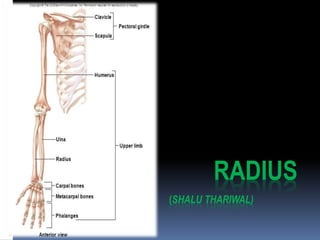
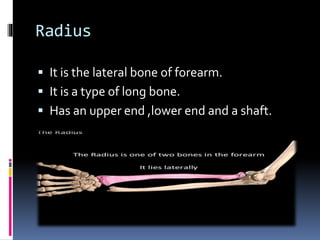
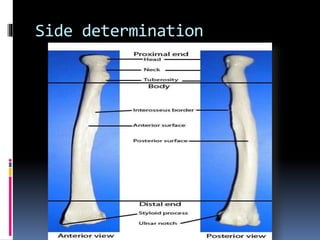
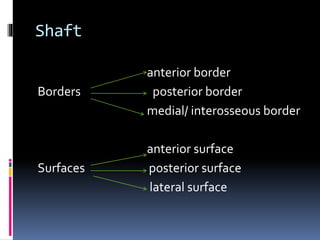
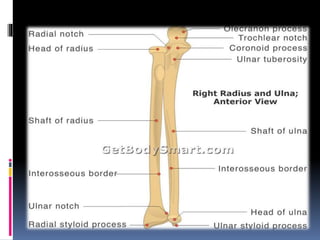
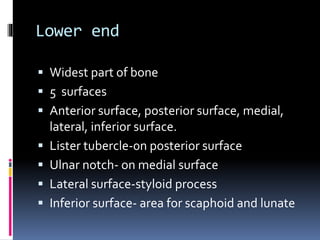
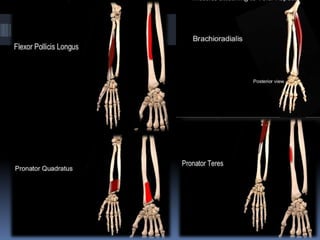
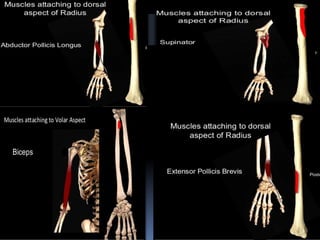
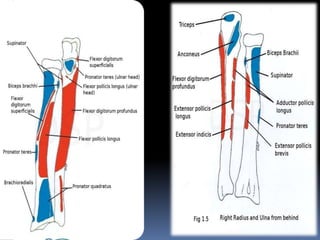
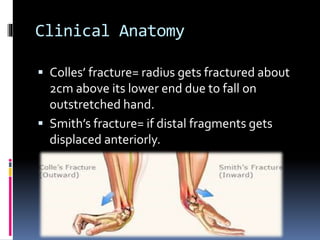
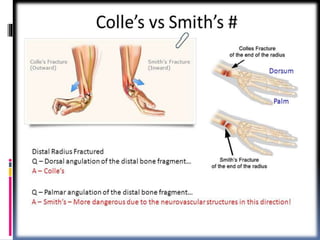
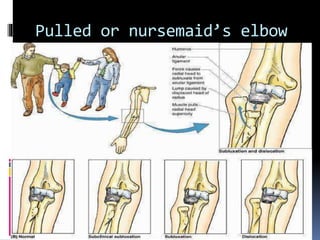
The radius is a long bone in the forearm with distinct upper and lower ends and a shaft, featuring specific anatomical landmarks for side determination. Key attachments include muscles like biceps brachii and pronator teres, and clinical conditions such as Colles' fracture and pulled elbow arise from injuries to this bone. Its notable features include the disc-shaped head at the upper end and various surfaces for muscle insertions at the lower end.