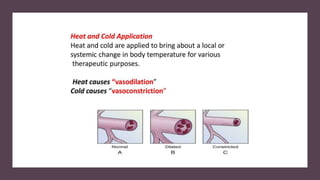
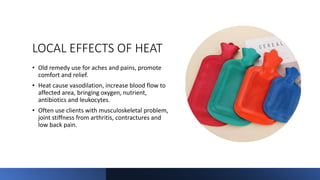
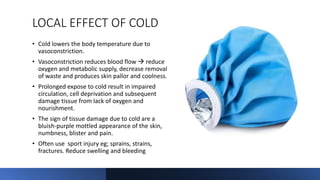
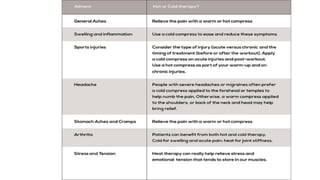
The document outlines the principles, applications, and physiological effects of heat and cold therapy in nursing practice. It covers the effects of these therapies on the body, specific conditions for their use, and the responsibilities of nurses in administering them safely. Additionally, it details various methods of application, including hot/cold packs, aquathermia pads, and sponge baths, while emphasizing the importance of client safety and monitoring.