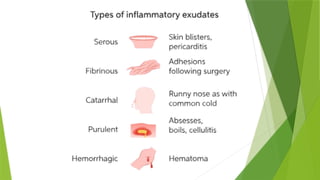
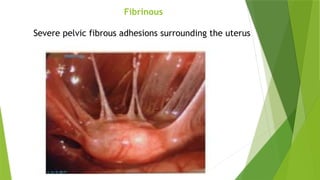
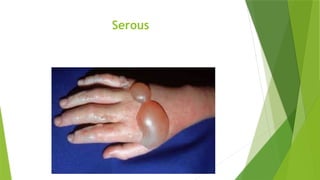
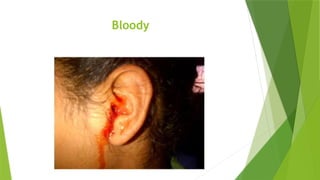
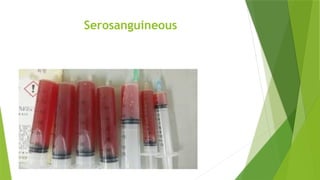
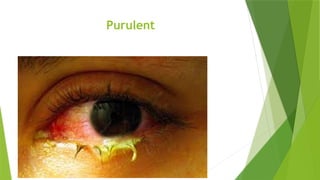
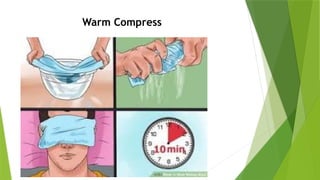
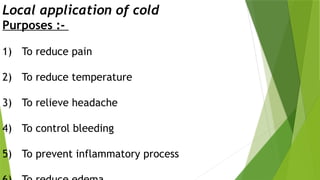
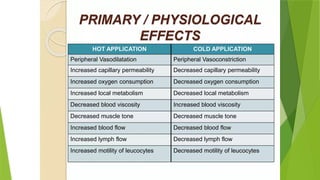
The document discusses the therapeutic applications of heat, cold, and counterirritants, detailing their physiological effects and purposes such as pain relief and inflammation reduction. It covers methods of application for both dry and moist heat, as well as cold therapies, including the precautions and considerations necessary for safe use. Factors affecting the efficacy of these treatments include body part sensitivity, individual tolerance, duration of application, and skin condition.