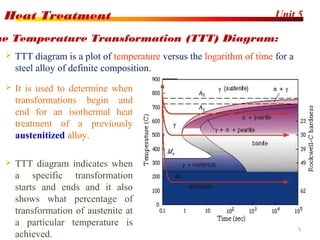
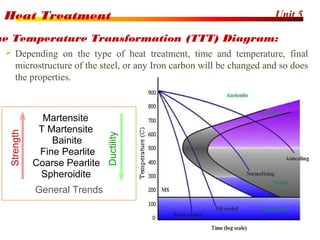
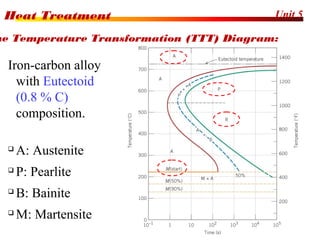
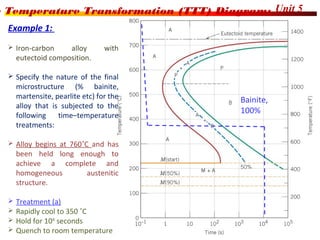
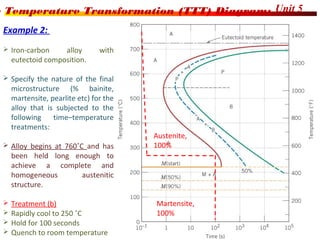
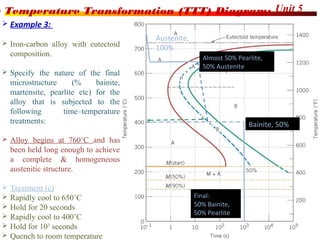
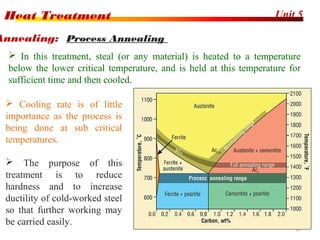
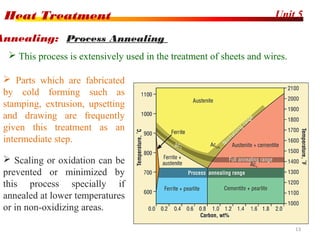
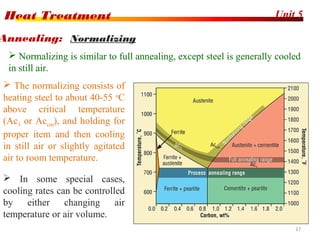
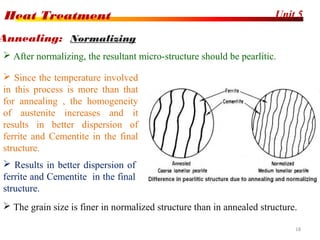
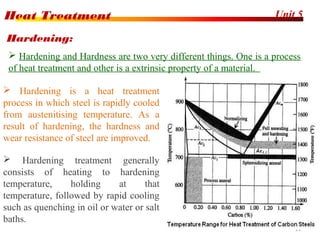
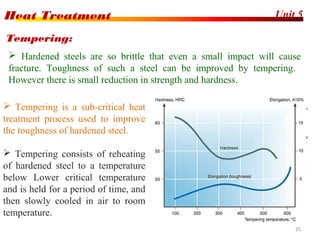
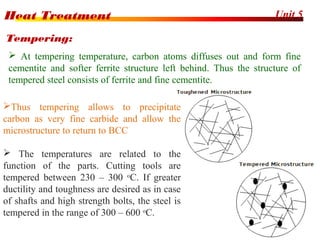
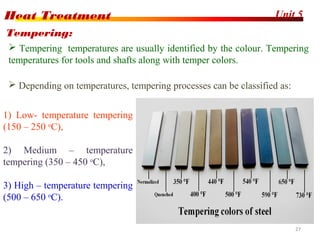
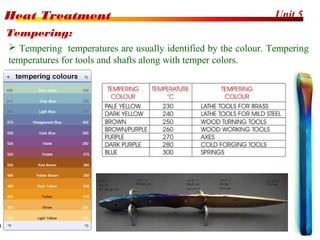
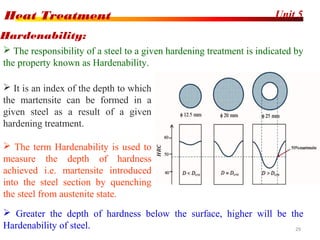
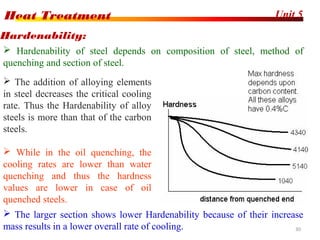
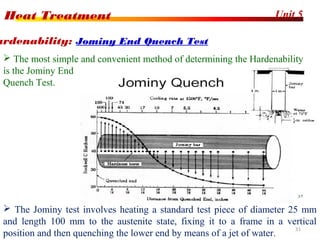
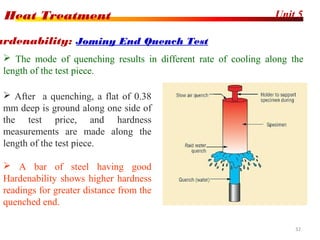
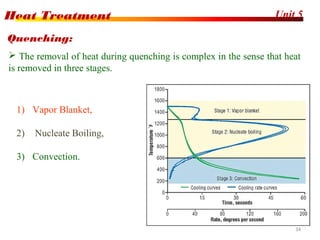
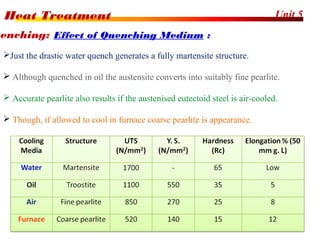
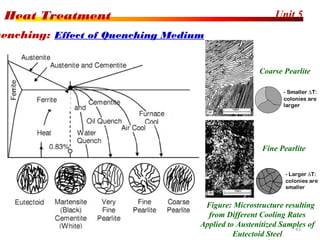
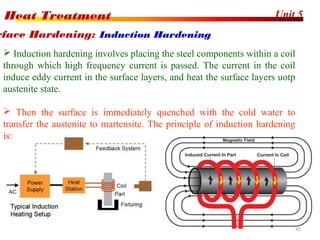
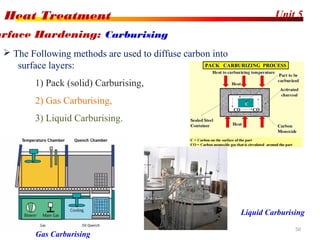
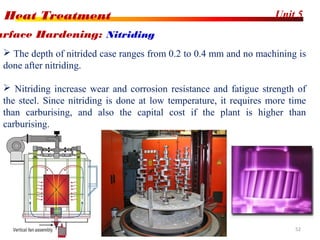
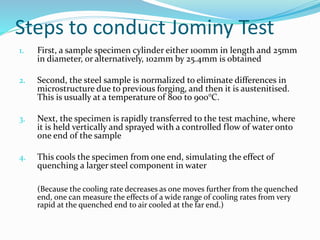
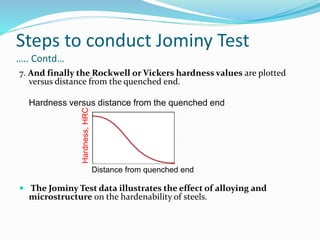
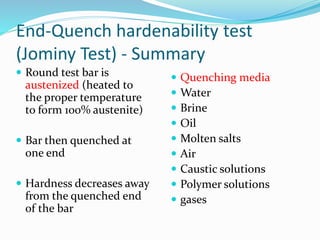
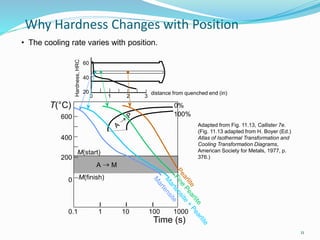
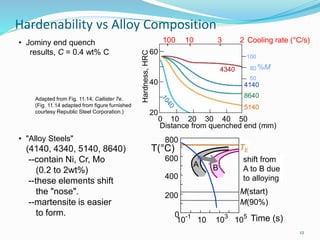
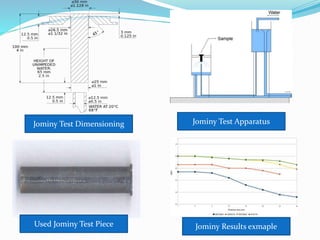
The document discusses various heat treatment processes including annealing, normalizing, hardening, tempering, and analyzing hardenability. Annealing involves heating material to relieve stresses and improve ductility. Normalizing is similar but involves faster cooling in air to refine grain structure. Hardening increases hardness through rapid quenching from austenitizing temperatures resulting in martensite formation. Tempering improves toughness of hardened steel by reheating to precipitate carbides. Hardenability is measured using the Jominy end quench test and indicates the depth of hardness achieved during quenching.