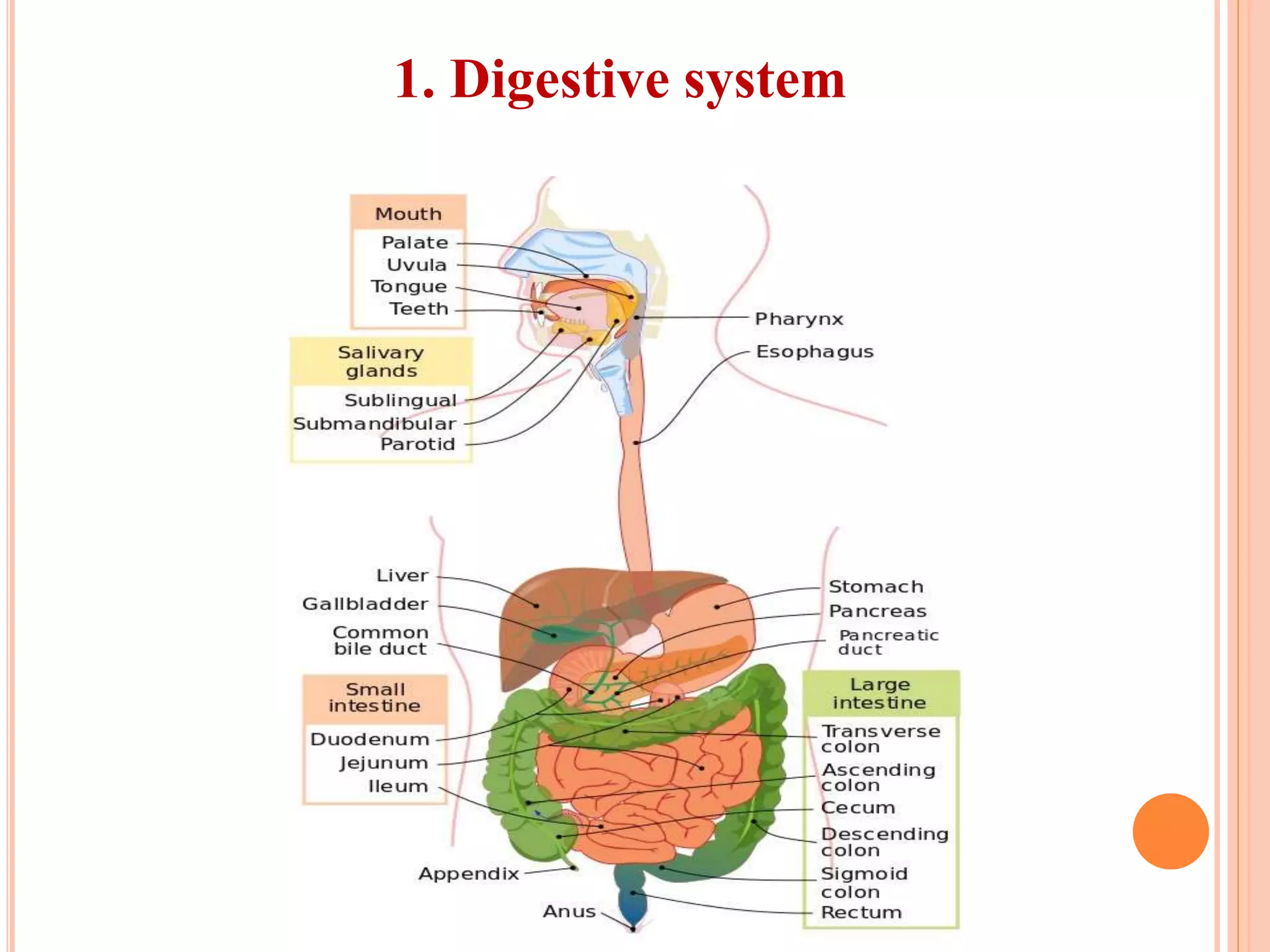
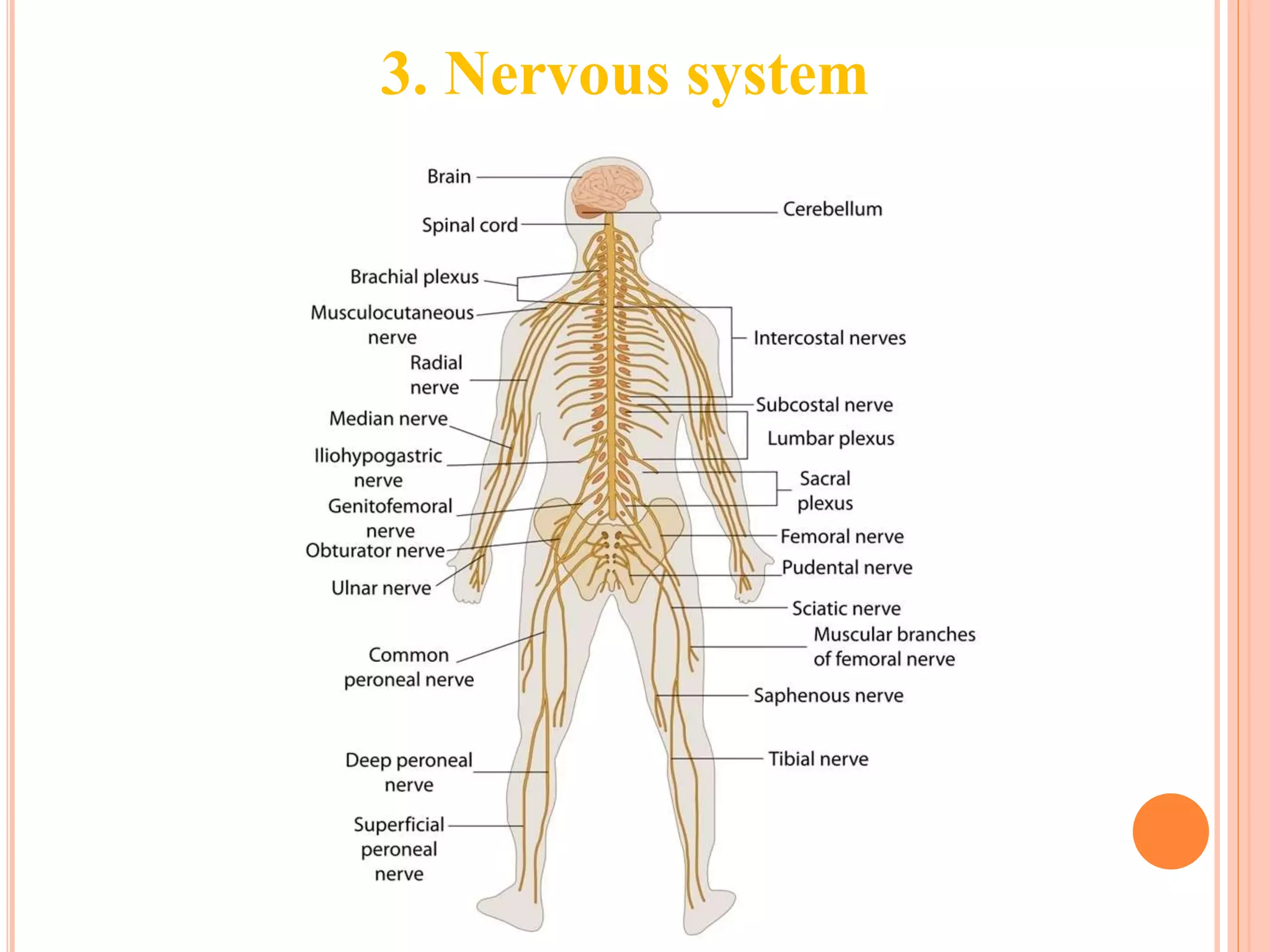
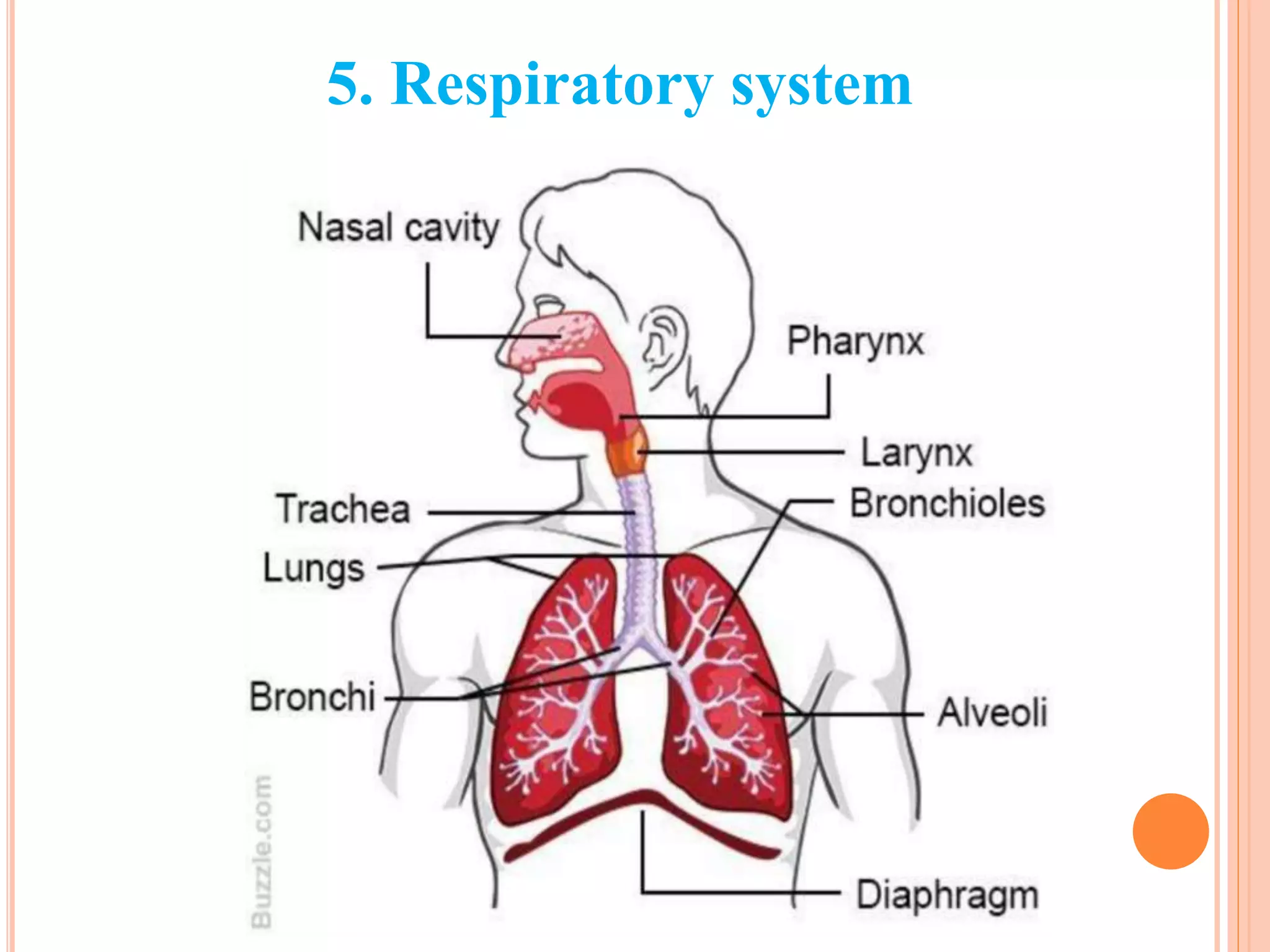
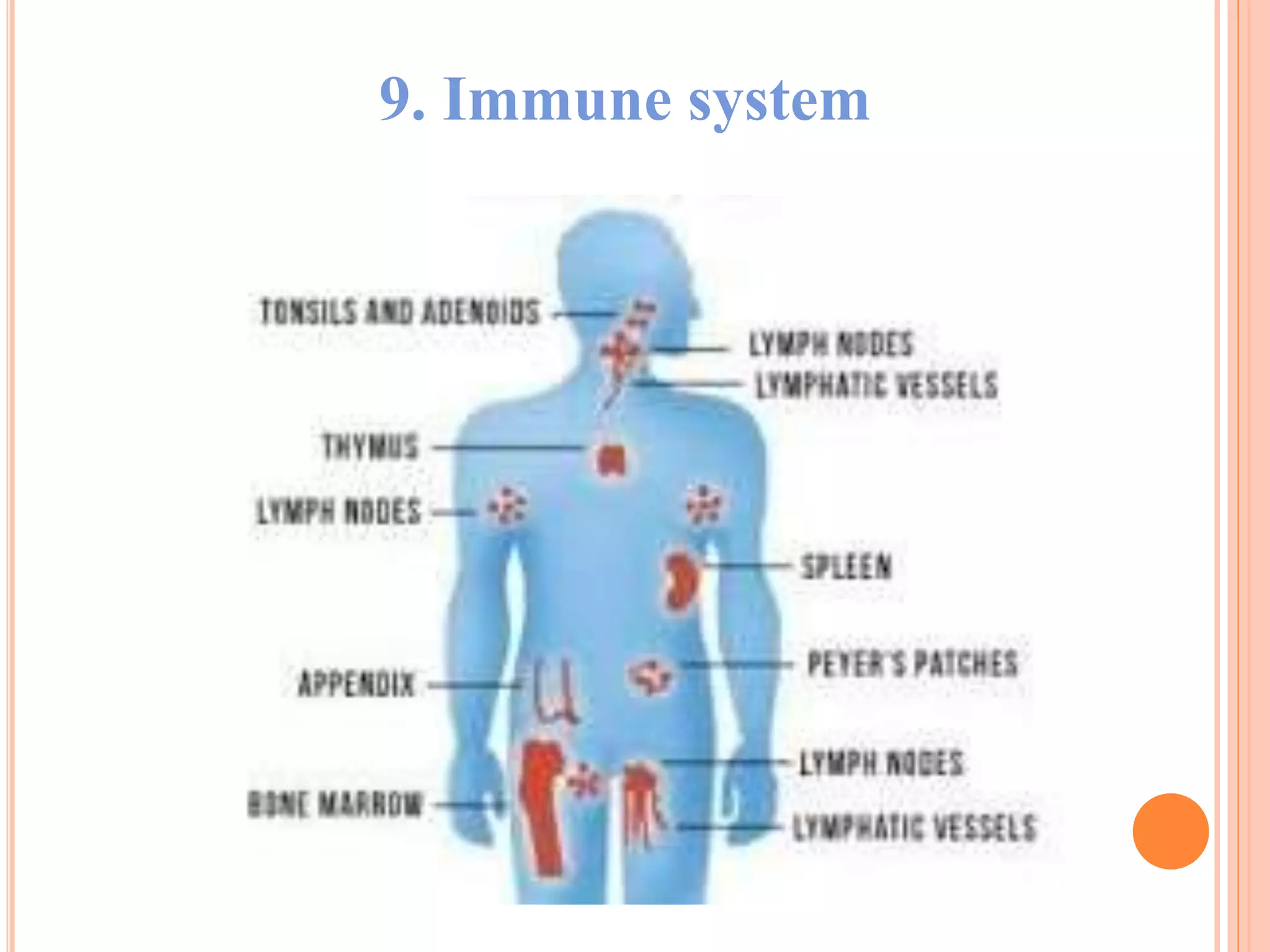
The document summarizes the 12 major systems of the human body. It lists each system and provides 1-2 sentences about their main functions. The systems are: 1) digestive, 2) circulatory, 3) nervous, 4) excretory, 5) respiratory, 6) skeletal, 7) muscular, 8) endocrine, 9) immune, 10) integumentary, 11) lymphatic, and 12) reproductive. Each system works with organs to perform important tasks that support life and homeostasis.