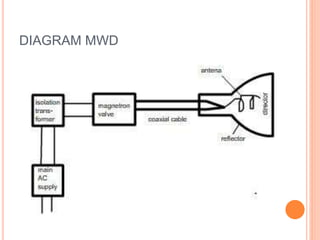
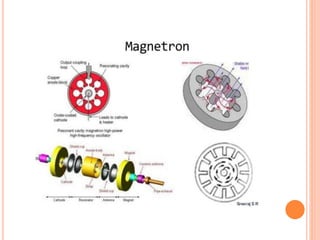
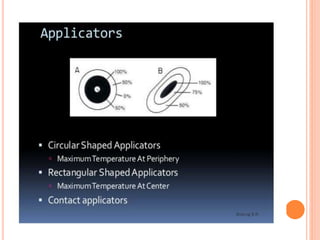
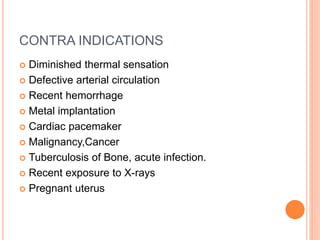
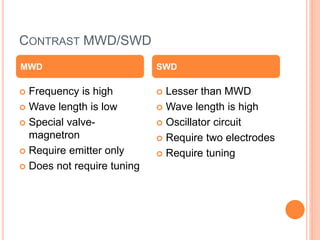
Microwave diathermy (MWD) uses electromagnetic radiation in the microwave frequency range to generate heat in tissue. MWD uses a magnetron to produce microwaves with frequencies commonly between 300 MHz to 300 GHz. These short wavelength microwaves generate strong electrical fields that cause heating through ionic movements and molecular distortion within tissues. MWD provides superficial heating that is more localized than shortwave diathermy and penetrates deeper than infrared radiation. Key uses of MWD include reducing pain, swelling and muscle spasm in inflammatory conditions like tendinitis as well as accelerating healing for injuries and infections.