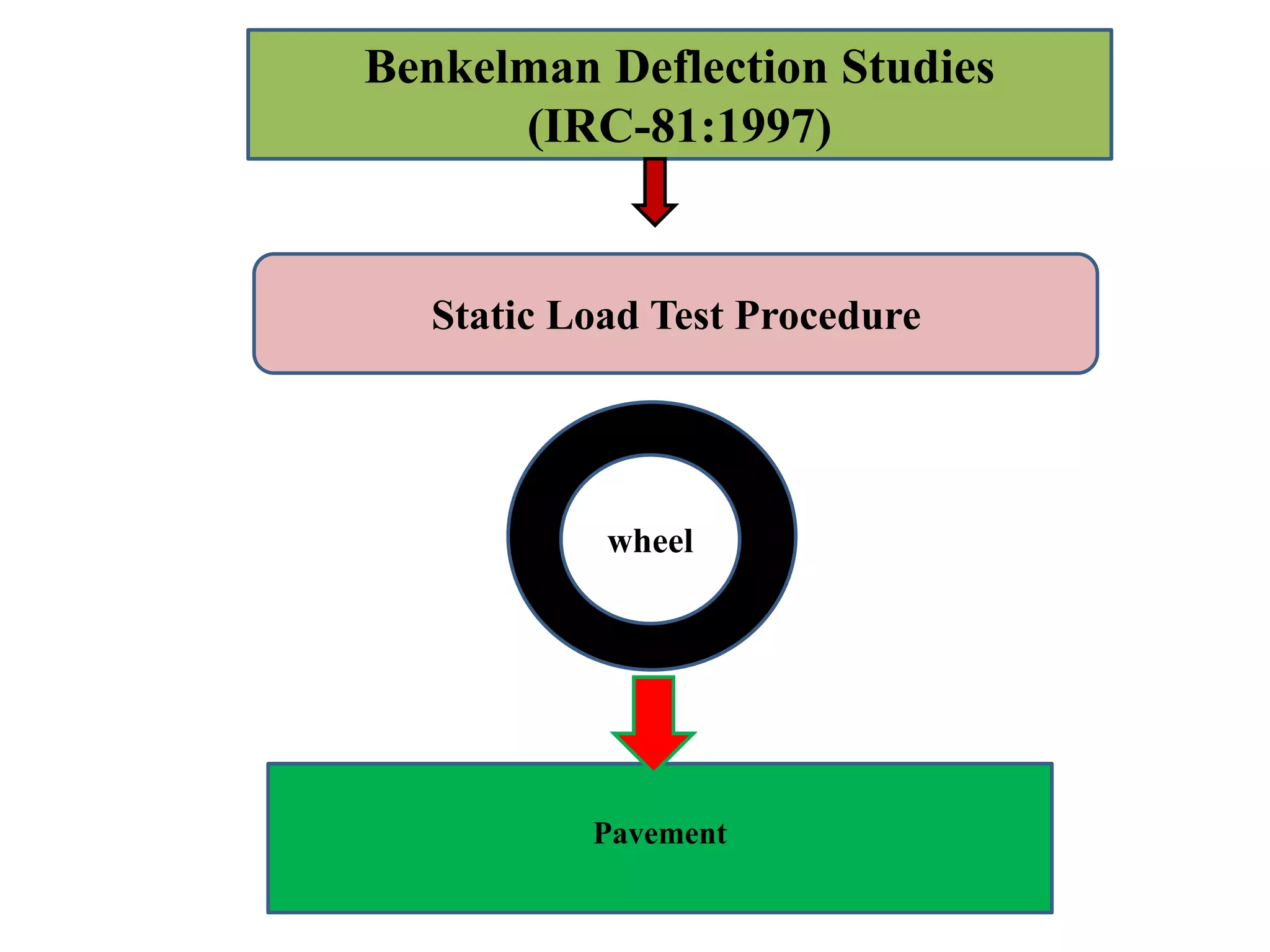
This document discusses Benkelman beam deflection studies, which are used to evaluate the structural capacity of existing pavements and estimate overlay designs for strengthening weak pavements. The Benkelman beam test procedure involves measuring the rebound deflection of a pavement under a standard wheel load. Deflection measurements are taken at intervals along the road using the Benkelman beam and loaded truck. The results are used to calculate the true rebound deflection and characterize pavement strength statistically based on mean, standard deviation, and characteristic deflection values. Overlay design is then determined based on the statistical analysis.