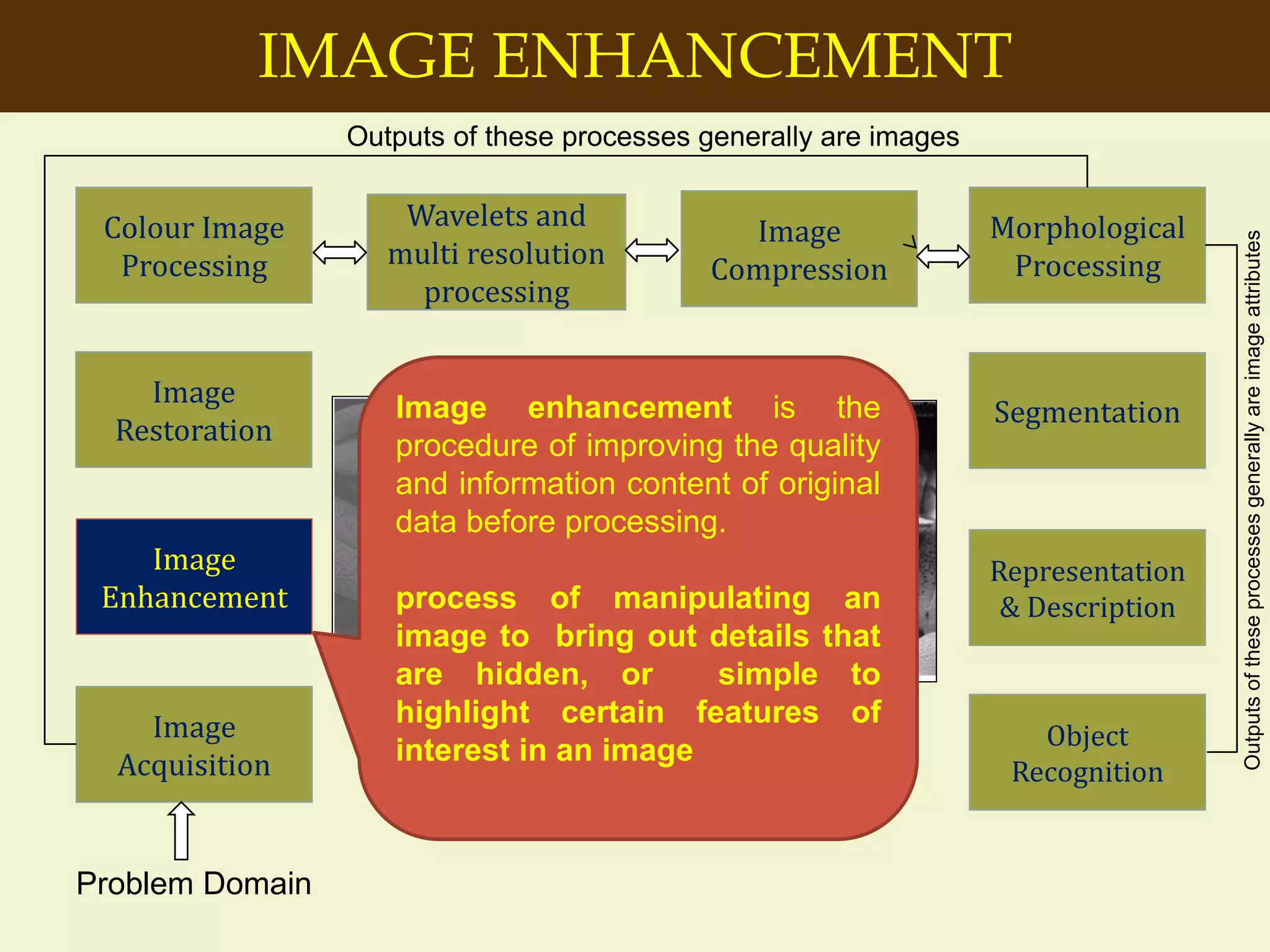
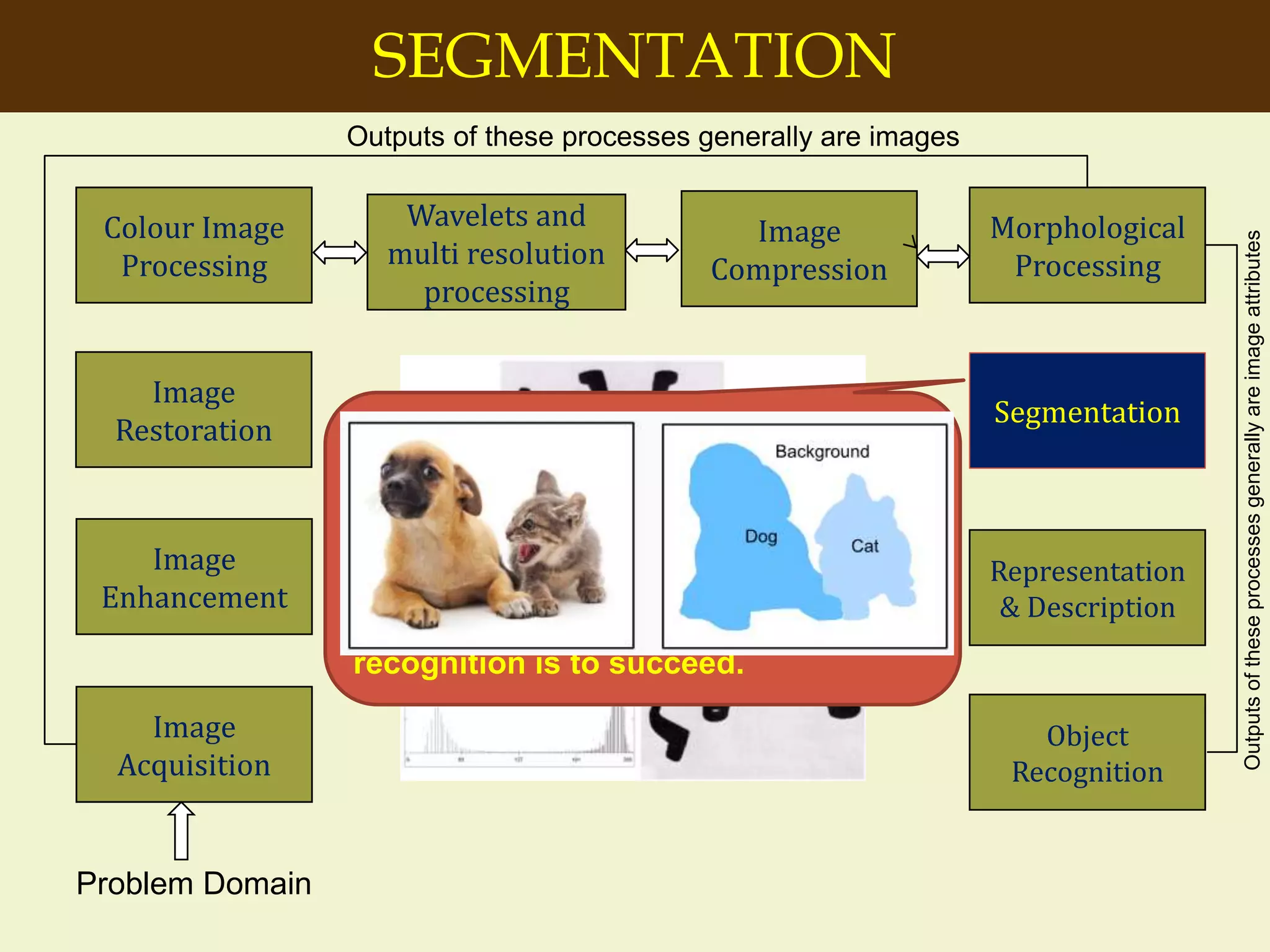
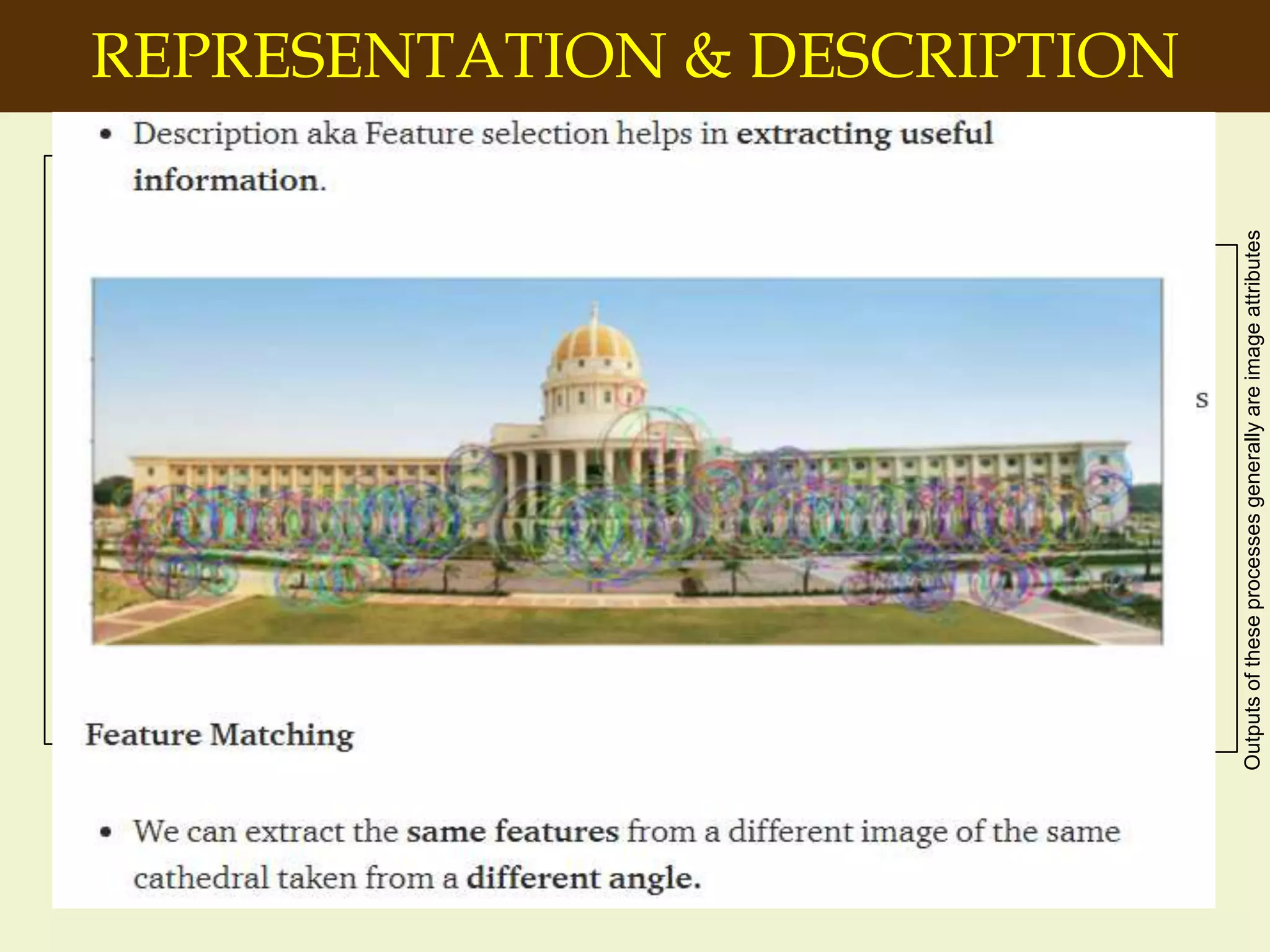
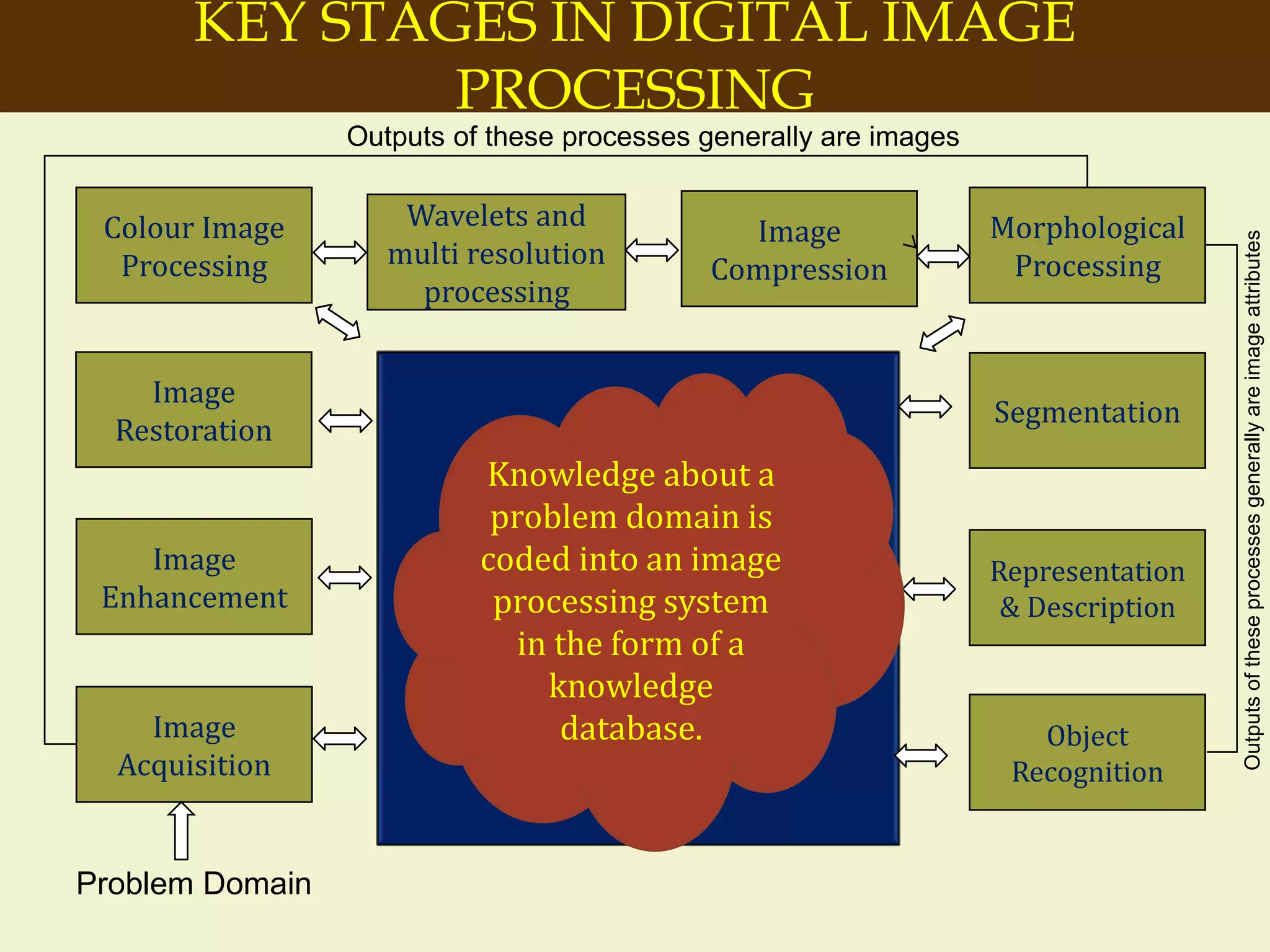
The document provides an overview of the key concepts and stages involved in digital image processing. It discusses image acquisition, preprocessing such as enhancement and restoration, and post-processing which includes tasks like segmentation, description and recognition. The goal is to introduce fundamental concepts and classical methods of digital image processing. Various applications are also highlighted including medical imaging, surveillance, and industrial inspection.
![SIPNA
College of Engineering & Technology, Amravati
Digital Image Processing[7ET2]
Subject In-charge
Chapter :- I
Introduction to
Digital Image Processing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part11introductiontosubject-200813065511/75/introduction-to-Digital-Image-Processing-1-2048.jpg)
![Signals and System
[4ET1]
Digital Signal Processing
[6ET4]
2
PRE-REQUISITES / PRIOR KNOWLEDGE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part11introductiontosubject-200813065511/75/introduction-to-Digital-Image-Processing-2-2048.jpg)
![INTRODUCTION
Image Processing [DIP]
Processing images which are
digital in nature.
Digital
Enhancement
Segmentation
Restoration
Transformation
Filtering
Signal Converson](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/part11introductiontosubject-200813065511/75/introduction-to-Digital-Image-Processing-3-2048.jpg)