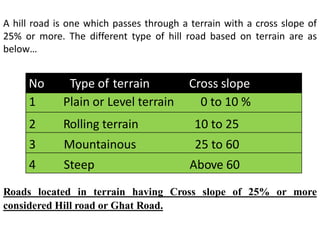
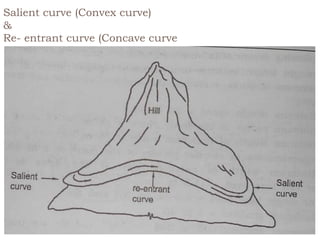
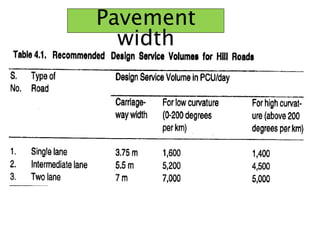
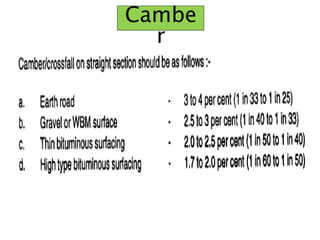
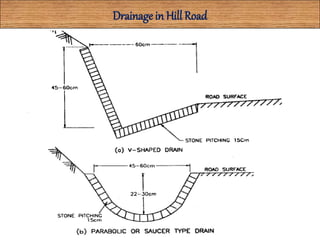
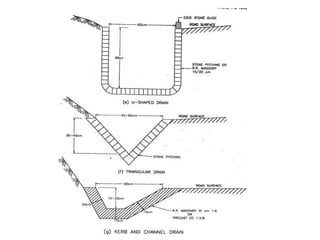
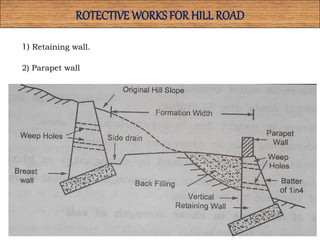
This document discusses hill roads and their design. It defines a hill road as one with a cross slope of 25% or more. It classifies hill roads based on their terrain and organization. Some key points:
- Hill roads are classified as plain/level, rolling, mountainous, or steep depending on their cross slope which can range from 0-10% to over 60%.
- They are also classified by organizations like BRO and by their use as motor roads, bridle paths, or village tracks.
- Important reasons for hill roads include economic development, industry, forests, tourism, and strategic needs.
- Design considers minimum costs, comfort, stability, drainage, and following geometric standards with easy