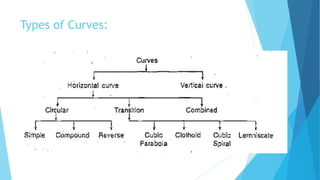
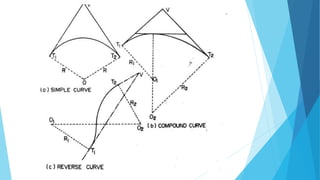
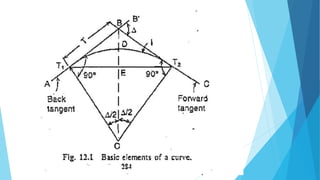
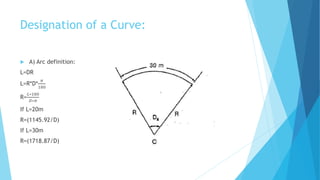
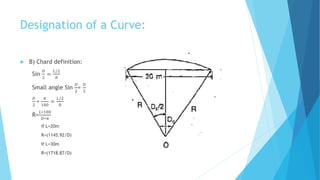
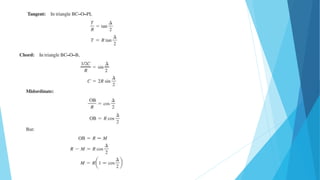
This document discusses methods for setting out simple circular curves in surveying. There are two main methods: linear and angular.
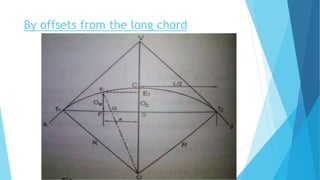
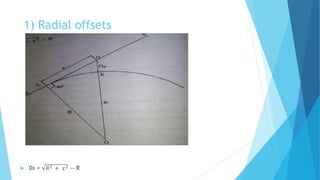
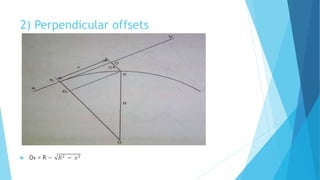
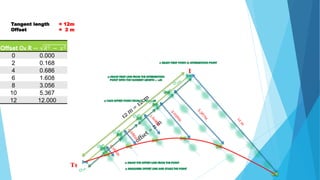
The linear method uses only a tape or chain and does not require angle measurement. It includes setting out curves by offsets from the long chord, by successive bisection of arcs, and by offsets from the tangents.
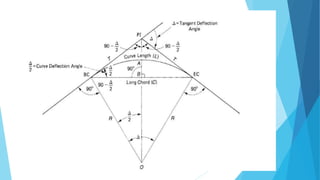
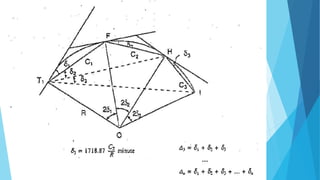
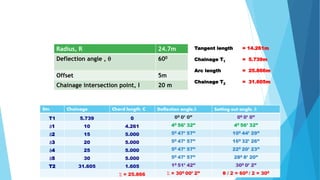
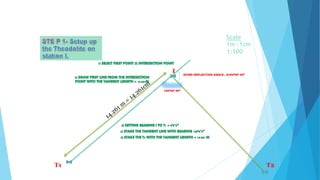
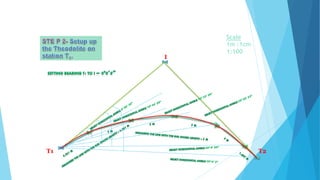
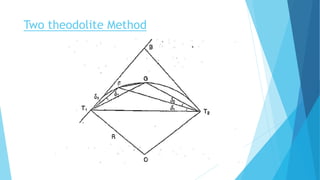
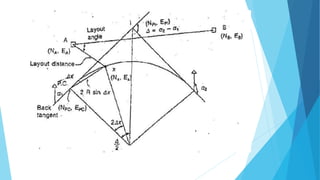
The angular method is used for longer curves and involves measuring deflection angles. It includes Rankine's method of tangential angles using a tape and theodolite to measure deflection angles from the back tangent to points on the curve. The two theodolite method also uses angle measurement between two theodolites.