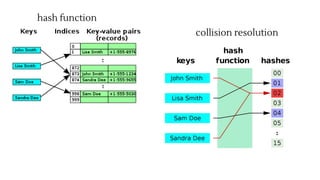
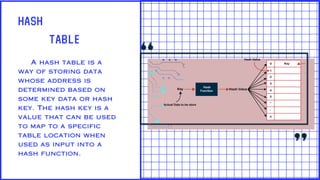
A hash table is a data structure that uses a hash function to map keys to unique indices in an underlying array. Collisions occur when two keys hash to the same index and must be resolved. Open addressing resolves collisions by probing through alternative array locations until an empty slot is found. Double hashing is an open addressing collision resolution technique that uses a secondary hash of the key as an offset when probing for the next index. Hash tables provide efficient lookup, insertion and deletion of key-value pairs and are used widely in applications like databases, caching and cryptography.