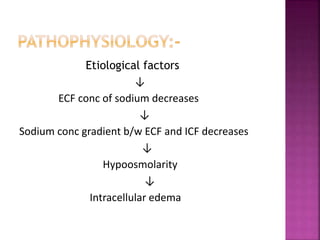
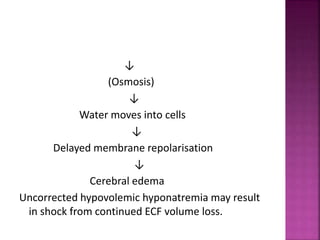
Hyponatremia is a low serum sodium level below 135 mEq/L. It can be caused by a decreased total body water, inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, or an inability of the kidneys to excrete diluted urine. Symptoms range from nausea and vomiting to neurological changes like confusion and seizures as water moves into brain cells. Treatment involves fluid restriction and sodium replacement through oral intake or intravenous solutions depending on the severity of low sodium levels. Close monitoring of fluid balance and serum sodium levels is needed to manage the condition and prevent complications.