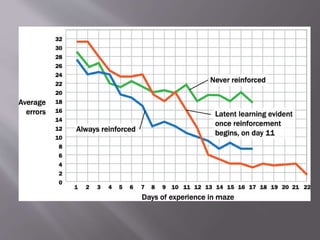
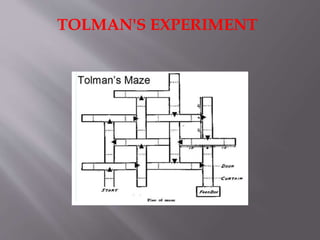
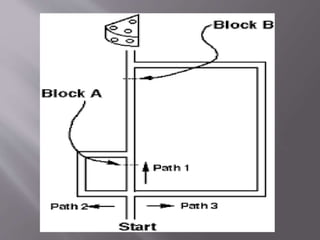
Tolman's purposive behaviorism theory posits that learning is always goal-directed and purposeful, not merely the formation of stimulus-response associations. According to Tolman, organisms form cognitive maps of their environment which allow them to navigate efficiently to goals. He demonstrated this concept through experiments showing that rats could learn maze patterns even without reinforcement, indicating latent or hidden learning had occurred through map formation. Tolman's theory moved beyond strict behaviorism to incorporate internal cognitive processes as mediators of learning and behavior.