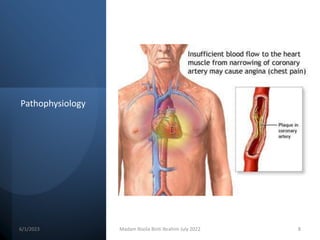
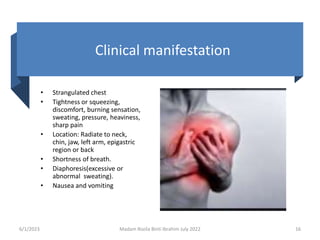
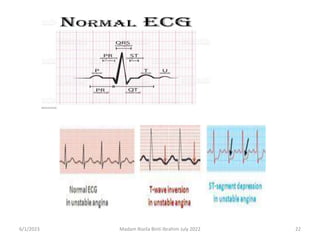
This document discusses angina pectoris, including its definition, risk factors, types, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment. Angina pectoris is a clinical syndrome characterized by chest pain or pressure due to insufficient blood flow to the heart. It discusses the three main types of angina - stable, unstable, and variant angina - and their distinguishing features. Treatment focuses on reducing oxygen demand on the heart and includes medications like nitroglycerin, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers. Nursing care involves health education regarding medication administration and lifestyle modifications.