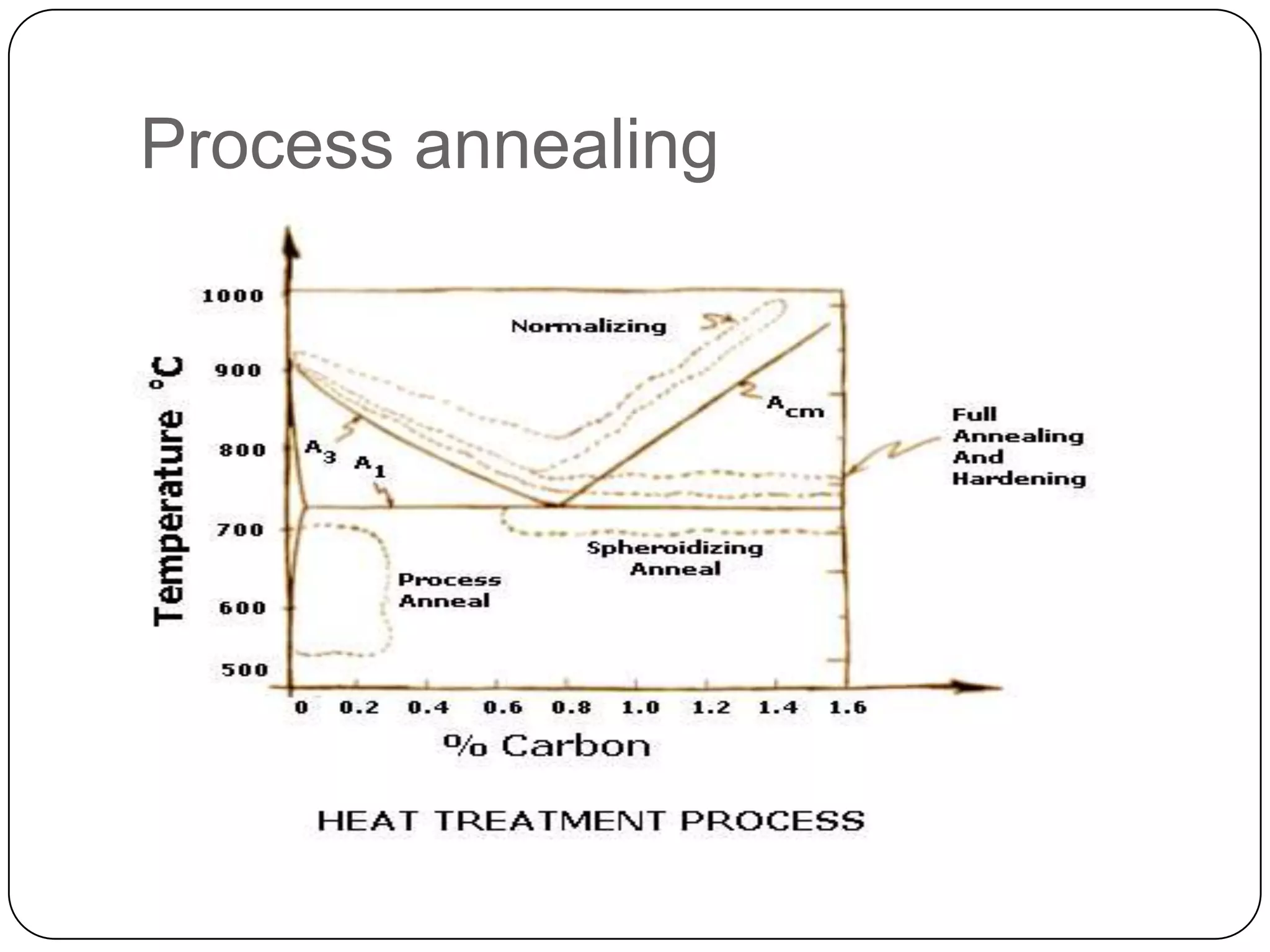
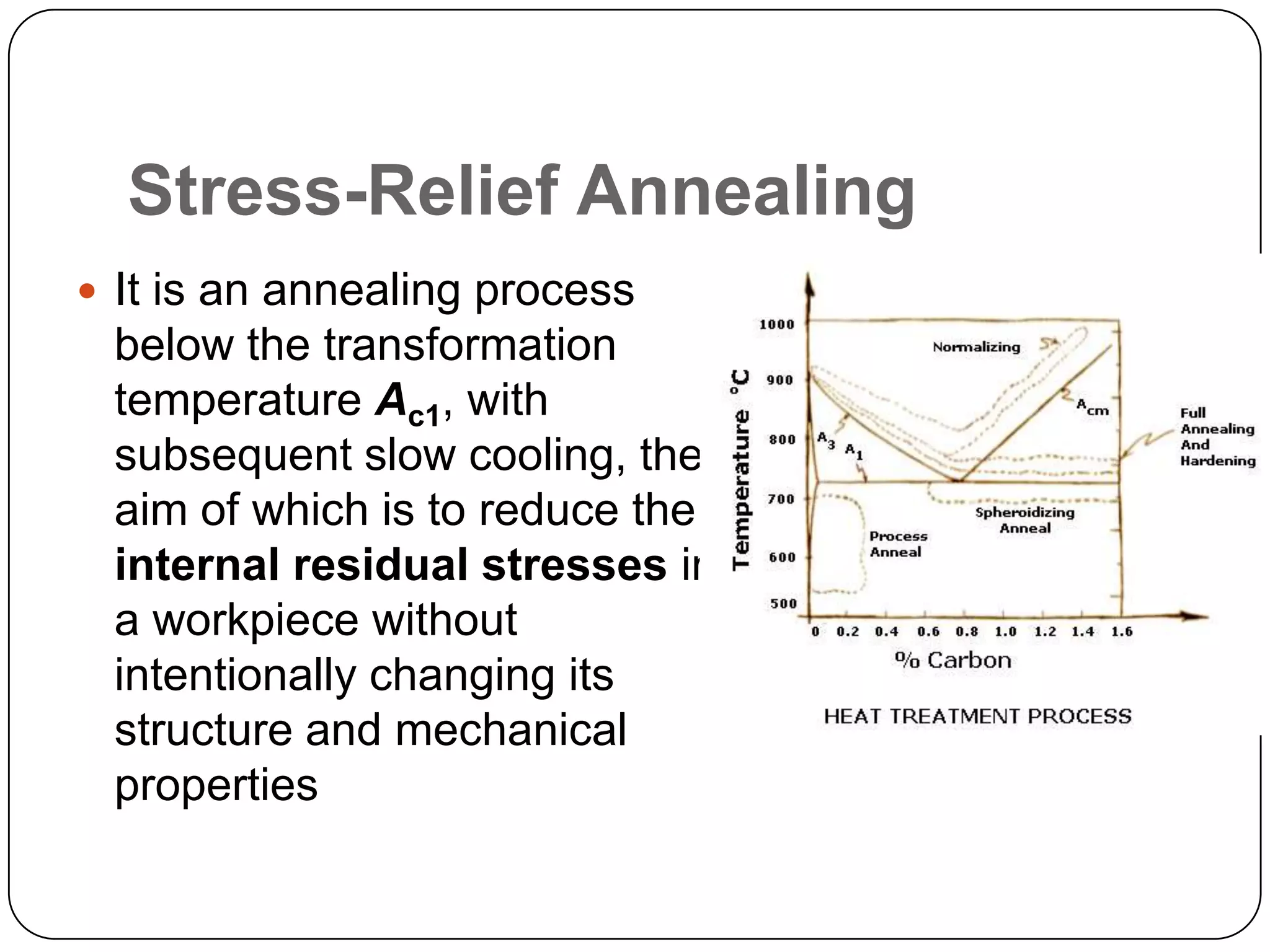
The document discusses various heat treatment processes including annealing, normalizing, quenching, and martensitic transformation. It provides details on the purposes, methods, and applications of each process. Annealing involves heating and slow cooling to relieve stresses and modify properties. Normalizing heats above the transformation temperature and air cools to produce a fine grain structure. Quenching rapidly cools steel above the transformation temperature to form very hard martensite. Martensitic transformation is the formation of acicular needlelike structures during rapid cooling of austenite.