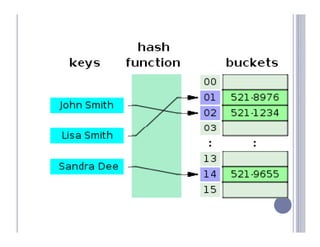
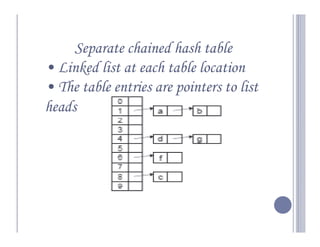
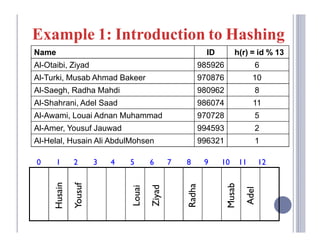
A hash table maps keys to values by applying a hash function to the keys, which then indexes into an array of buckets or slots. There are two main types: open-addressing hash tables, where keys are stored directly in the array slots, and separate chaining, where each slot contains a linked list of key-value entries. Some example applications include databases, symbol tables for compilers, and network processing algorithms.