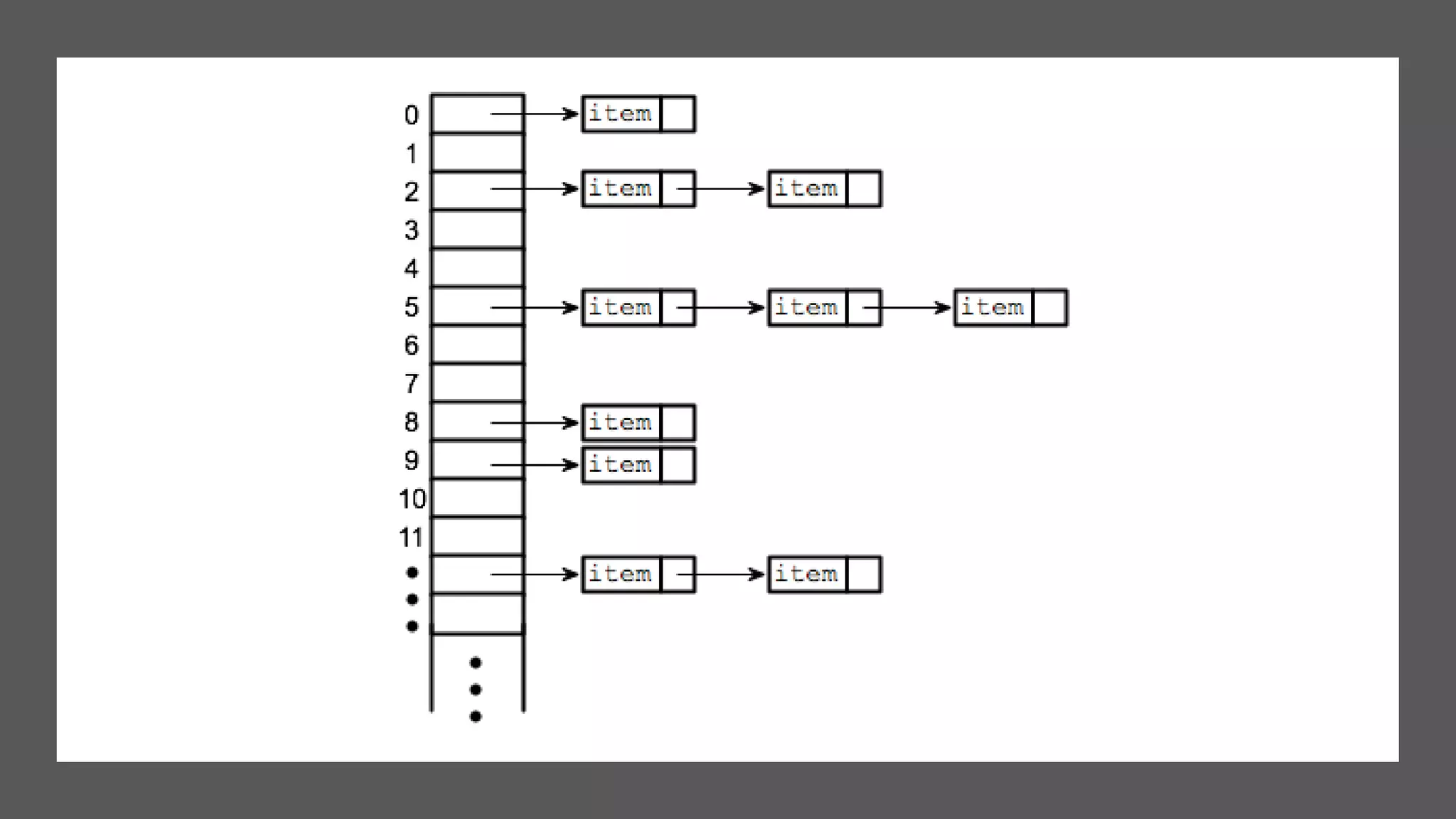
Hashing is a technique used to uniquely identify objects by assigning each object a key, such as a student ID or book ID number. A hash function converts large keys into smaller keys that are used as indices in a hash table, allowing for fast lookup of objects in O(1) time. Collisions, where two different keys hash to the same index, are resolved using techniques like separate chaining or linear probing. Common applications of hashing include databases, caches, and object representation in programming languages.