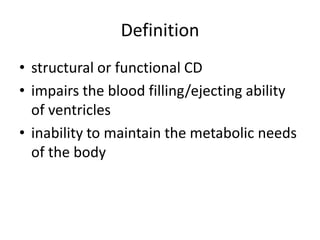
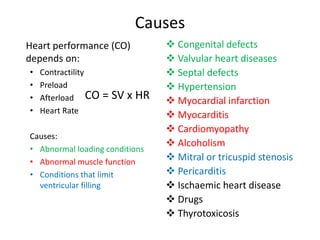
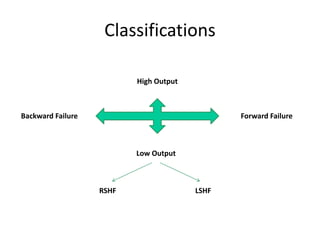
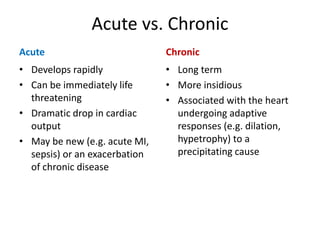
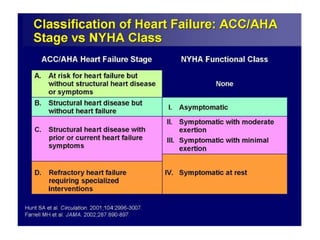
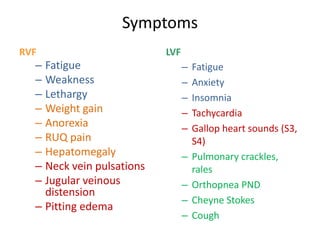
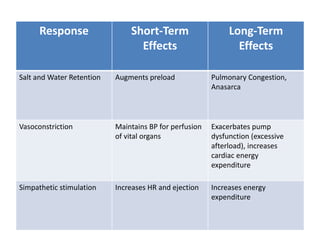
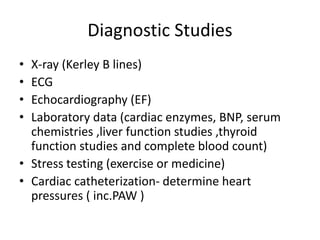
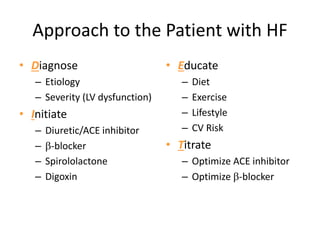
Heart failure is defined as a structural or functional impairment of the heart that prevents it from maintaining an adequate blood supply to meet the body's needs. It can be caused by conditions that overload or damage the heart such as hypertension, heart attacks, and cardiomyopathy. Heart failure is classified as acute or chronic and as forward or backward based on its location and symptoms. While compensatory mechanisms initially help the heart function, long term they cause further damage and worsening of heart failure over time. Diagnosis involves tests like echocardiograms, EKGs and blood tests, and treatment focuses on diuretics, ACE inhibitors and beta blockers to manage symptoms and slow progression of the disease.