1. Planning involves finding a sequence of actions that achieves a goal starting from an initial state. It uses a set of operators that define the possible actions and their effects.
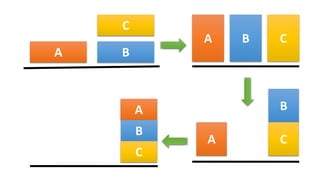
2. A plan is a sequence of operator instances that transforms the initial state into a goal state. Classical planning assumes fully observable, deterministic environments.
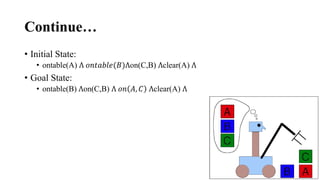
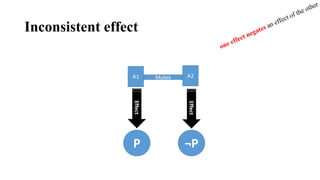
3. Planning problems can be represented using a logical language that describes states, goals, actions and their preconditions and effects. This representation allows planning algorithms to operate over problems.