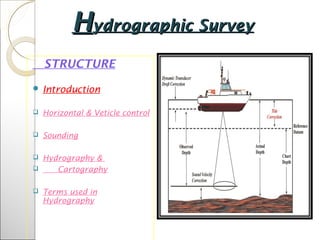
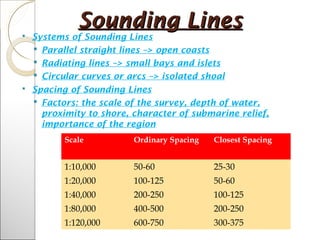
This document provides information about hydrographic surveying and sounding. It discusses the instruments used for horizontal and vertical control as well as sounding. Methods for locating soundings from shore or boat are described. Common instruments for sounding include sounding poles, leadlines, sounding machines, registering sheaves, and echo sounding instruments. Soundings must be reduced based on tide levels. A hydrographic survey team typically includes roles like the officer in charge, anglemen, recorder, and helmsman. The results of a survey are used to produce nautical charts, which should contain elements like depth curves, datums, and safety symbols. Plotting of soundings can be done mechanically or graphically. Other tools mentioned include the sextant,