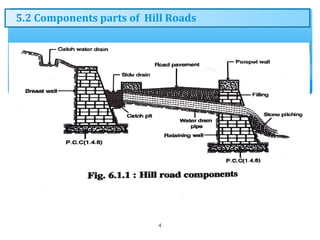
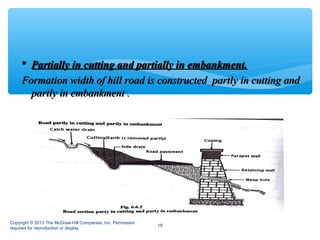
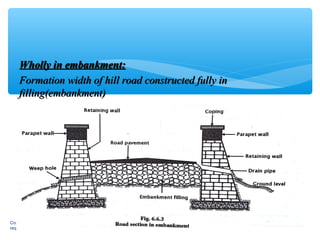
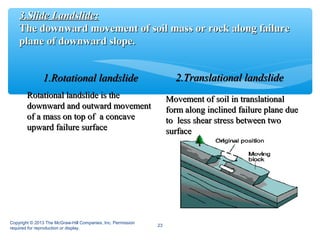
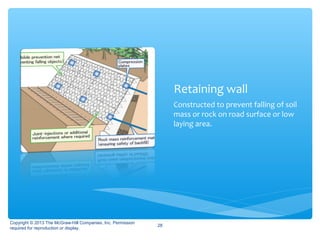
Hill roads require special design considerations due to mountainous terrain. They include curved alignments, retaining walls, drainage features, and formation in cuttings or embankments. Landslides are a key hazard for hill roads and can be caused by heavy rainfall, erosion, earthquakes, or human activities like mining. Prevention methods involve benching slopes, installing drainage, constructing retaining structures, soil stabilization, and increasing vegetation.