Embed presentation
Downloaded 229 times









This document provides an overview of instance-based learning and k-nearest neighbors (kNN) classification. It discusses how kNN works by storing all training examples and classifying new instances based on the majority class of the k nearest neighbors. It covers selecting k, different distance functions, variants like distance-weighted and attribute-weighted kNN, and the strengths and weaknesses of the approach. The next class will discuss case-based reasoning and learning distance functions and prototypes.
























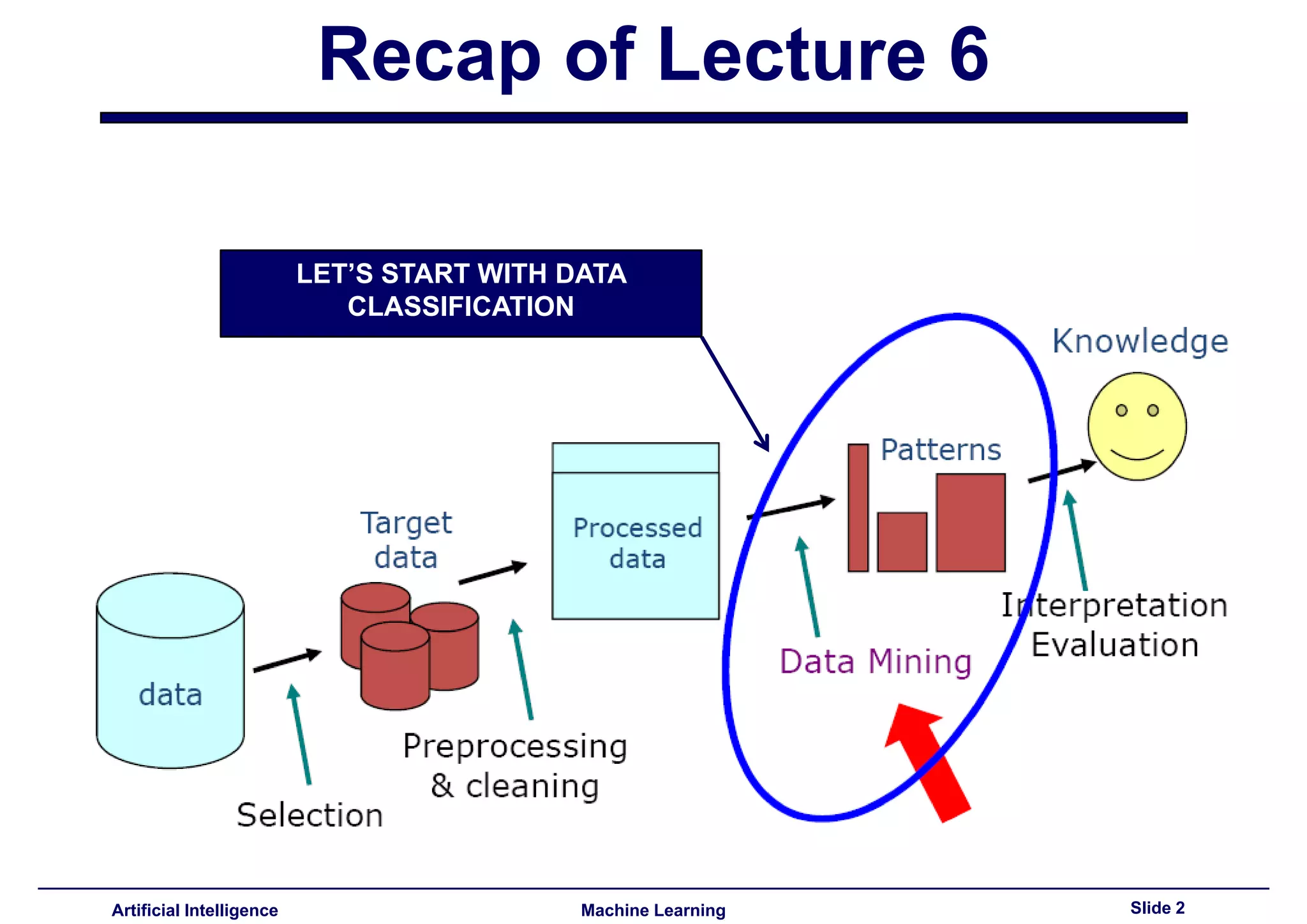
Introduction to Machine Learning, Instance Based Learning, covering recap of Lecture 6 and focus on data classification.
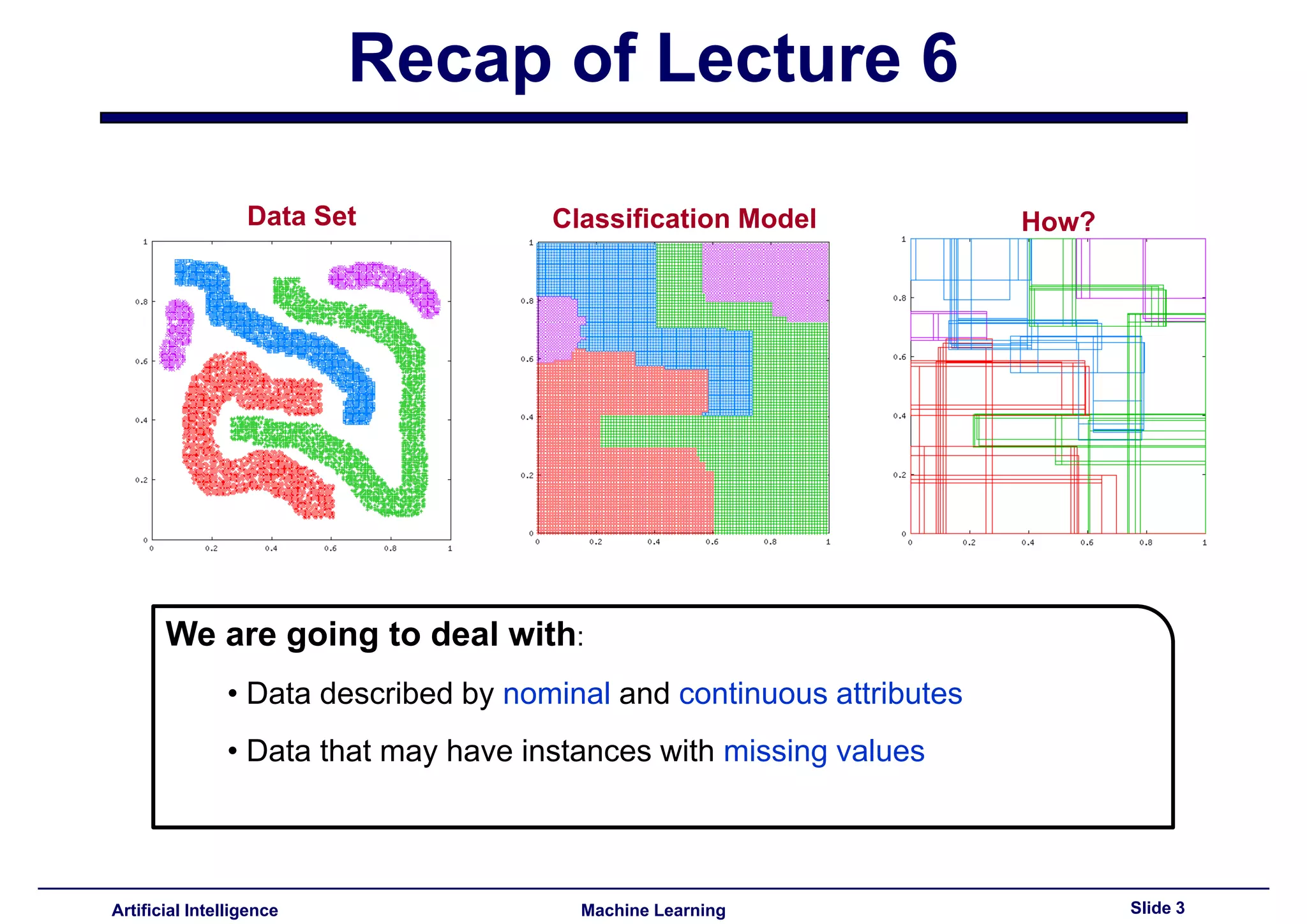
Discusses dataset attributes and classification models addressing nominal and continuous data with missing values.
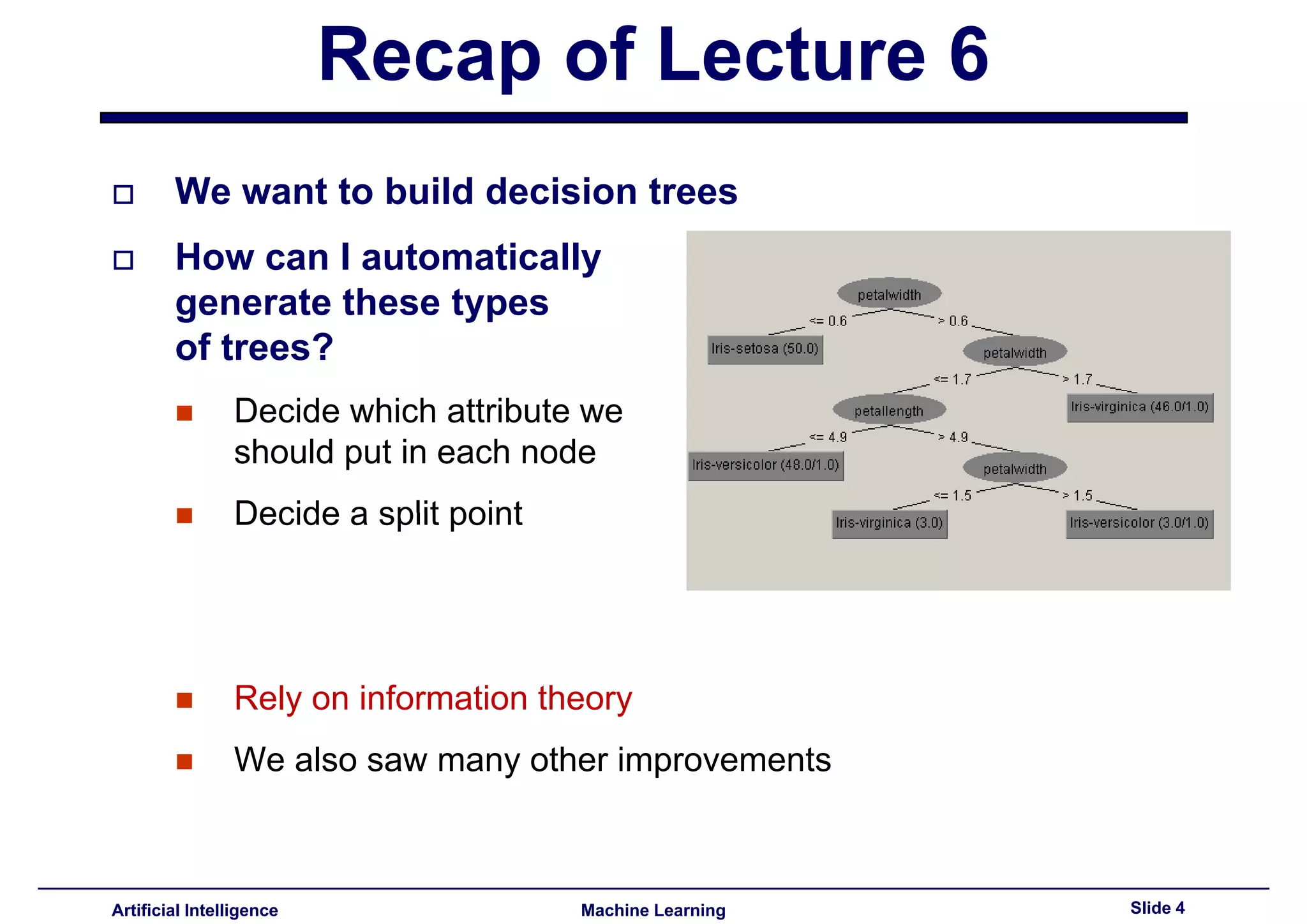
Explains generating decision trees, choosing attributes for nodes, and utilization of information theory.
Focus areas include classification through k-Nearest Neighbors, effect of k, distance functions, and k-NN variants.
Classification without a global model, storing training examples to create local models as lazy learners.
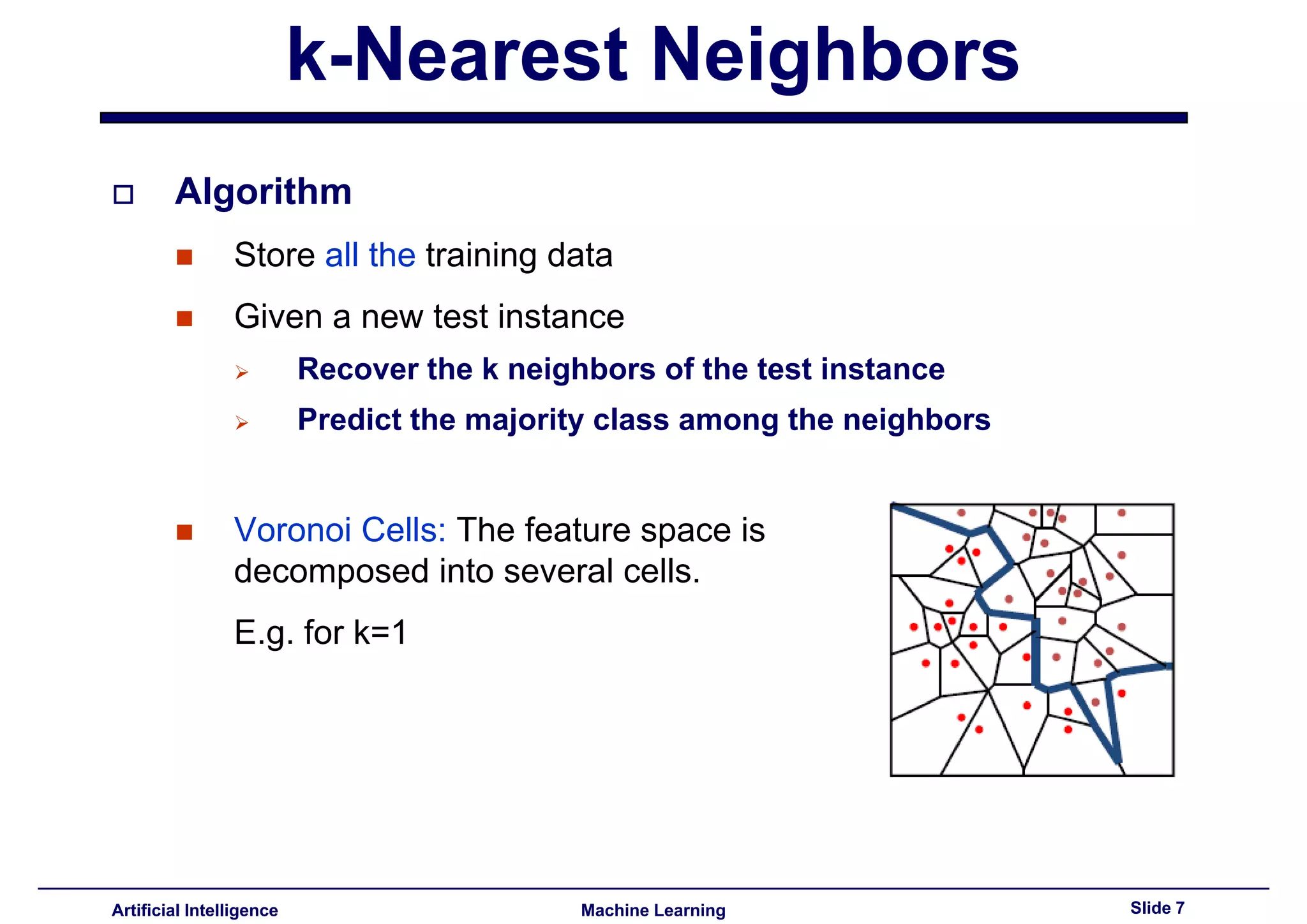
Overview of k-NN algorithm detailing storage of training data and neighbor retrieval for predictions.
Questions the learning aspect of k-NN, discusses challenges including the choice of k and distance functions.
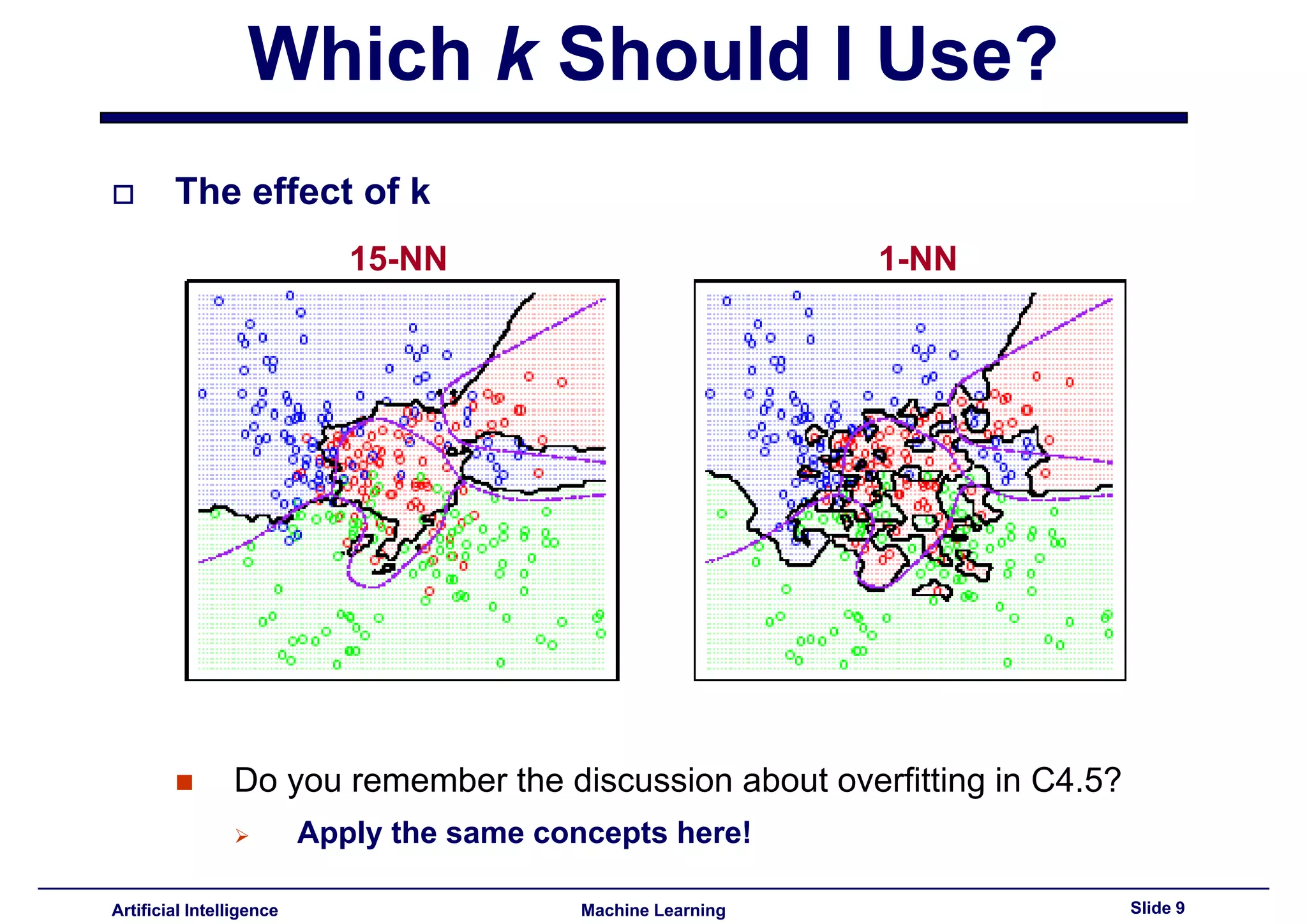
Explains effect of k in k-NN, referencing overfitting concepts similar to C4.5 decision trees.
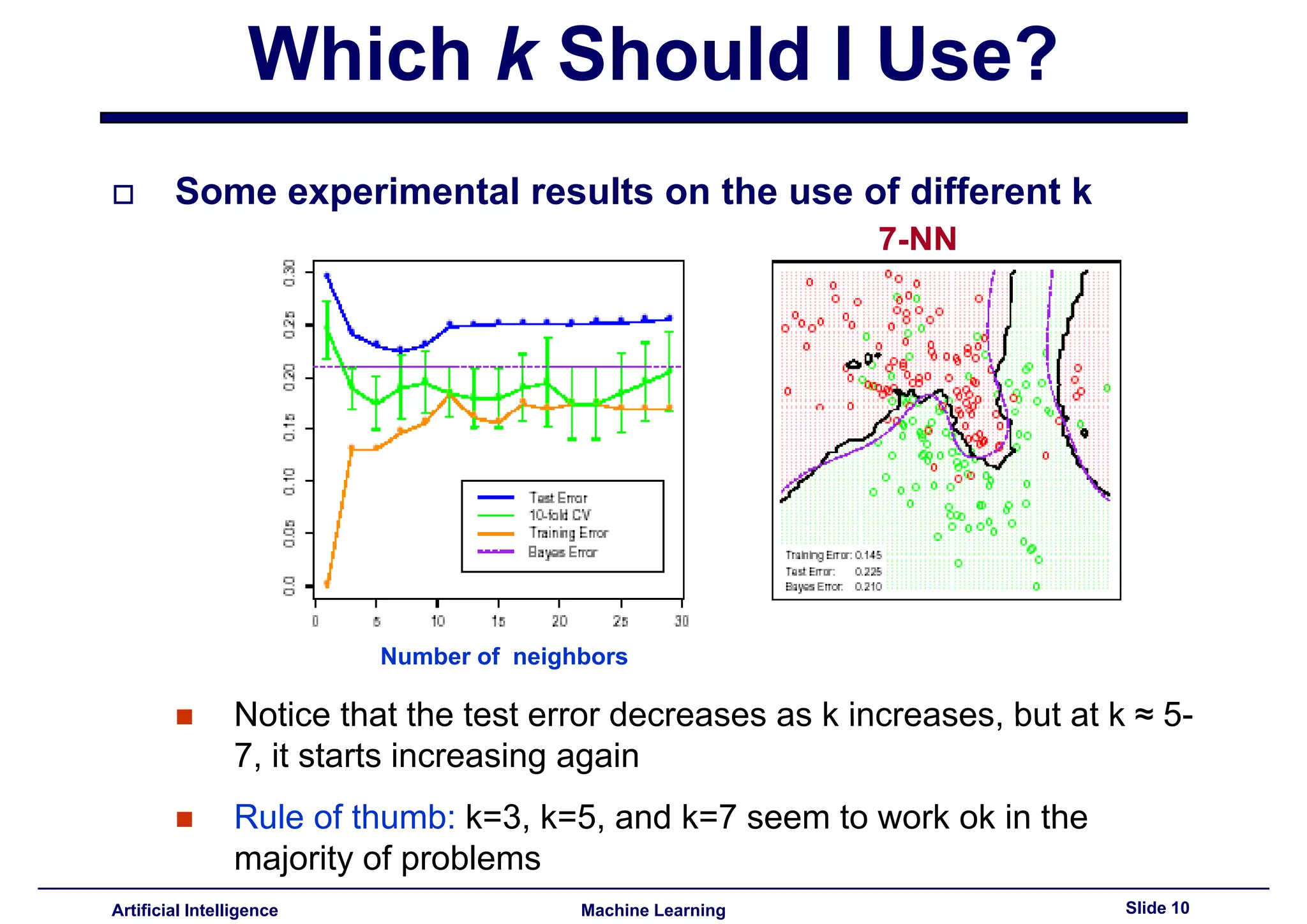
Experimental data showing test error trends with varying k values, suggesting k=3, k=5, and k=7.
Details required properties of distance functions for both nominal and continuous attributes.
Highlights the general properties expected from distance metrics, such as non-negativity and symmetry.
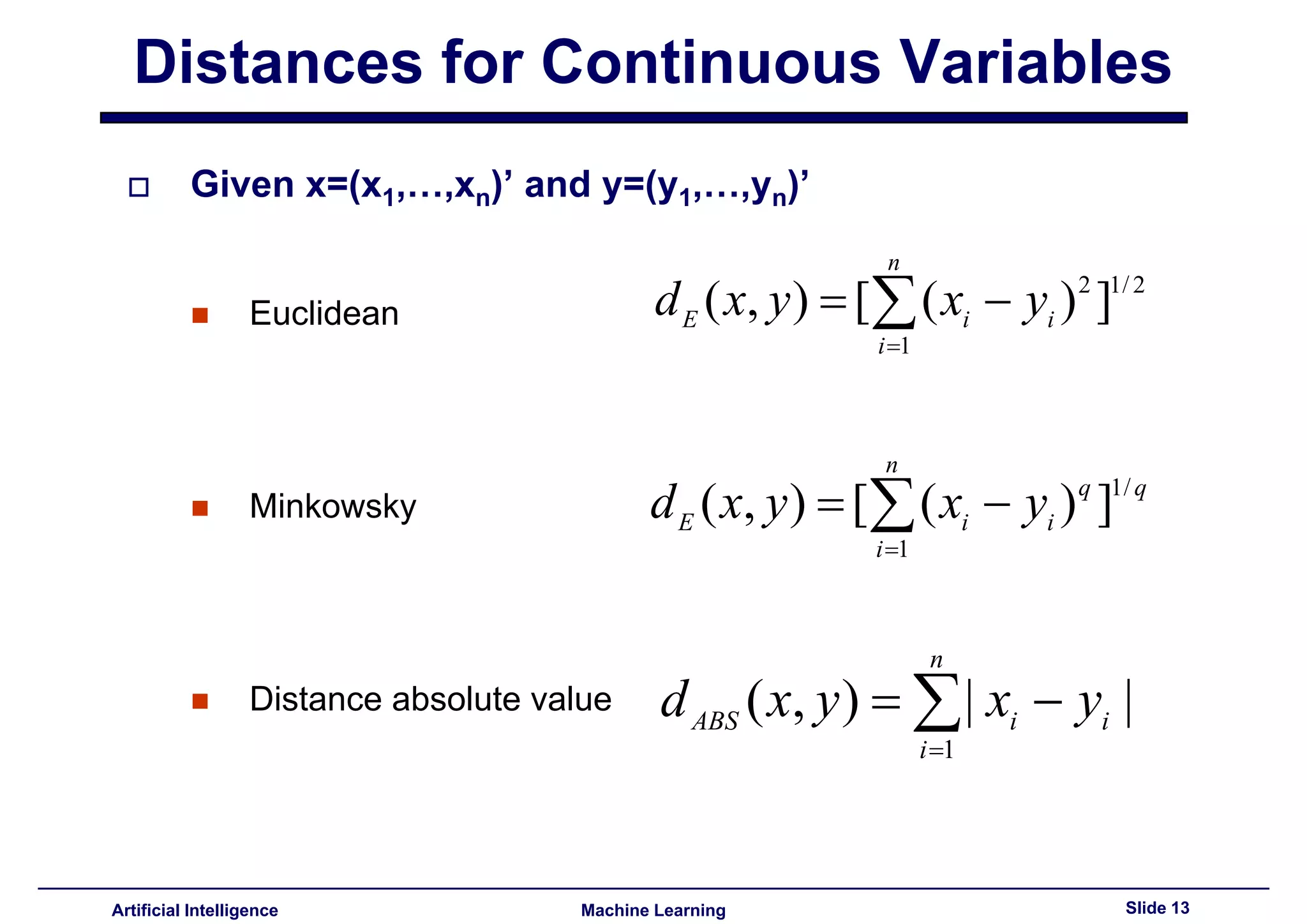
Introduces distance measures like Euclidean, Minkowski, and absolute value for continuous variables.
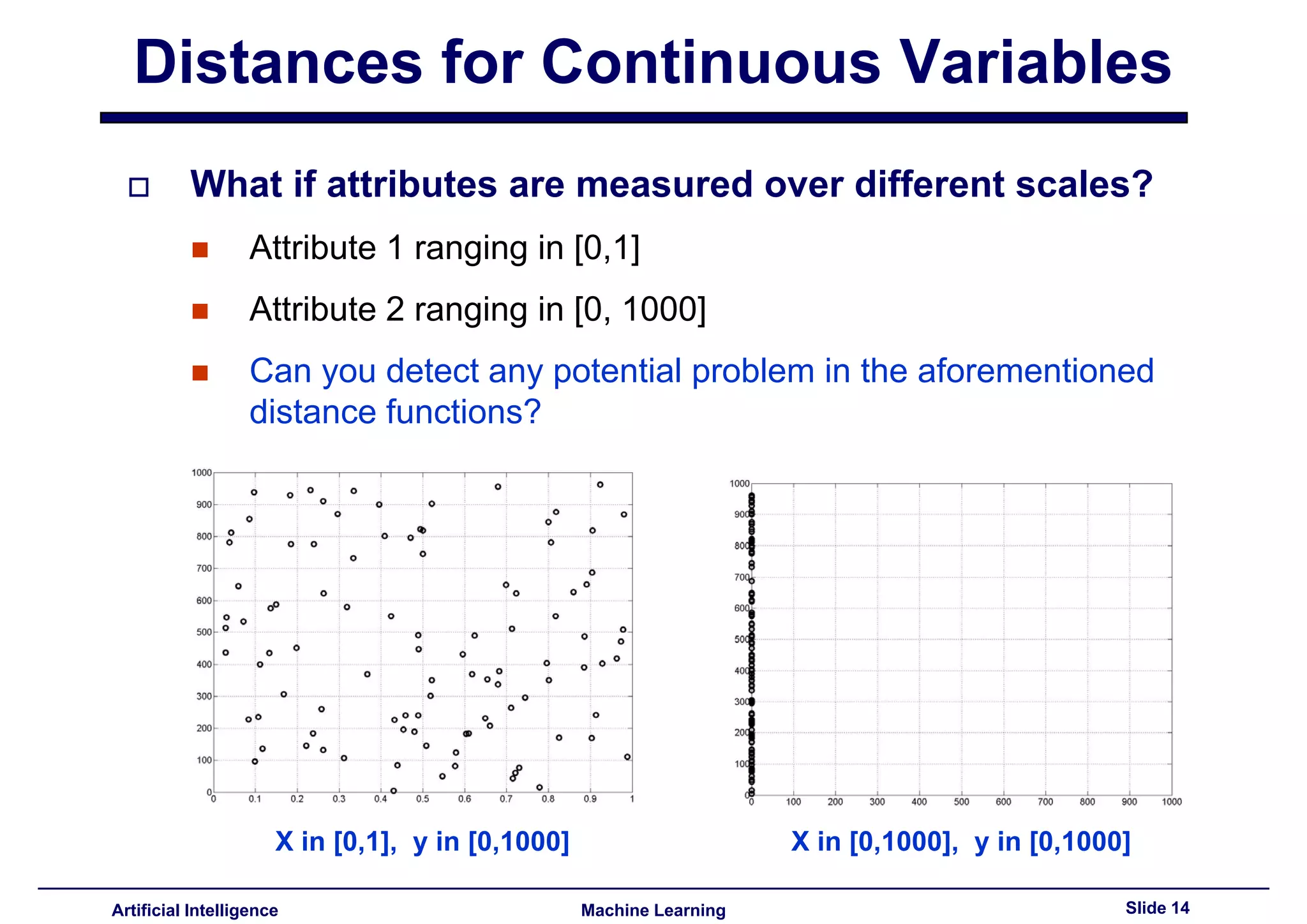
Discusses potential problems when attributes are measured on different scales.
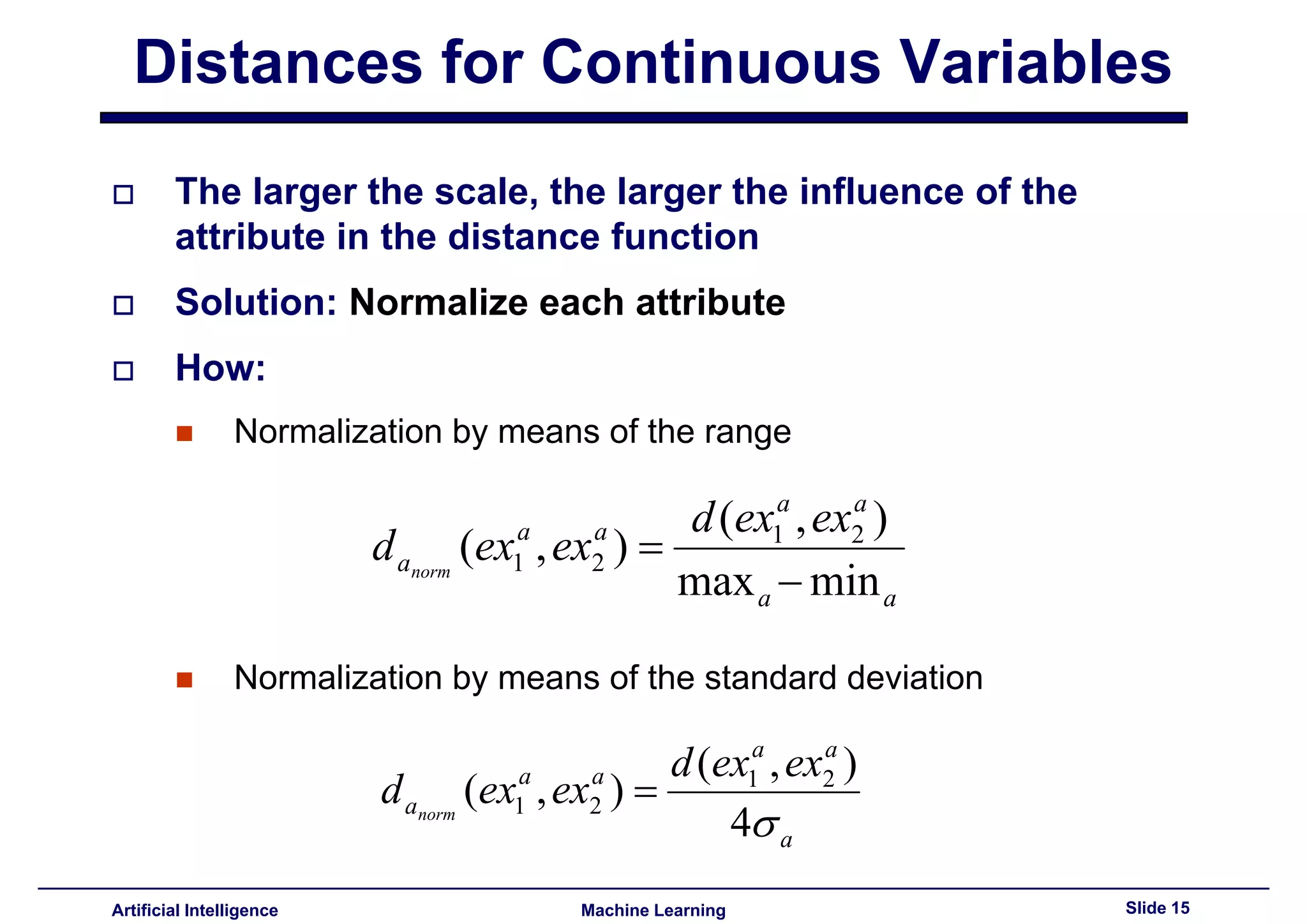
Describes normalization methods to handle attribute scale discrepancies in distance functions.
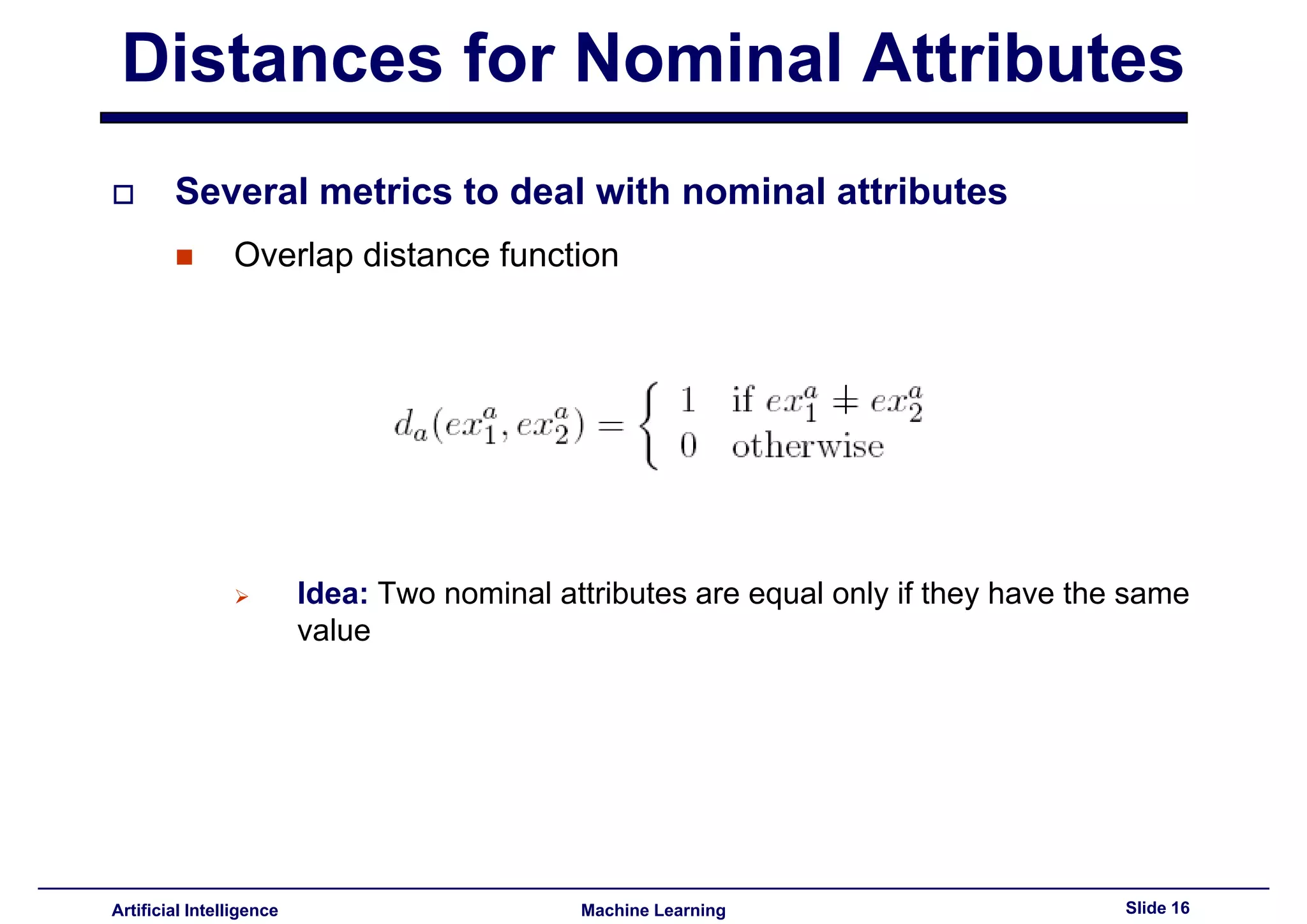
Introduces overlap distance function for comparing nominal attributes.
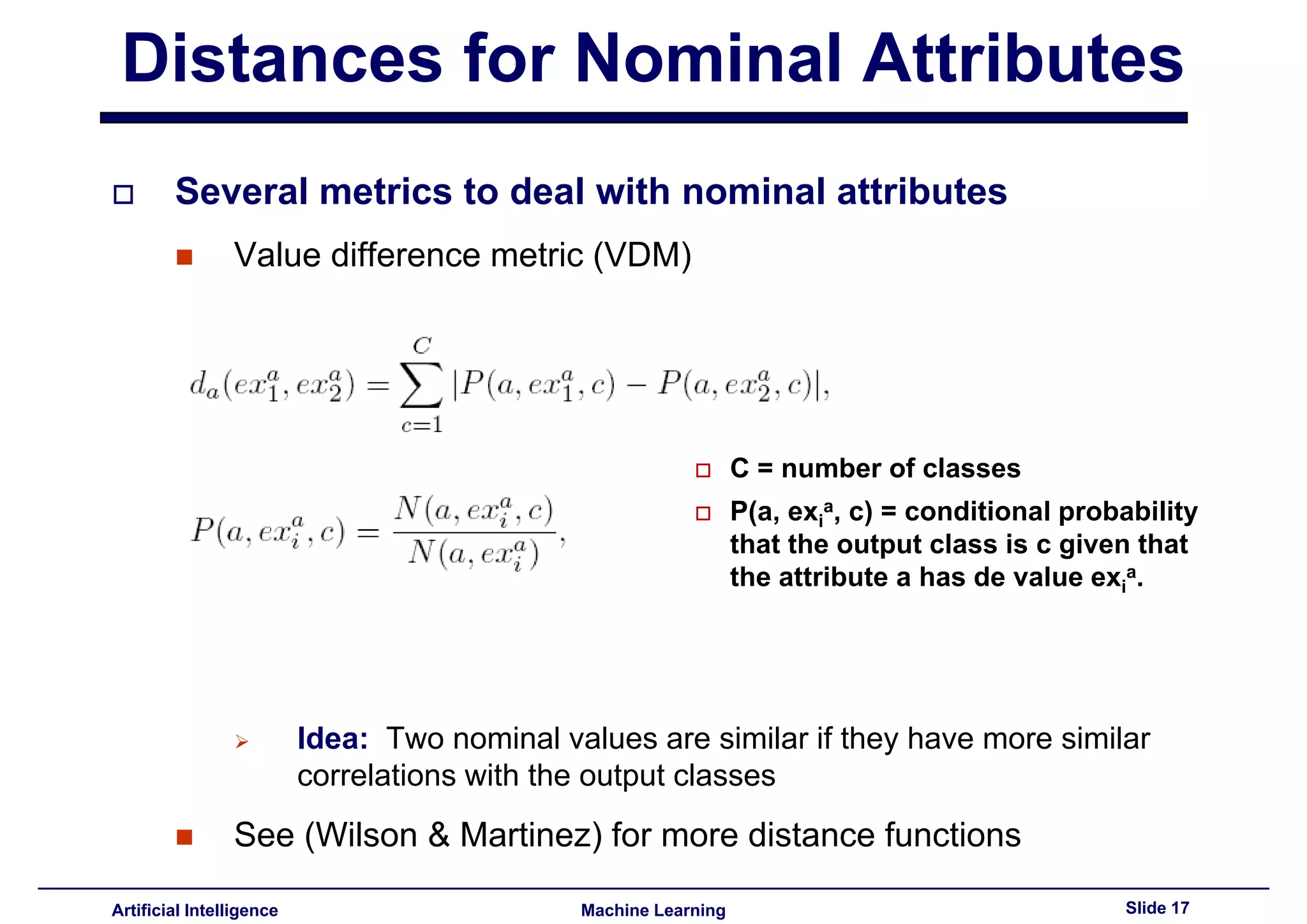
Explains value difference metrics for nominal attributes based on class correlation similarity.
Proposes solutions for datasets with nominal and continuous attributes by applying respective distance functions.
Explores different k-NN variants like distance-weighted k-NN and attribute-weighted k-NN.
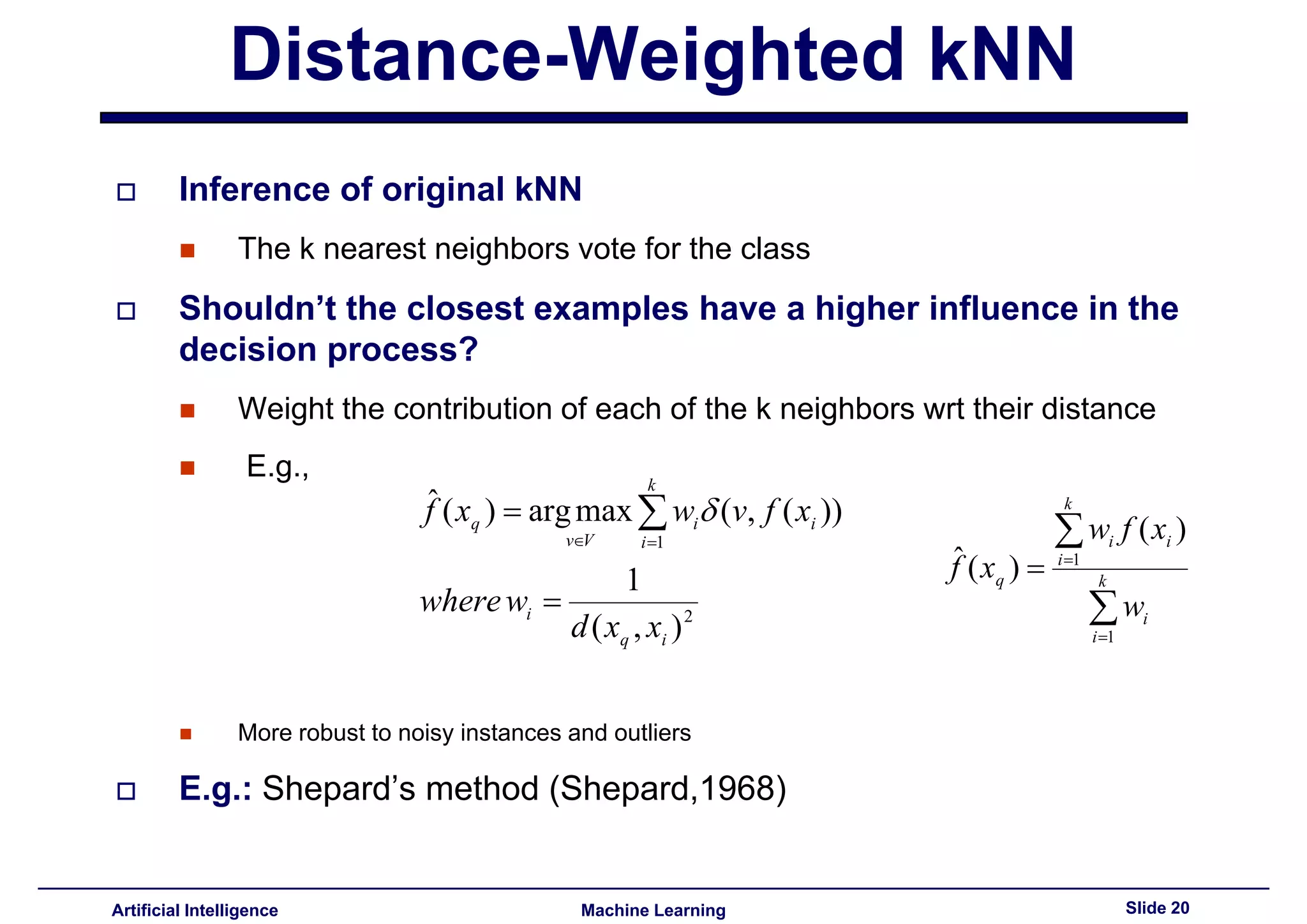
Discusses how k-NN can give higher influence to closer neighbors, enhancing decision-making.
Describes how to weight attributes based on relevance to improve accuracy in predictions.
Lists pros and cons of k-NN, including high accuracy, retrieval approach, and challenges with dimensionality.
Preview of upcoming class topics: transition from instance-based to case-based reasoning and discussions on distance functions.
Restatement of Machine Learning, Lecture 7 focusing on Instance Based Learning.