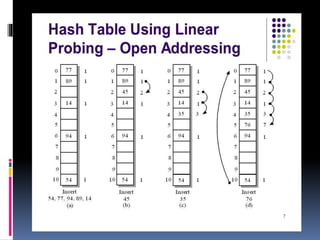
Linear probing is a collision resolution technique for hash tables that uses open addressing. When a collision occurs by inserting a key-value pair, linear probing searches through consecutive table indices to find the next empty slot. This provides constant expected time for search, insertion, and deletion when using a random hash function. However, linear probing can cause clustering where many elements are stored near each other, degrading performance.