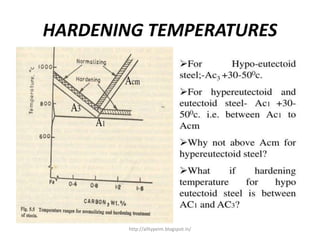
The document discusses the hardening process used to increase the hardness of metals. Hardening involves heating metals to their hardening temperature, holding at that temperature, and then rapidly cooling via quenching. This rapid cooling results in the formation of martensite, giving the metal a high hardness. The main purposes of hardening are to improve wear resistance, tensile strength, and yield strength. Factors like chemical composition, size and shape of the metal, and the quenching medium used affect how effective the hardening process is. Various hardening methods are discussed, like conventional quenching, quenching in stages, spray quenching, and quenching with self-tempering. Hardened metals find