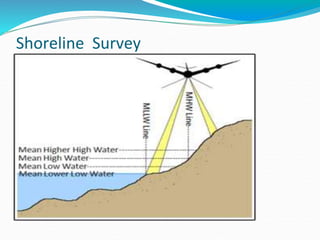
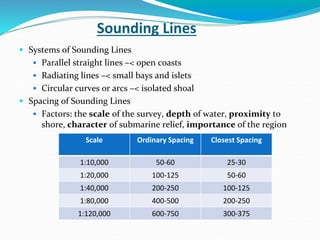
The document summarizes key aspects of hydrographic surveys. It discusses controlling horizontal and vertical positions, measuring depths through sounding, and producing charts. Soundings are taken using various instruments and referenced to tidal datums. Depths are plotted on charts along with shorelines, depth contours, and navigational features. Hydrographic surveys provide critical data for safe navigation and engineering projects.