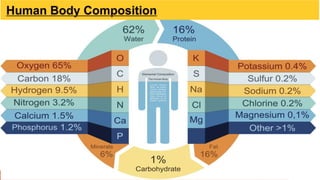
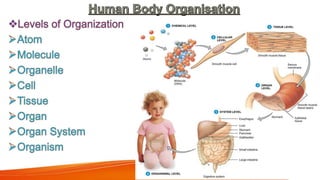
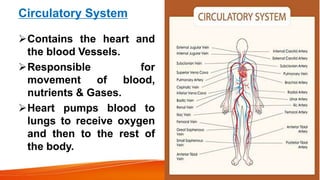
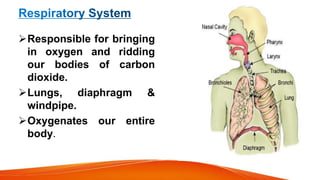
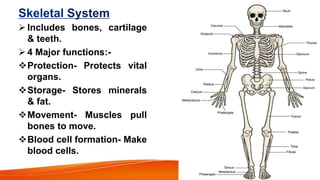
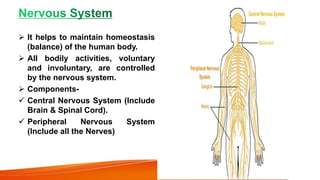
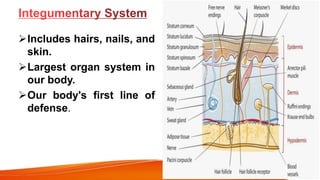
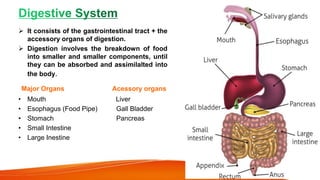
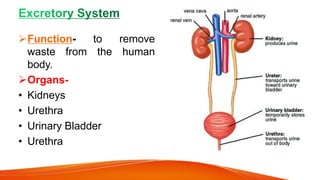
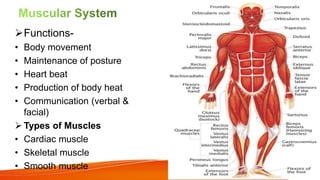
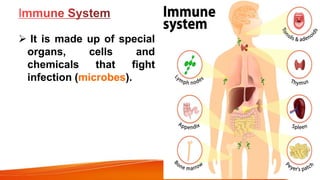
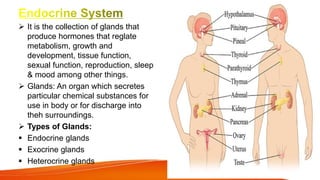
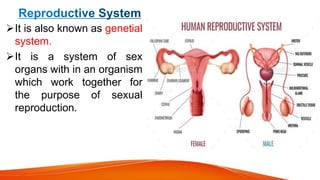
The document provides an overview of the major human body systems. It discusses 12 key systems: circulatory, respiratory, skeletal, nervous, integumentary, digestive, excretory, muscular, immune, endocrine, reproductive, and lymphatic. For each system, it outlines the main organs and functions. The goal is to explain at a high level how each system works and its role in the overall human body.