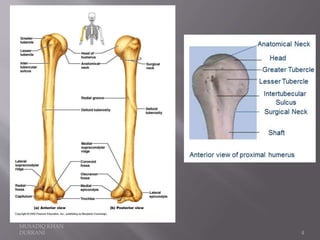
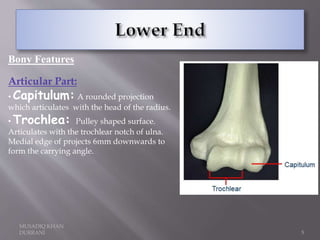
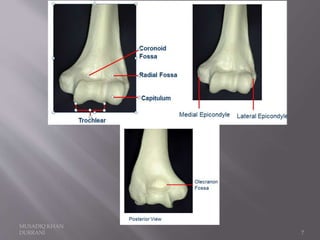
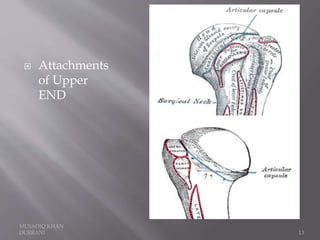
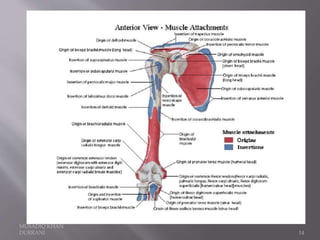
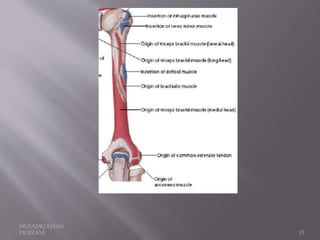
The document describes the anatomical features of the humerus bone. It discusses the upper end, which includes the head, anatomical neck, lesser tubercle, and greater tubercle. The lower end includes the capitulum, trochlea, medial and lateral epicondyles. The shaft has borders, surfaces, and features muscle attachments from various muscles including the deltoid, pectoralis major, and triceps brachii. Ligaments like the shoulder and elbow joint capsules are also attached. Major nerves like the axillary, radial, and ulnar nerves are related to specific parts of the humerus.