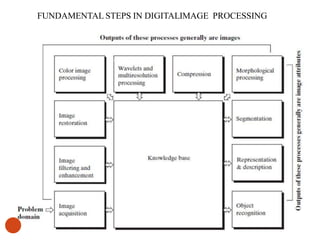
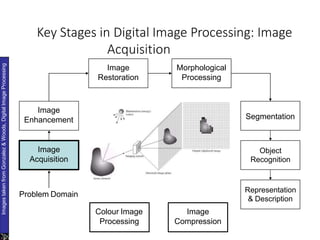
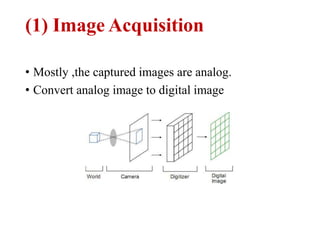
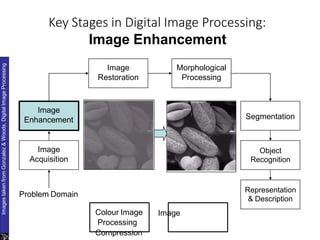
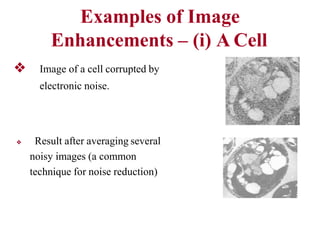
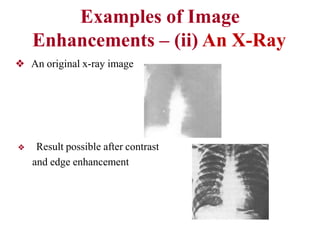
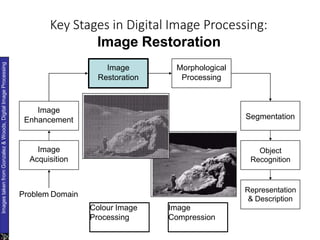
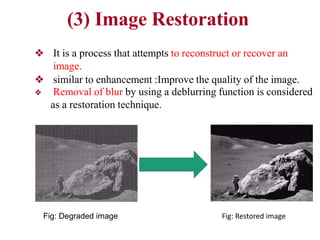
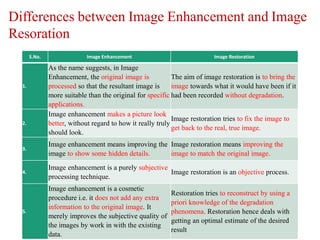
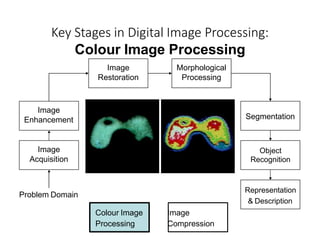
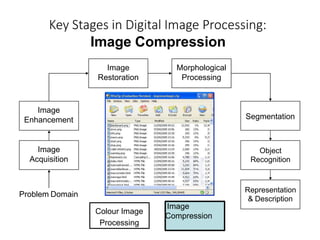
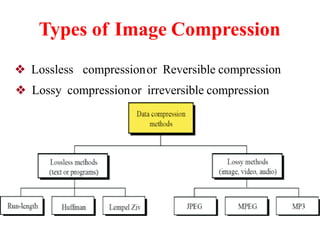
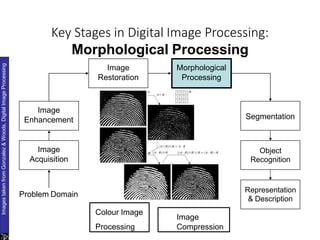
The document discusses the fundamental steps in digital image processing. It describes 7 key steps: (1) image acquisition, (2) image enhancement, (3) image restoration, (4) color image processing, (5) wavelets and multiresolution processing, (6) image compression, and (7) morphological processing. For each step, it provides brief explanations of the techniques and purposes involved in digital image processing.