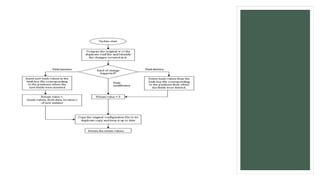
The document describes a hash-based inventory system that uses hashing algorithms to create a list of inventory parts and quantities sold. The system has three modules: constructing a hash table, searching for inventory items by generating hash codes, and generating reports of parts and quantities. It discusses hash tables, hashing functions, and basic hash table operations like search, insert, and delete. The document also provides examples of hash functions and how they map strings to indexes in a hash table to enable fast retrieval of data.