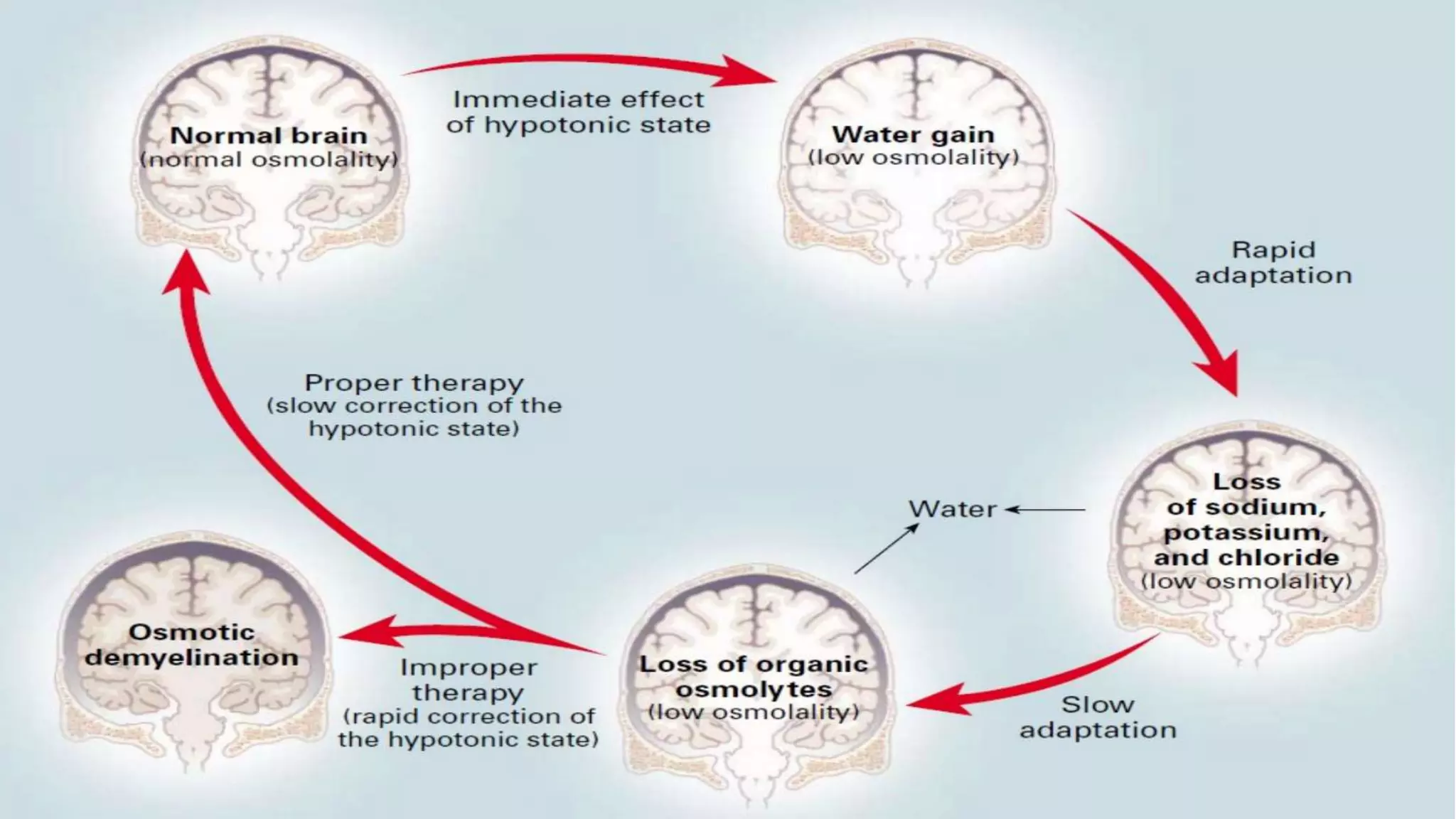
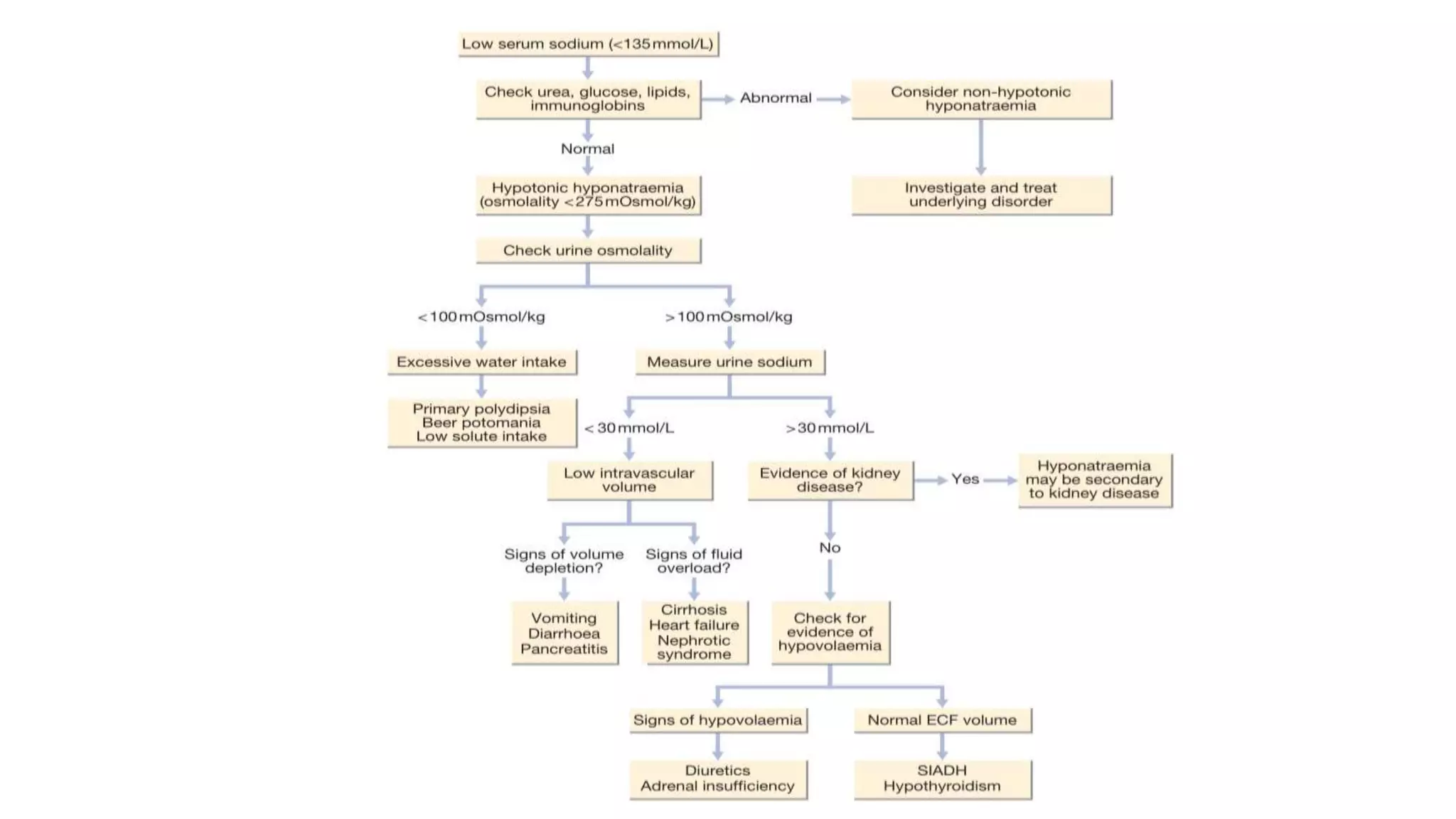
Hyponatremia is a common electrolyte abnormality seen in clinical practice. It is defined as a serum sodium level below 135 mmol/L. The main types are isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic hyponatremia. Causes include diuretic use, liver cirrhosis, heart failure, and SIADH. Diagnosis involves lab tests and imaging. Management depends on severity and rate of onset, with slow correction for chronic cases to avoid osmotic demyelination syndrome. Fluid restriction and vasopressin antagonists are often used to treat euvolemic hyponatremia.






![Isotonic hyponatremia
• Expansion of extracellular fluid with isotonic fluids that do not contain
Na, here is no transcellularshift of water but the [Na+] decreases
Ex- Hypertriglyceridemia
Hyperproteinemia( as in Multiple Myeloma)
• Rise in plasma lipids of 4.6 g/L or plasma protein concentrations
greater than 10 g/dL will decrease the sodium concentration by
approximately 1 mEq/L.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremia-181021100249/75/Hyponatremia-7-2048.jpg)


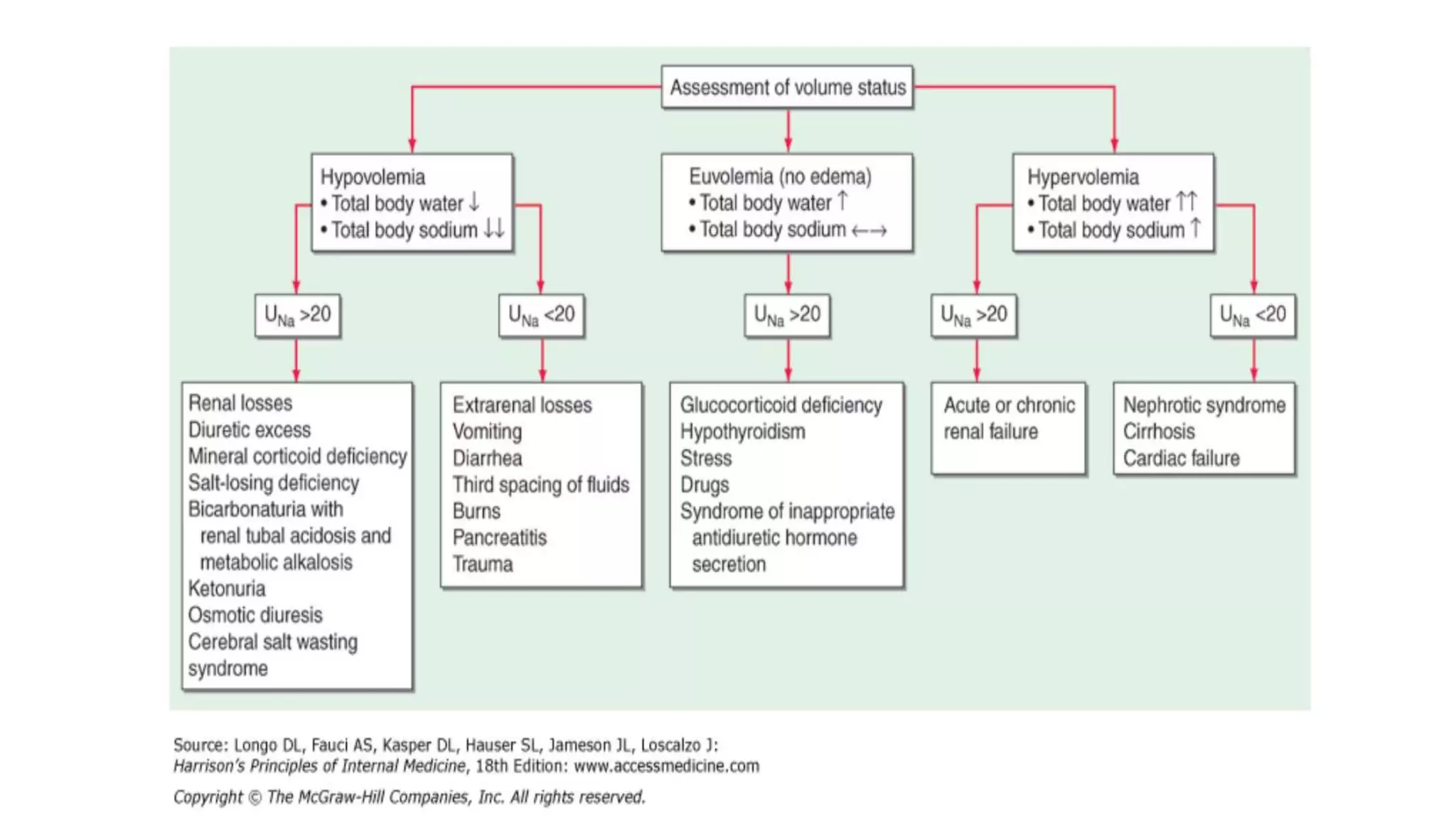

![Mineralocorticoid (Aldosterone) Deficiency
• Characterized by hyponatremia with ECF volume contraction.
• Hypotensive and/or hypovolemic patient present with Urine [Na + ]
above 20 mmol/l, and high serum K +.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremia-181021100249/75/Hyponatremia-12-2048.jpg)













![• Equations are available to help calculate the initial rate of fluids to be
administered.
• A widely used formula is the Adrogue-Madias formula
• Change in serum Na+ with infusing solution=
[infusate Na]-serum Na / (total body water +1)
• Infusate Na+ is the [Na+] in the infused fluid (154meq/l in 0.9%NS,
513meq/l in 3%NS, 77meq/l in 0.45%NS)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremia-181021100249/75/Hyponatremia-28-2048.jpg)




![• Glucocorticoid Deficiency-
Glucocorticoid replacement at either maintenance or stress
doses, depending on the degree of intercurrent illness.
• Severe Hypothyroidism-
Thyroid hormone replacement at standard weight-based doses;
several days may be needed to normalize the serum [Na].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyponatremia-181021100249/75/Hyponatremia-33-2048.jpg)