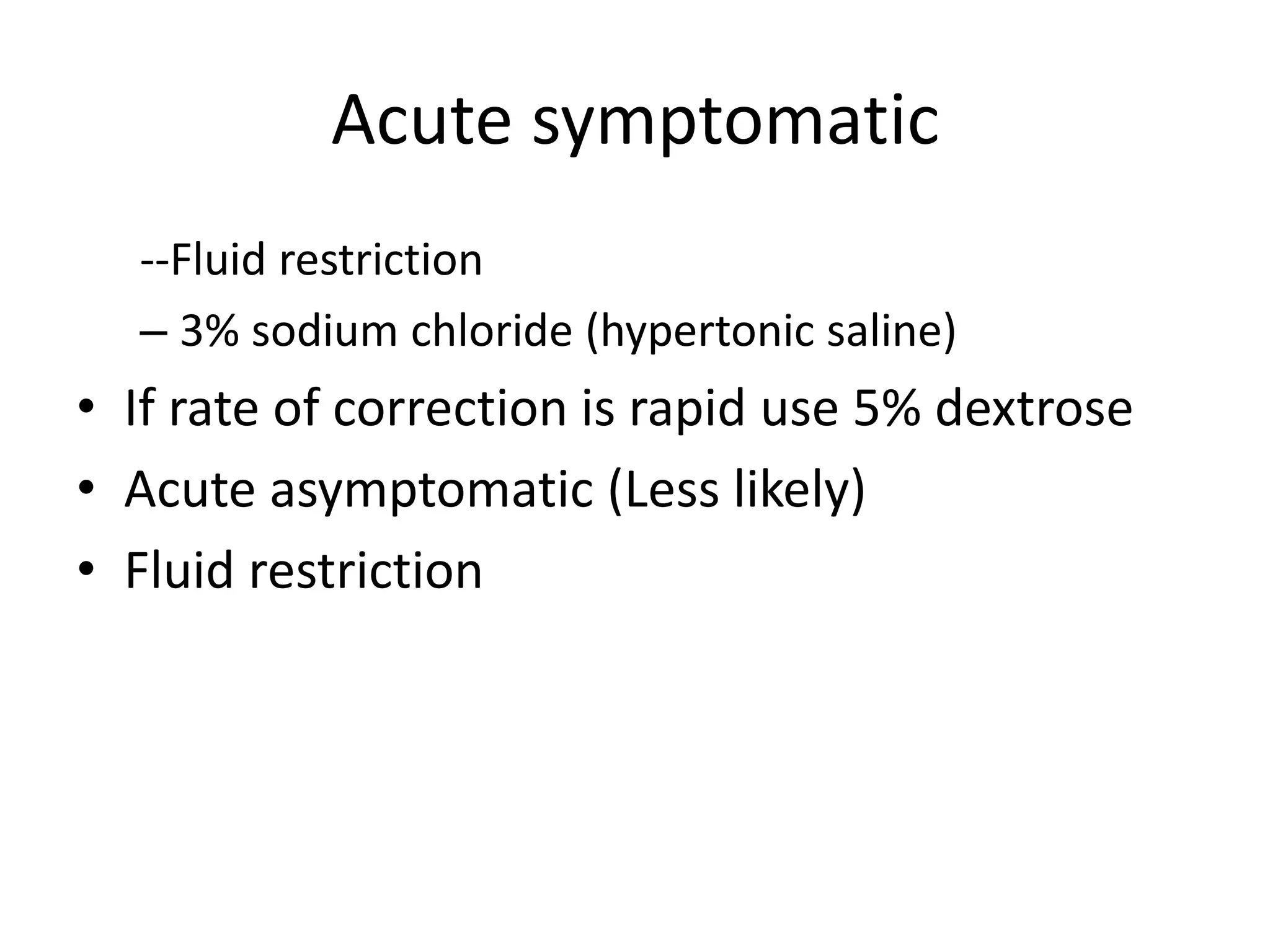
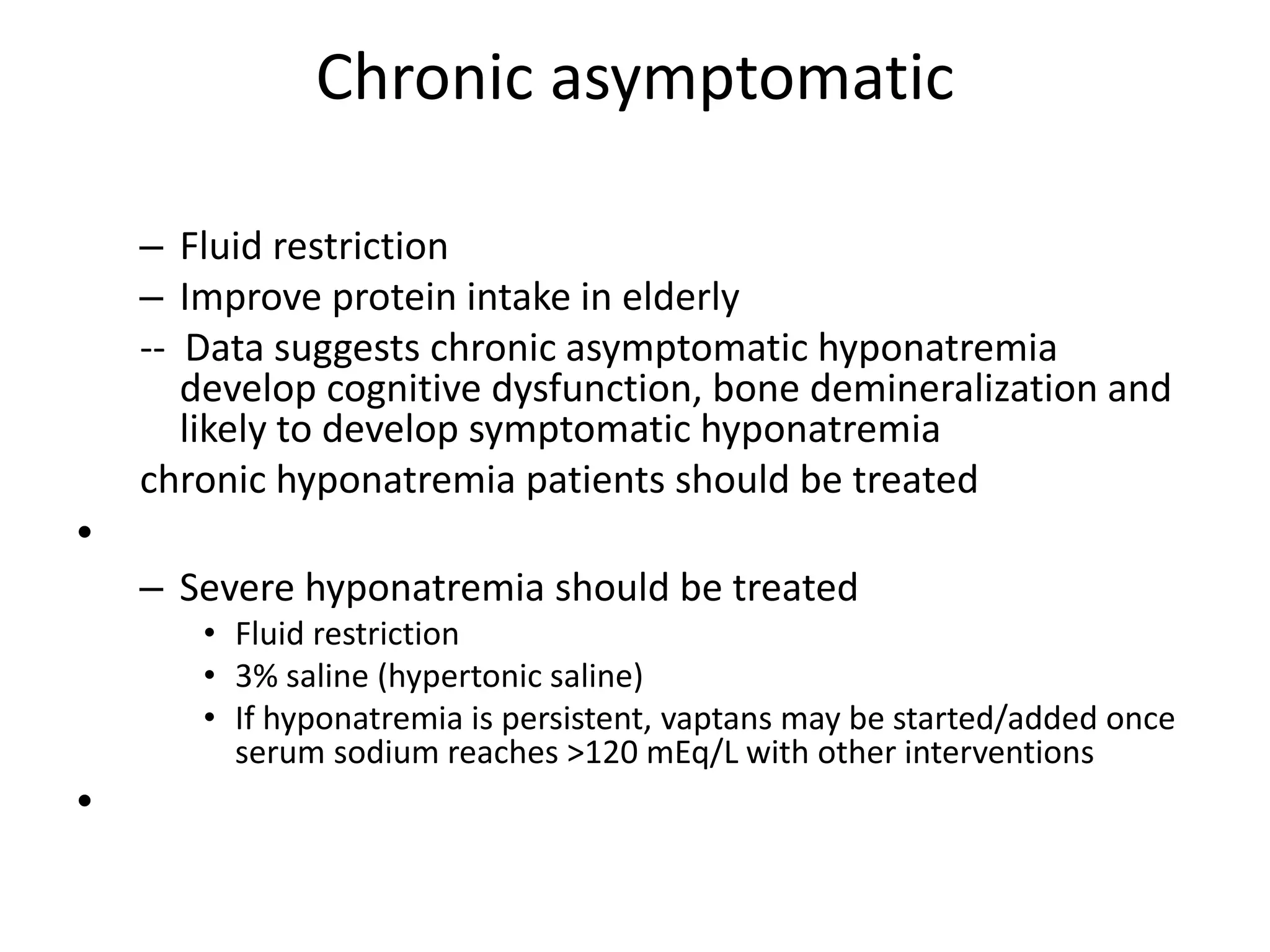
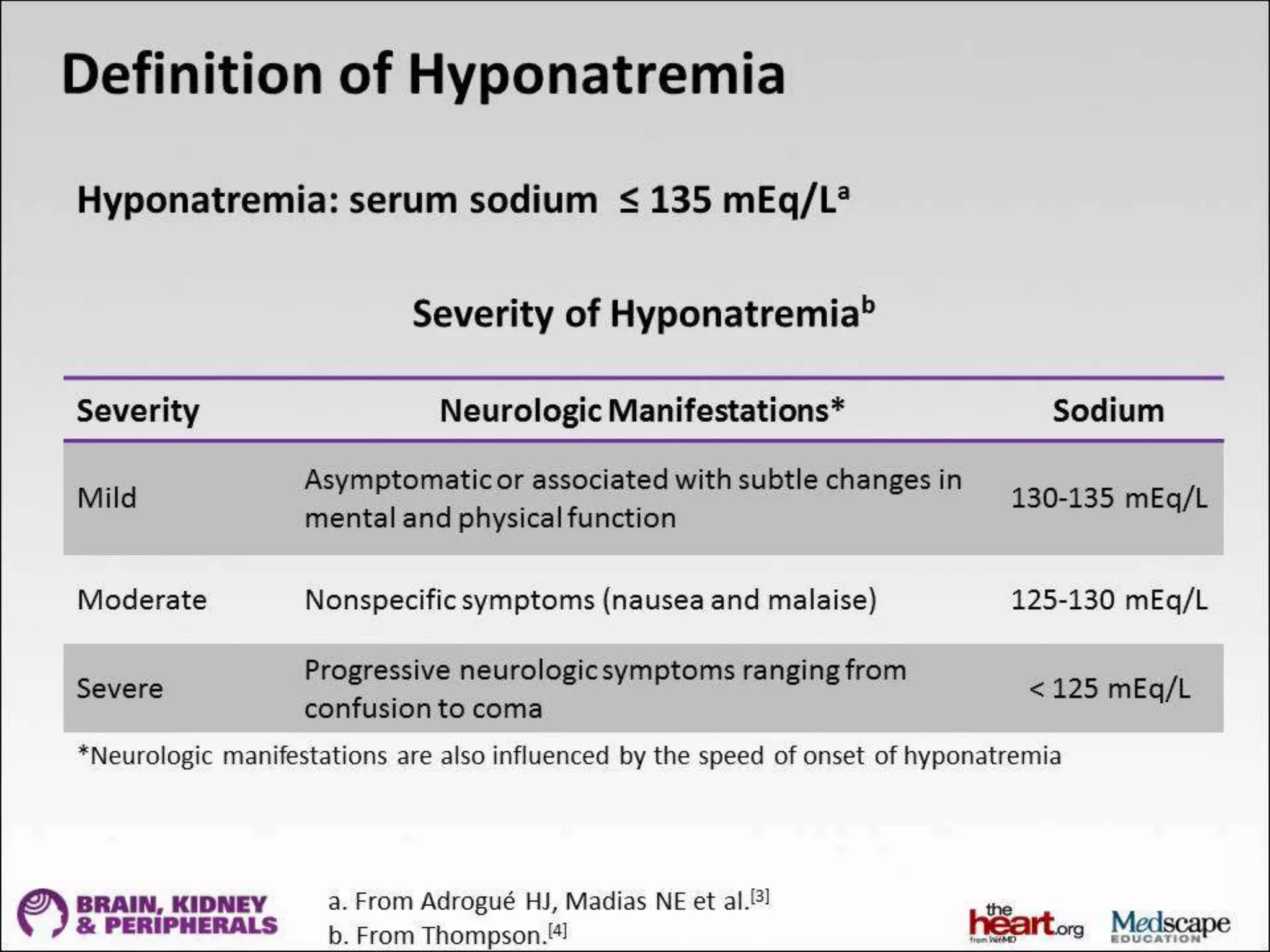
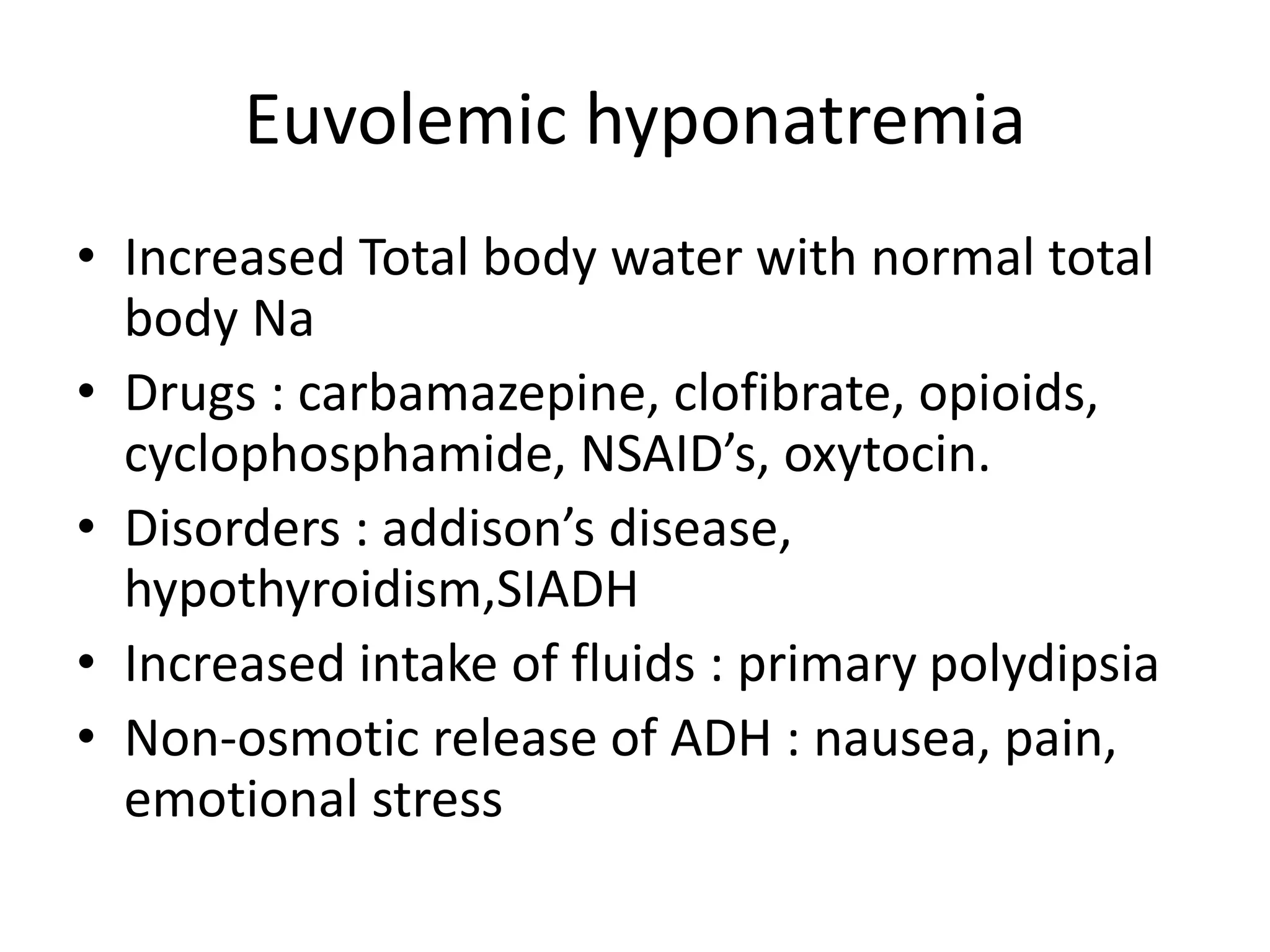
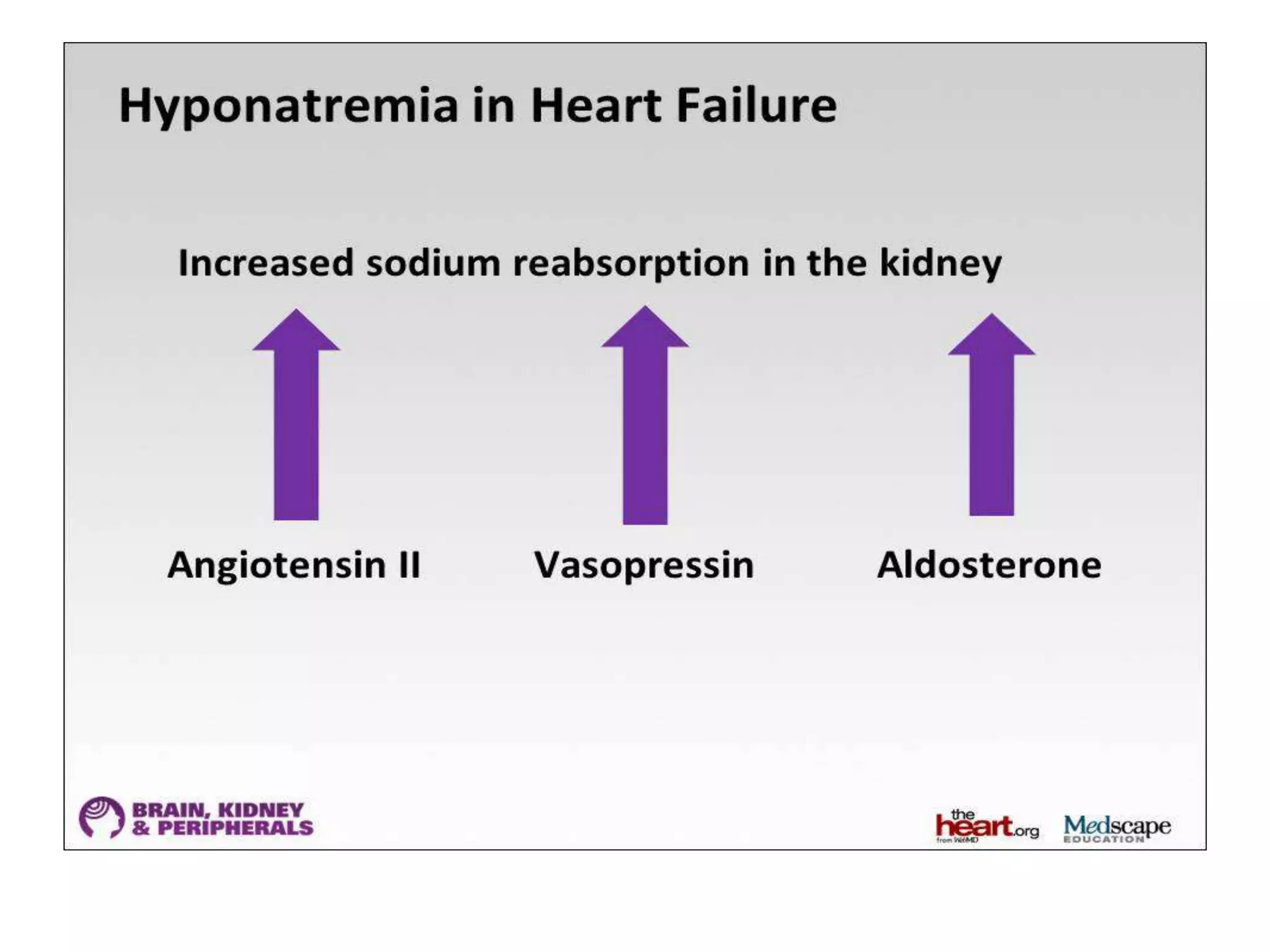
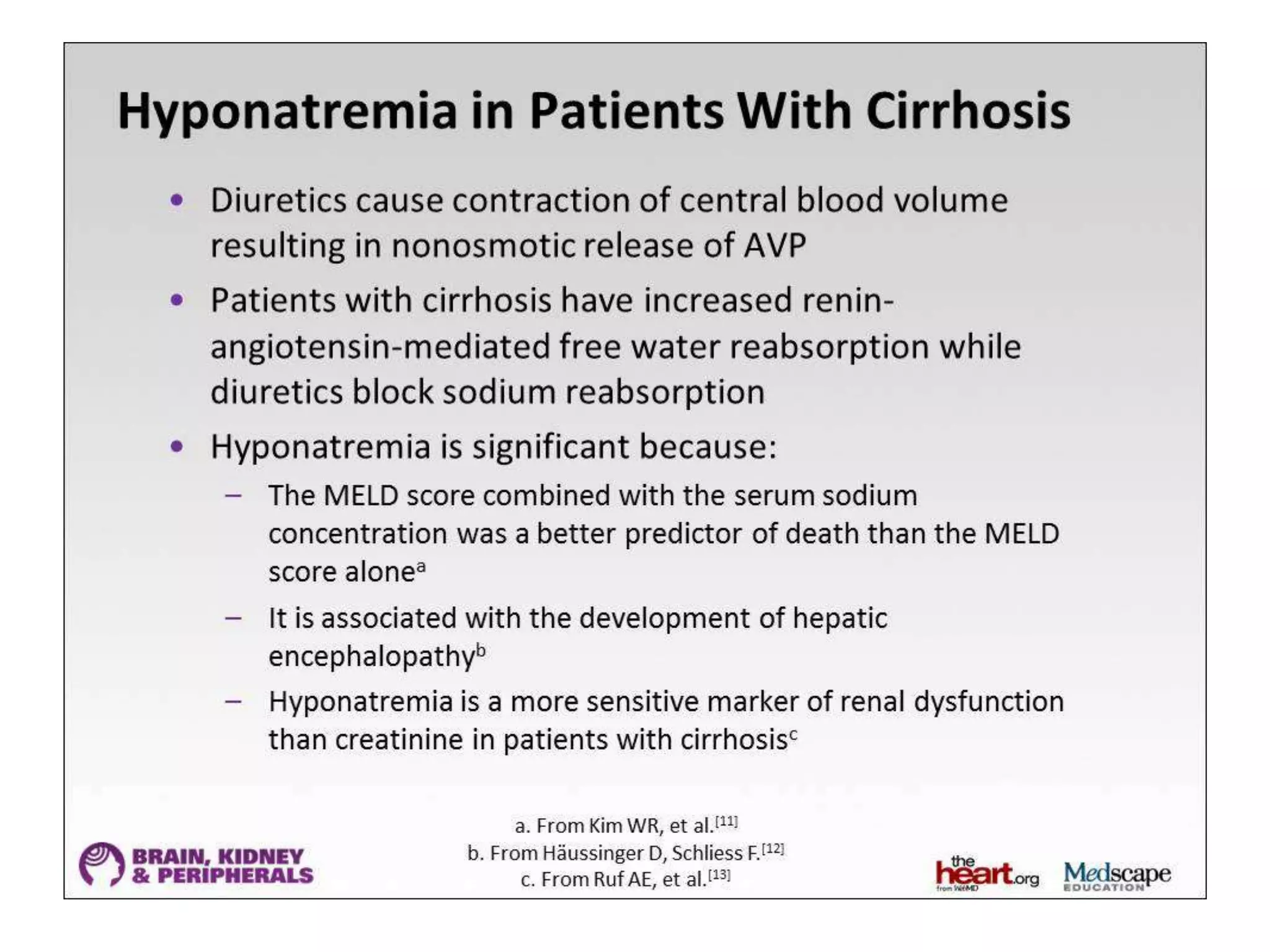
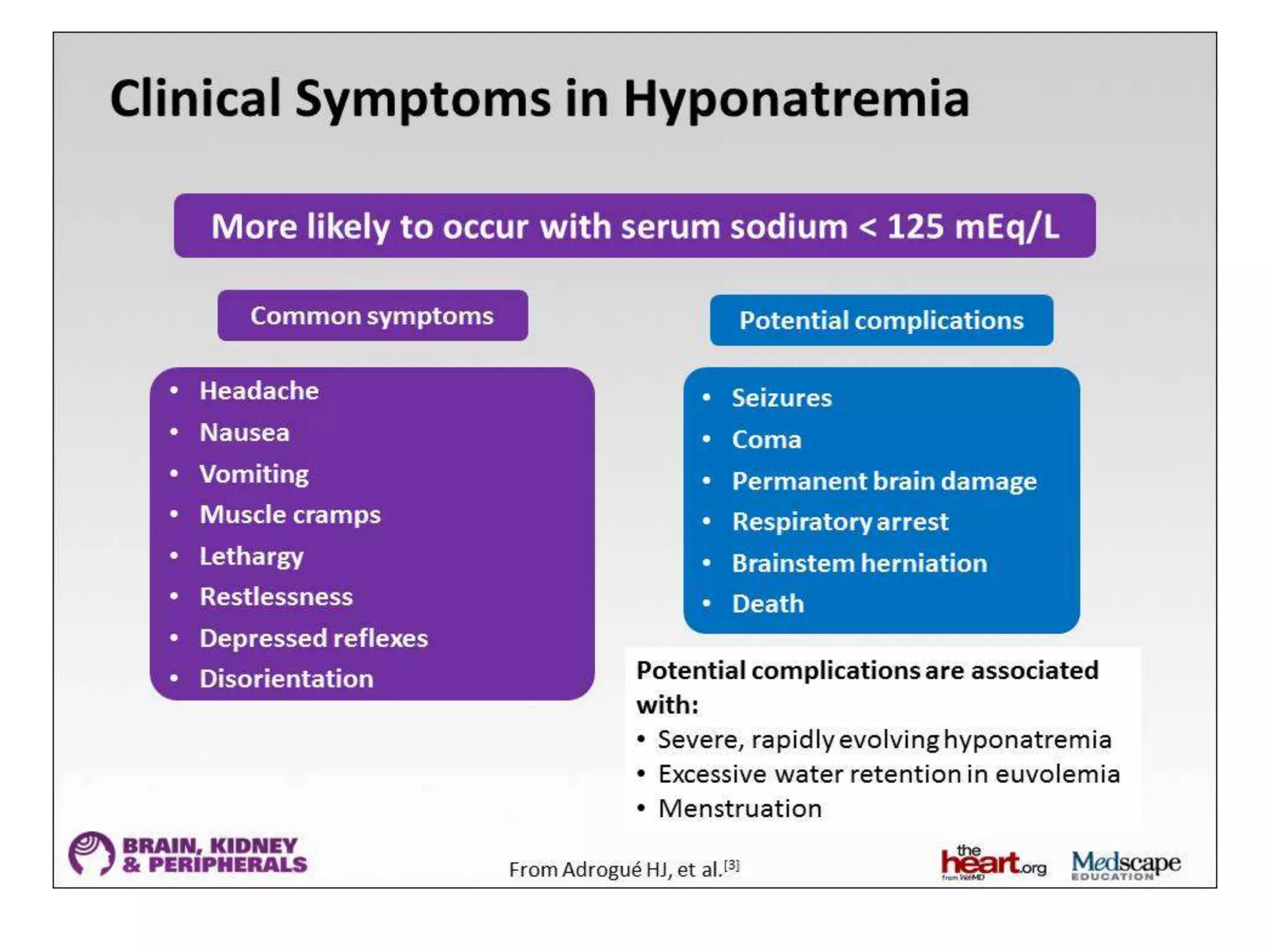
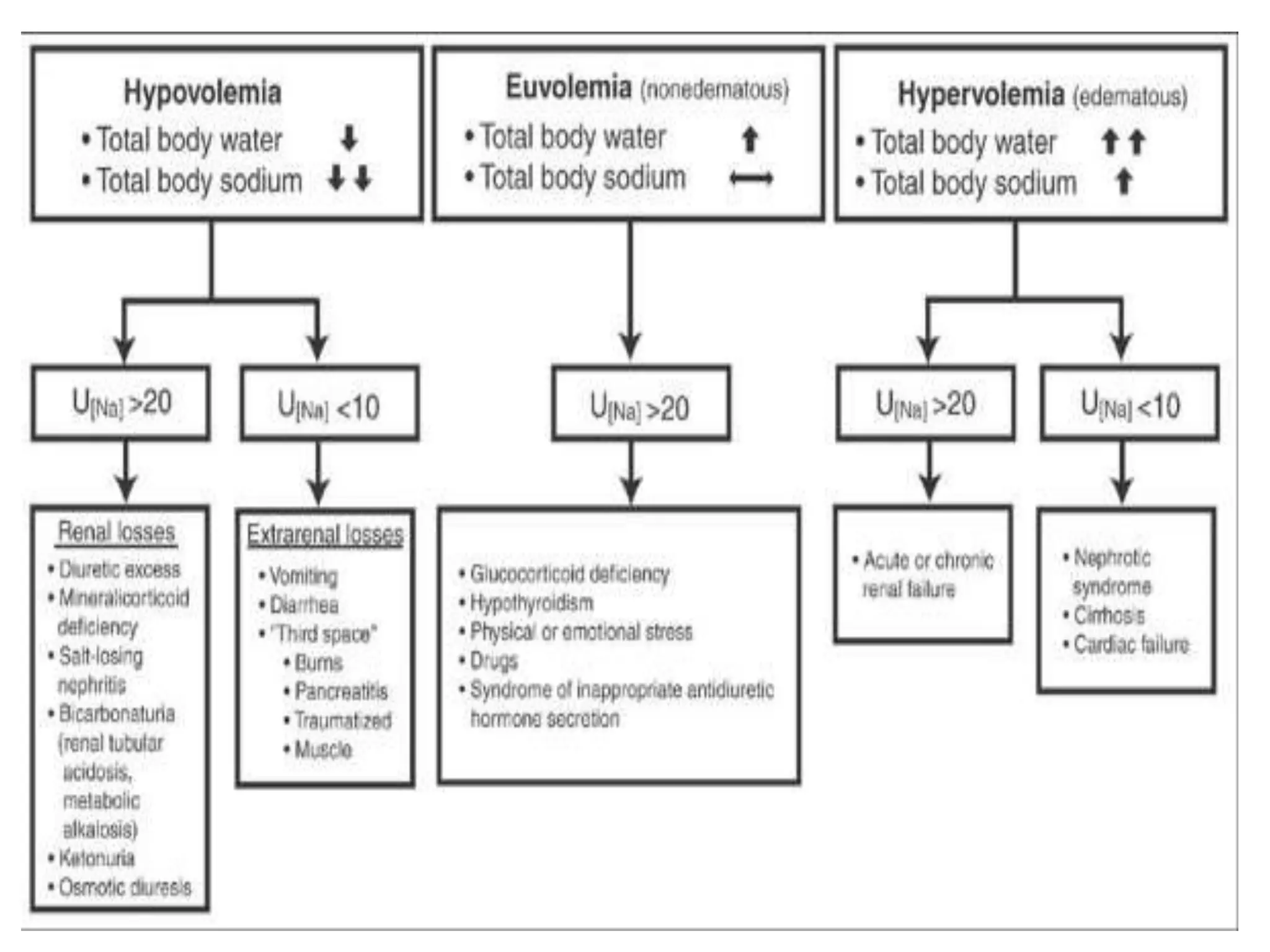
This document provides guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hyponatremia. It defines hyponatremia as a serum sodium concentration of less than 135 mEq/L. It notes that hyponatremia is commonly seen in hospitalized patients and can cause neurological symptoms if left untreated. The guidelines recommend a systematic approach to hyponatremia involving assessing volume status, urine and serum osmolality to determine the cause (hypovolemic, euvolemic, or hypervolemic), and correcting any underlying conditions and sodium levels slowly to avoid complications. Newer vasopressin receptor antagonists called vaptans can be useful for treating euvolemic or hypervolemic hy












![Diagnostic criteria for SIADH
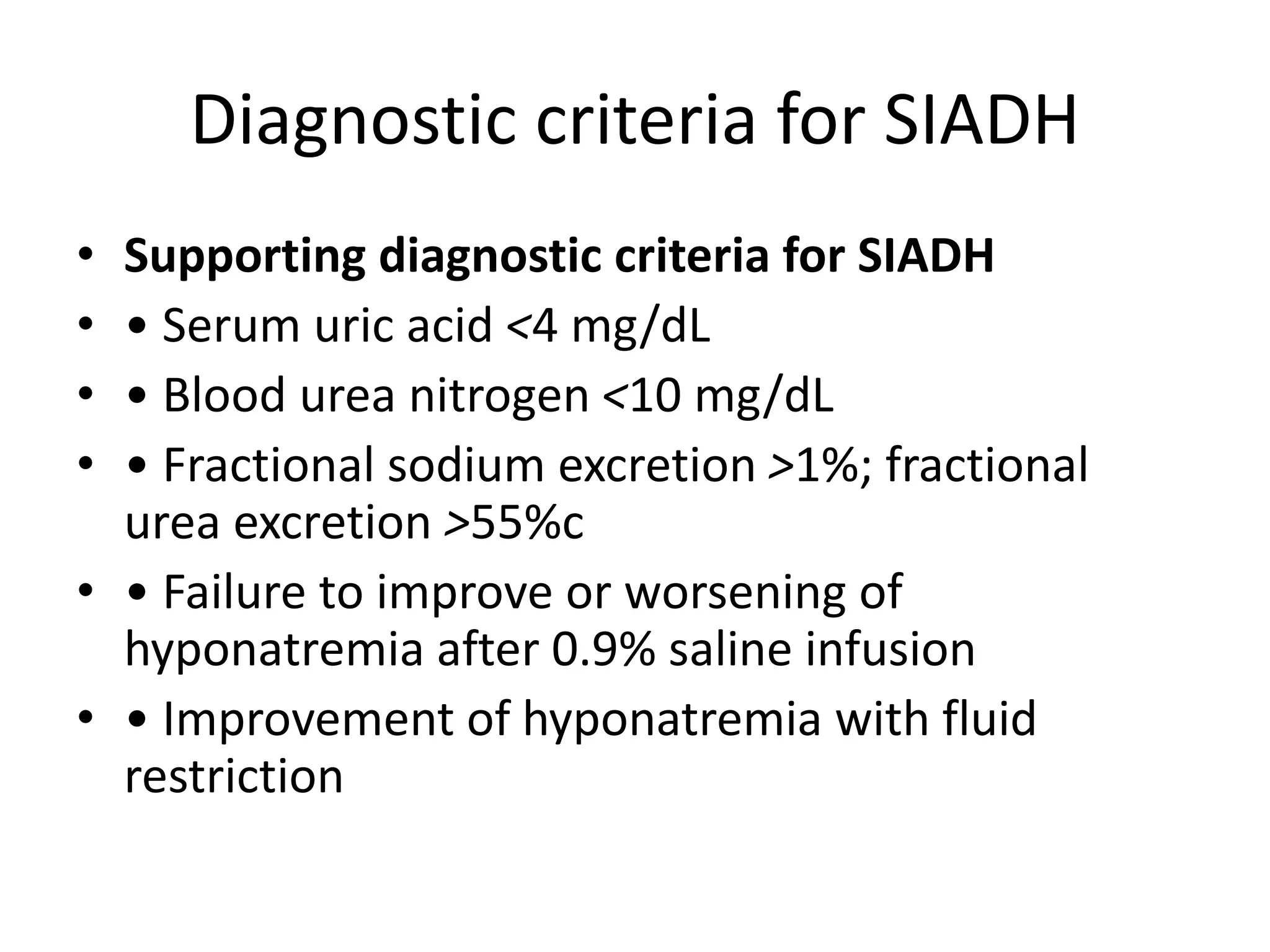
• Essential diagnostic criteria for SIADH
• • Decreased measured serum osmolality (<275 mOsm/kg
H2O)
• • Clinical euvolaemia. Exclude hypovolemia and
hypervolemia
• • Urinary osmolality >100 mOsm/kg H2O during hypo-
osmolality
• • Urinary [Na+] >40 mmol/L with normal dietary sodium
intake
• • Normal thyroid and adrenal function. Exclude renal
failure and use of diuretic agents within the week prior to
evaluation
• • No hypokalemia, no acid base disorders](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremia-gulidelines-140501083918-phpapp01/75/Hyponatremia-gulidelines-19-2048.jpg)